A Comprehensive Guide to the Map of Nigeria: Understanding its 36 States
Related Articles: A Comprehensive Guide to the Map of Nigeria: Understanding its 36 States
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to A Comprehensive Guide to the Map of Nigeria: Understanding its 36 States. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Comprehensive Guide to the Map of Nigeria: Understanding its 36 States
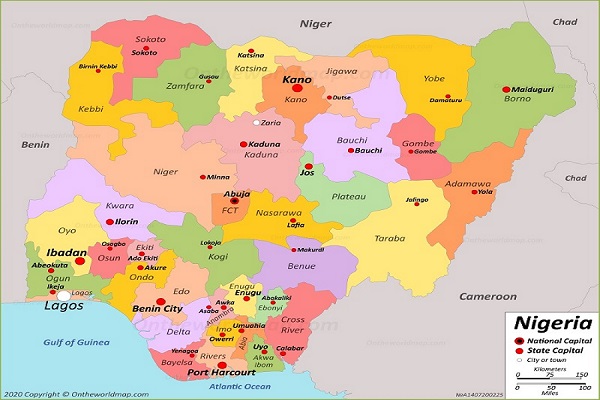
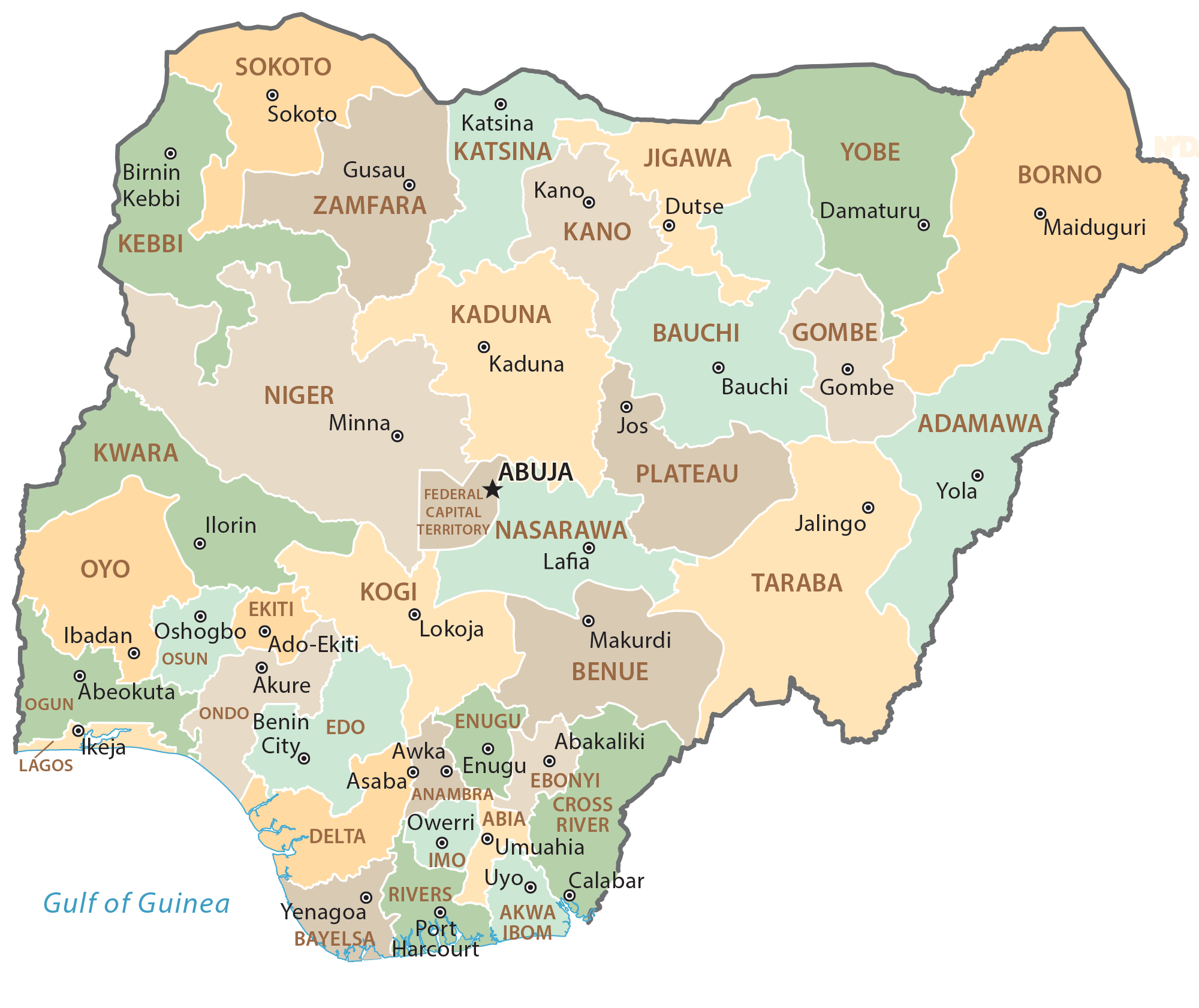
The map of Nigeria, with its intricate network of 36 states, provides a visual representation of the country’s complex and diverse geography. This article delves into the significance of this map, exploring its historical context, geographical features, and the vital role it plays in understanding Nigeria’s socio-economic landscape.
