A Visual History: Understanding Chicago’s Racial Landscape Through Mapping
Related Articles: A Visual History: Understanding Chicago’s Racial Landscape Through Mapping
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to A Visual History: Understanding Chicago’s Racial Landscape Through Mapping. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Visual History: Understanding Chicago’s Racial Landscape Through Mapping
Chicago, a city renowned for its dynamic history and diverse population, is a fascinating case study in urban development and social change. The city’s racial composition has evolved significantly over time, reflecting both national and local trends. Understanding these shifts requires a nuanced approach, and one valuable tool for visualizing this evolution is the use of race maps.
The Power of Visualization
Race maps, also known as demographic maps, are visual representations of population distribution based on race or ethnicity. They provide a powerful means to understand the spatial patterns of racial and ethnic groups within a city. By visualizing the distribution of different groups, these maps reveal insights that might not be readily apparent from raw data alone.
Chicago’s Racial History in Maps
Throughout the 20th and 21st centuries, Chicago’s racial landscape has been shaped by a complex interplay of factors, including migration patterns, housing policies, economic opportunities, and social forces. Maps documenting these changes offer a unique window into the city’s past and present.
Early 20th Century:
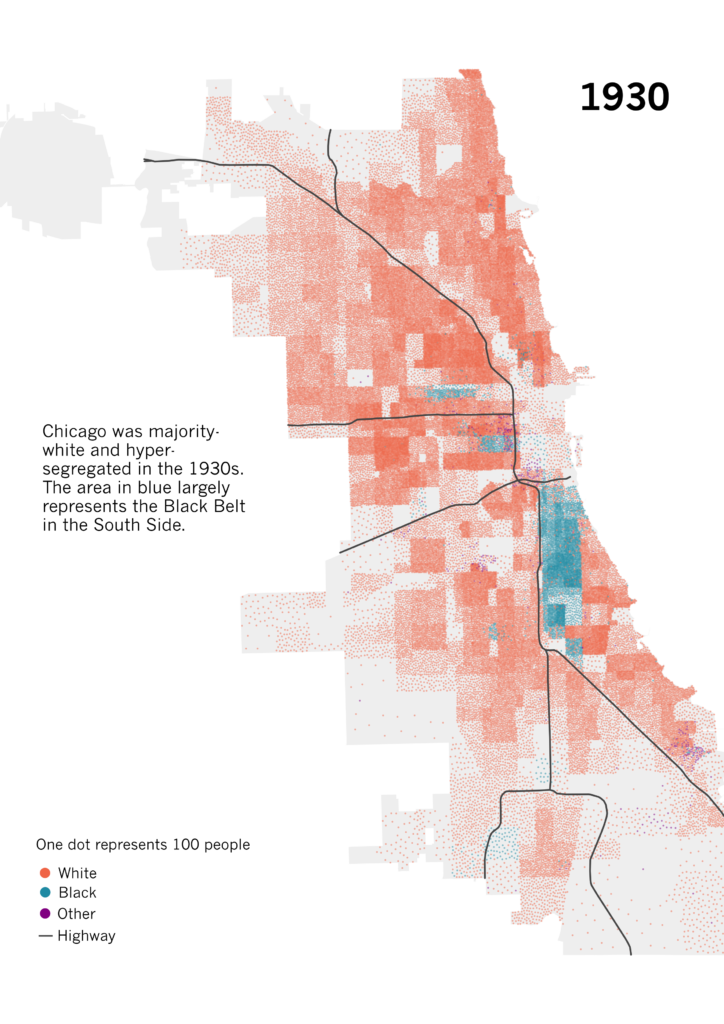
- Early 20th-century maps: The early 20th century witnessed significant migration of African Americans from the South to northern cities, including Chicago. These maps often depict a concentrated African American population within specific neighborhoods, primarily on the South Side, reflecting the impact of segregation and discriminatory housing practices.