The Evolution of Nigeria’s State Structure:
Nigeria’s journey to its current state structure has been marked by significant historical milestones. Initially, the country was divided into three regions – the North, East, and West – upon independence in 1960. However, the increasing demands for regional autonomy and representation led to a series of state creations.
The 1967 creation of 12 states marked a turning point, followed by further divisions in 1976 and 1991. The 1996 creation of the 36 states and the Federal Capital Territory (FCT), Abuja, established the current administrative framework. Each state is governed by a state government with its own legislature, executive, and judiciary, ensuring a decentralized system of governance.
Understanding Nigeria’s Geographic Diversity:
The map of Nigeria, with its 36 states, reveals the vast and diverse geographical landscape of the nation. From the coastal plains of the south to the rugged highlands of the north, the country encompasses a wide range of ecosystems.
- The Coastal Region: This area, stretching along the Atlantic coast, is characterized by mangrove swamps, rainforests, and fertile plains. States like Akwa Ibom, Rivers, and Delta are situated in this region, known for its oil and gas resources.
- The Middle Belt: This region, also known as the "Heartland" of Nigeria, lies between the north and south. It is a transitional zone with diverse landscapes, including savannas, grasslands, and forests. States like Benue, Plateau, and Kwara are located in this region, known for its agricultural potential.
- The Northern Region: This region comprises the northernmost states and is characterized by the Sahel, a semi-arid zone with extensive grasslands and savannas. States like Borno, Kano, and Katsina are situated in this region, known for its rich cultural heritage and agricultural practices.
The Significance of the Map of Nigeria:
The map of Nigeria, with its 36 states, holds immense significance for various reasons:
- Administrative Governance: It serves as a visual representation of the country’s administrative structure, illustrating the boundaries and jurisdictions of each state. This facilitates efficient governance by clearly defining responsibilities and authorities.
- Economic Development: The map helps identify regions with specific economic strengths and potential. For example, the oil-producing states in the south contribute significantly to the national economy, while the agricultural states in the north play a crucial role in food security.
- Cultural Diversity: The map highlights the cultural richness of Nigeria, showcasing the distinct languages, traditions, and customs of each state. This understanding fosters national unity and appreciation for the country’s diverse heritage.
- Resource Management: The map aids in the identification and management of natural resources, enabling sustainable development practices. It helps in understanding the distribution of mineral resources, water bodies, and other vital assets.
- Infrastructure Development: The map facilitates planning and development of infrastructure, including roads, railways, and communication networks. It ensures efficient connectivity and accessibility across the country.
- Disaster Management: The map is essential for disaster preparedness and response. It helps in identifying vulnerable areas and coordinating relief efforts during natural disasters like floods, droughts, and earthquakes.