- The Great Migration: This period saw a massive influx of African Americans to Chicago, seeking better economic opportunities and escaping racial oppression in the South. Maps from this era reveal the rapid growth of African American neighborhoods and the expansion of the "Black Belt" on the South Side.
Mid to Late 20th Century:
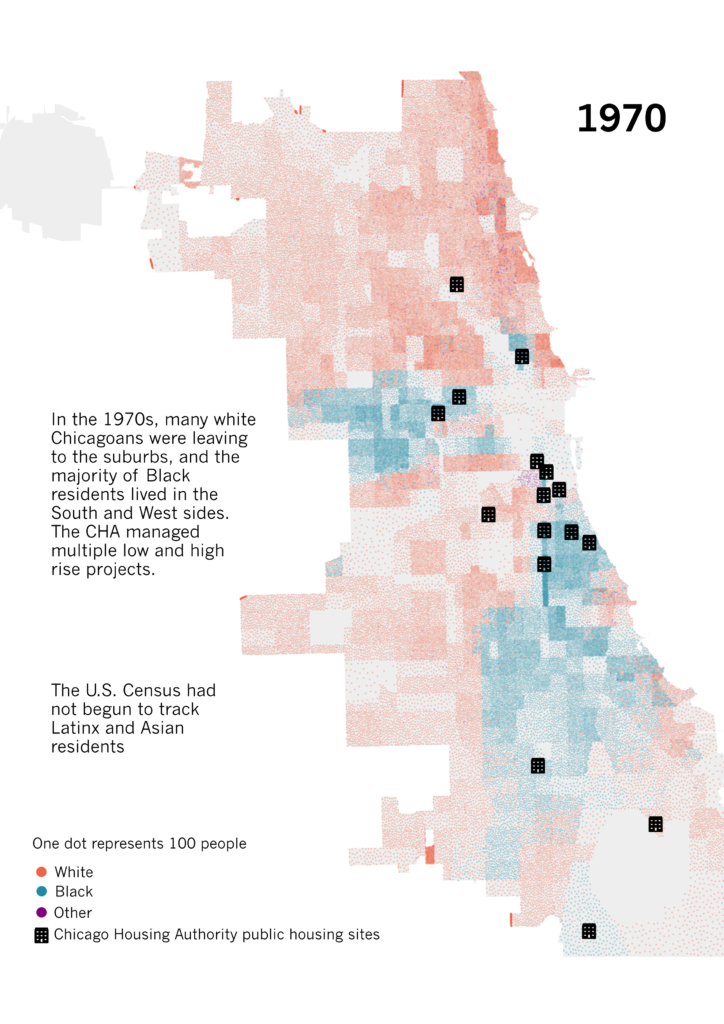
- Post-World War II: The post-war era witnessed continued suburbanization and white flight, contributing to the further segregation of Chicago. Maps from this period show the growth of predominantly white suburbs surrounding the city, while the central city became increasingly segregated along racial lines.
- The Civil Rights Movement: The Civil Rights Movement of the 1960s and 1970s brought about significant legal challenges to segregation and discrimination. However, maps from this era still reveal persistent racial disparities in housing and access to resources.
The 21st Century:
- Gentrification: The turn of the millennium saw the emergence of gentrification in several neighborhoods, leading to shifts in racial demographics. Maps from this period show the influx of new residents into previously predominantly African American or Hispanic neighborhoods, often accompanied by rising property values and displacement of long-time residents.
- Changing Demographics: The 21st century has witnessed a growing diversity within Chicago’s population, with increasing numbers of Asian Americans, Latinos, and immigrants from various backgrounds. Maps from this period reflect this changing landscape, showing a more complex and nuanced distribution of racial and ethnic groups across the city.
Beyond Visualization: Understanding the Implications
While race maps provide a visual representation of racial distribution, it’s crucial to understand the social, economic, and historical context behind these patterns. These maps are not merely static snapshots but rather reflections of policies, practices, and societal forces that have shaped Chicago’s racial landscape.
- Housing Segregation: Maps often highlight the persistent segregation of neighborhoods along racial lines, a legacy of discriminatory housing policies and practices. This segregation can perpetuate disparities in access to quality housing, education, and other essential resources.
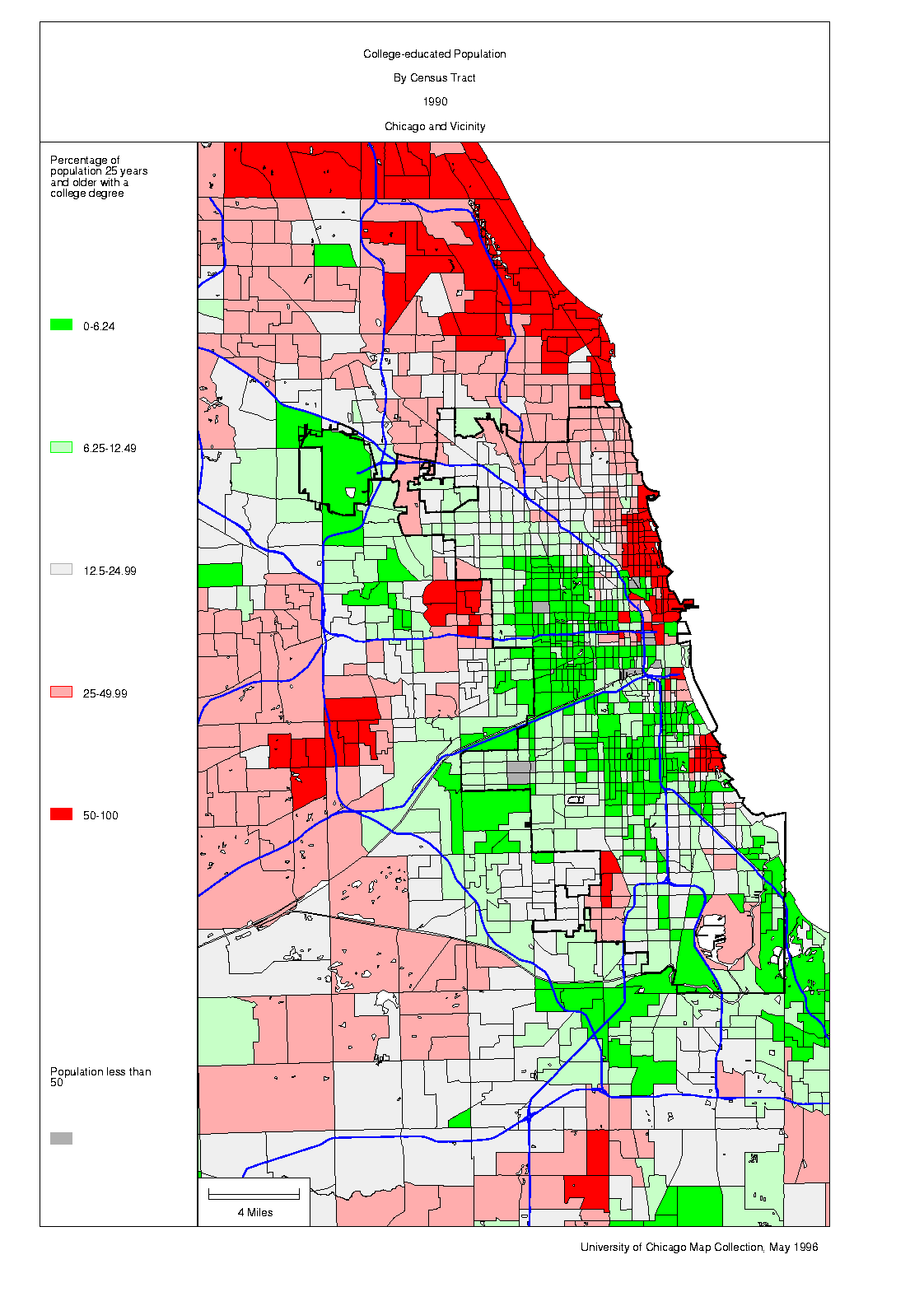
- Economic Disparities: Maps can reveal the concentration of poverty and unemployment within specific neighborhoods, often coinciding with racial and ethnic boundaries. This underscores the deep-rooted economic disparities that continue to affect different communities within the city.