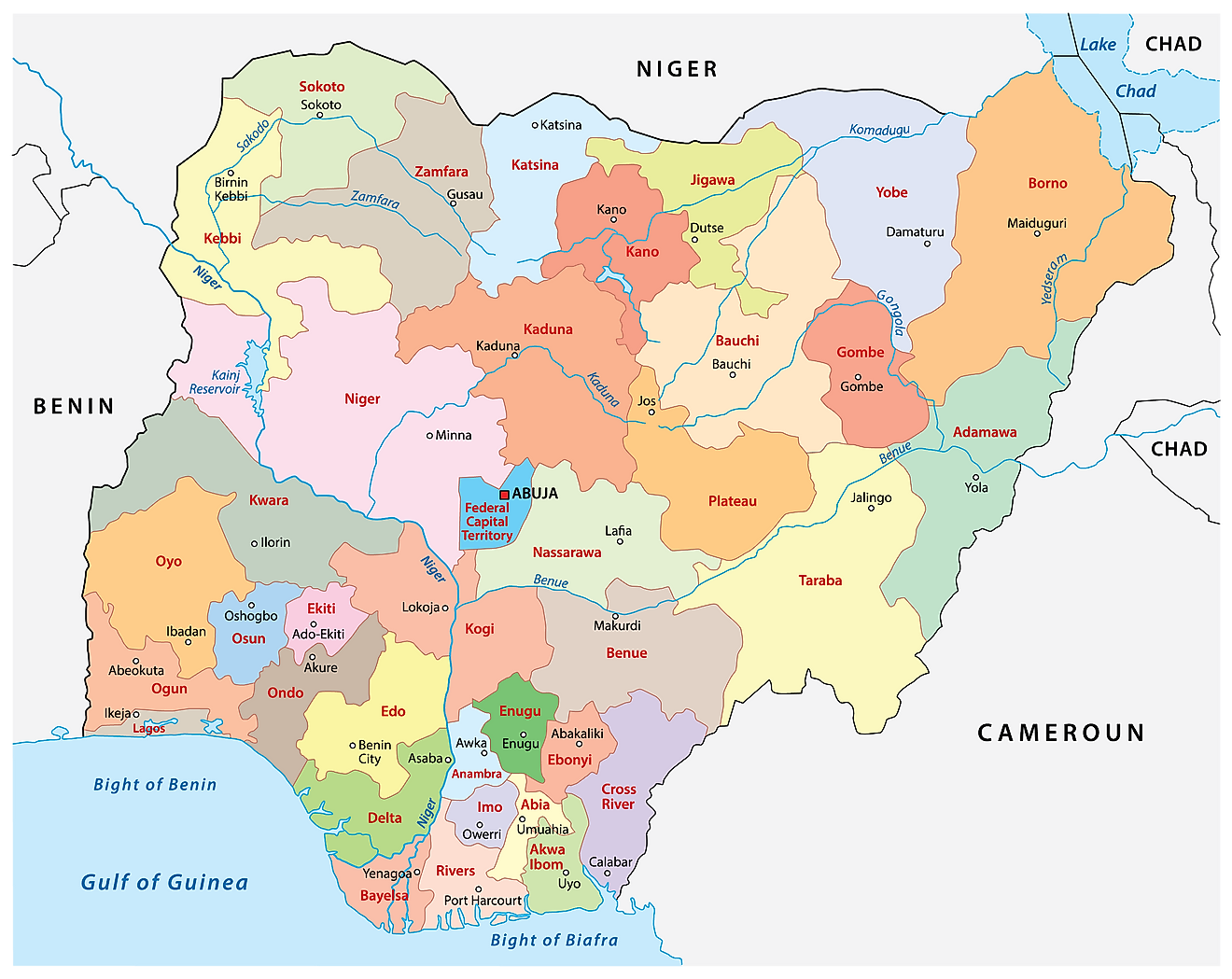
Understanding the Map: A Closer Look at Each State
North-Central:
- Abuja (FCT): The capital city of Nigeria, known for its modern architecture and administrative functions.
- Benue: Known for its agricultural production, especially rice and yam.
- Kogi: Rich in mineral resources, including gold and iron ore.
- Kwara: A major producer of agricultural products like cassava and cocoa.
- Nasarawa: Known for its scenic landscapes and tourism potential.
- Niger: A key producer of agricultural commodities like millet and sorghum.
- Plateau: Known for its diverse landscapes, including Jos Plateau, and tourism attractions.
North-East:
- Adamawa: Known for its agricultural produce, including cotton and maize.
- Bauchi: A major producer of agricultural products like groundnuts and millet.
- Borno: Known for its Lake Chad region and its challenges with insurgency.
- Gombe: Known for its agricultural potential and its proximity to the Bauchi state.
- Taraba: Known for its diverse landscapes, including Mambilla Plateau, and its agricultural produce.