- Social Justice: Analyzing race maps can shed light on the challenges faced by minority communities and the need for policies and initiatives aimed at achieving greater equity and social justice.
Analyzing Race Maps: A Multifaceted Approach
To gain a comprehensive understanding of Chicago’s racial landscape, it’s important to consider multiple perspectives and data sources when analyzing race maps.
- Historical Context: Understanding the historical factors that have shaped racial segregation and inequality is essential for interpreting present-day patterns.
- Socioeconomic Indicators: Examining data on poverty, income, education, and employment alongside racial demographics can provide a more nuanced understanding of the social and economic conditions of different communities.
- Community Perspectives: Engaging with community members and organizations can provide valuable insights into the lived experiences of residents and the challenges they face.
FAQs
Q: What are the main sources for obtaining race map data for Chicago?
A: The primary sources for race map data in Chicago include:
- U.S. Census Bureau: The Census Bureau provides comprehensive demographic data at the national, state, county, and city levels, including information on race and ethnicity.
- Chicago Metropolitan Agency for Planning (CMAP): CMAP collects and analyzes data on a variety of urban planning issues, including demographics and spatial patterns.
- Local Research Institutions: Universities and research centers in Chicago, such as the University of Chicago and Northwestern University, often conduct studies and collect data on the city’s racial demographics.
- Community Organizations: Local community organizations and advocacy groups may also collect and share data on racial demographics and community needs.
Q: How can I access and use these maps for research or personal projects?
A: Accessing and utilizing race maps requires a combination of data retrieval, visualization tools, and analytical skills:
- Data Retrieval: Data sources like the Census Bureau website provide downloadable data files that can be used to create maps.
- Visualization Tools: Software programs such as ArcGIS, QGIS, and Tableau allow users to visualize data in the form of maps, charts, and graphs.
- Analytical Skills: Interpreting and analyzing the information presented in the maps requires a strong understanding of statistical concepts, spatial patterns, and the social and historical context.
Q: What are some of the ethical considerations when working with race maps?
A: Working with race maps raises ethical considerations that must be carefully addressed:
- Privacy and Confidentiality: Ensuring the privacy and confidentiality of individual data is paramount, especially when working with sensitive information like race and ethnicity.
- Stereotyping and Generalization: It’s crucial to avoid using maps to reinforce stereotypes or make generalizations about entire groups of people.
- Context and Interpretation: Presenting maps without adequate context or interpretation can lead to misinterpretations and biased conclusions.
Tips for Utilizing Race Maps
- Use multiple data sources: Combining data from different sources can provide a more comprehensive understanding of the complex patterns of racial distribution.
- Consider historical context: Understanding the historical events and policies that have shaped the city’s racial landscape is essential for interpreting present-day patterns.
- Focus on equity and social justice: Utilize maps to identify disparities and inequalities, and advocate for policies and initiatives that promote equity and social justice.
- Engage with communities: Collaborate with community members and organizations to ensure that data and visualizations are relevant to their needs and perspectives.
Conclusion
Race maps provide a powerful tool for visualizing and understanding the complex dynamics of racial and ethnic distribution within Chicago. By exploring the historical evolution of these maps and analyzing the social and economic factors that have shaped them, we gain a deeper understanding of the city’s past and present. This knowledge is essential for addressing the ongoing challenges of racial inequality and working towards a more just and equitable future for all Chicagoans.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Visual History: Understanding Chicago’s Racial Landscape Through Mapping. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!