- Yobe: Known for its agricultural production, especially millet and sorghum.
North-West:
- Jigawa: A major producer of agricultural products like rice and millet.
- Kaduna: Known for its industrial activities and its historical significance.
- Kano: A major commercial hub and a significant producer of agricultural products.
- Katsina: Known for its agricultural production, especially groundnuts and millet.
- Kebbi: A major producer of rice and other agricultural products.
- Sokoto: Known for its historical significance and its agricultural production, especially millet and sorghum.
- Zamfara: Known for its gold mining activities and its agricultural production, especially millet and sorghum.
South-East:
- Abia: Known for its agricultural production, especially palm oil and cassava.
- Anambra: Known for its industrial activities and its agricultural production, especially yam and cassava.
- Ebonyi: Known for its agricultural production, especially yam and cassava.
- Enugu: Known for its coal mining activities and its agricultural production, especially palm oil and cassava.
- Imo: Known for its industrial activities and its agricultural production, especially palm oil and cassava.
South-South:
- Akwa Ibom: A major oil-producing state and known for its agricultural production, especially palm oil and cassava.
- Bayelsa: A major oil-producing state and known for its mangrove forests.
- Cross River: Known for its tourism attractions, including the Cross River National Park, and its agricultural production, especially cocoa and rubber.
- Delta: A major oil-producing state and known for its agricultural production, especially palm oil and cassava.
- Edo: Known for its industrial activities and its agricultural production, especially rubber and cocoa.
- Rivers: A major oil-producing state and known for its agricultural production, especially palm oil and cassava.
South-West:
- Ekiti: Known for its agricultural production, especially cocoa and cassava.
- Lagos: The commercial capital of Nigeria, known for its vibrant economy and its diverse population.
- Ogun: Known for its industrial activities and its agricultural production, especially cocoa and rubber.
- Ondo: Known for its agricultural production, especially cocoa and palm oil.
- Osun: Known for its agricultural production, especially cocoa and cassava.
- Oyo: Known for its industrial activities and its agricultural production, especially cocoa and cassava.
FAQs about the Map of Nigeria:
Q: What is the purpose of the map of Nigeria showing 36 states?
A: The map serves as a visual representation of Nigeria’s administrative structure, outlining the boundaries and jurisdictions of each state. It is vital for efficient governance, resource management, infrastructure development, and disaster preparedness.
Q: How does the map of Nigeria reflect the country’s cultural diversity?
A: The map highlights the geographical distribution of different ethnic groups, languages, and cultural practices across the country. It emphasizes the importance of understanding and appreciating Nigeria’s rich cultural tapestry.
Q: What are the key economic sectors represented on the map of Nigeria?
A: The map reveals the diverse economic landscape of Nigeria, showcasing regions with significant oil and gas production, agriculture, industry, and commerce. It highlights the country’s economic strengths and potential.
Q: How does the map of Nigeria facilitate infrastructure development?
A: The map helps planners and developers identify areas that require infrastructure improvements, such as roads, railways, and communication networks. It ensures efficient connectivity and accessibility across the country.
Q: What are the challenges associated with the map of Nigeria?
A: The map can sometimes be seen as a reflection of historical divisions and political boundaries, leading to inter-state conflicts and resource disputes. It is crucial to address these challenges through inclusive governance and equitable development.
Tips for Utilizing the Map of Nigeria:
- Identify key geographical features: Analyze the map to understand the location of major rivers, mountains, and other significant geographical features.
- Explore state-specific information: Research the economic activities, cultural heritage, and historical significance of each state.
- Compare and contrast different regions: Analyze the map to understand the variations in climate, population density, and economic activities across different regions.
- Use the map for planning and development: Utilize the map to identify areas for infrastructure development, resource management, and disaster preparedness.
- Engage in discussions about the map: Discuss the map with others to gain diverse perspectives and foster a deeper understanding of Nigeria’s geography and its challenges.
Conclusion:
The map of Nigeria, with its 36 states, serves as a powerful tool for understanding the country’s complex and diverse landscape. It facilitates efficient governance, economic development, cultural appreciation, and resource management. By studying and analyzing this map, we gain valuable insights into the challenges and opportunities that define Nigeria’s journey toward a prosperous and unified future.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Comprehensive Guide to the Map of Nigeria: Understanding its 36 States. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!