Charting New Waters: Samuel de Champlain’s Exploration of North America
Related Articles: Charting New Waters: Samuel de Champlain’s Exploration of North America
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Charting New Waters: Samuel de Champlain’s Exploration of North America. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Charting New Waters: Samuel de Champlain’s Exploration of North America

Samuel de Champlain, a French explorer, cartographer, and soldier, played a pivotal role in shaping the early European understanding of North America. His voyages, meticulous observations, and detailed maps provided invaluable insights into the geography, indigenous cultures, and natural resources of the region. This article delves into the significance of Samuel de Champlain’s map route, examining its impact on exploration, trade, and the development of European settlements in North America.
A Journey of Discovery: Following Champlain’s Trail
Champlain’s voyages, spanning over four decades, took him across vast stretches of the North American continent. His travels, meticulously documented and mapped, provided a foundation for future exploration and colonization. Here is a breakdown of his key expeditions, highlighting the routes he charted:
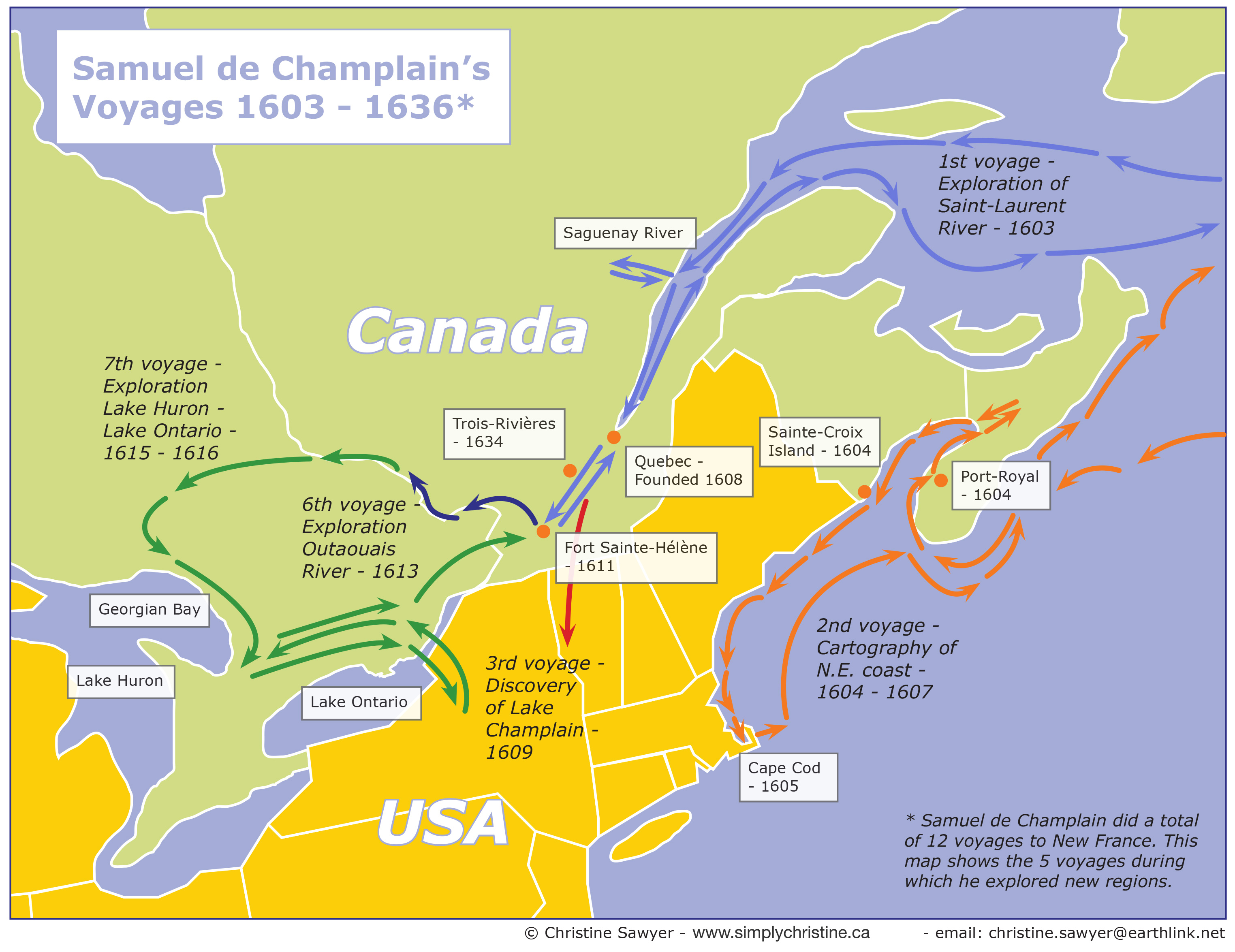
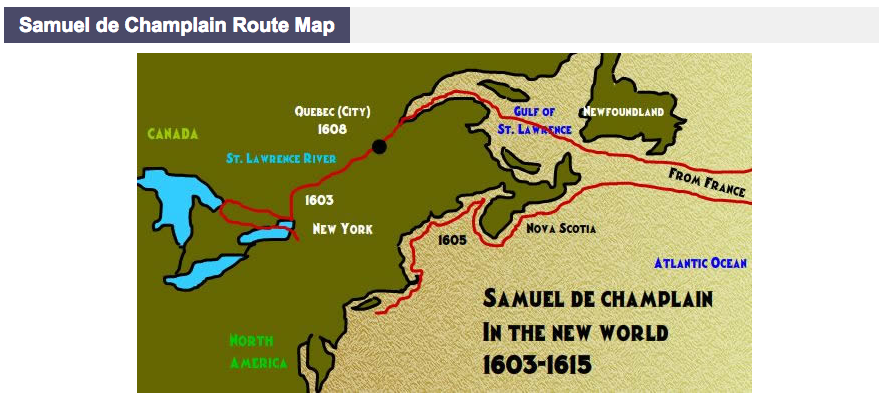
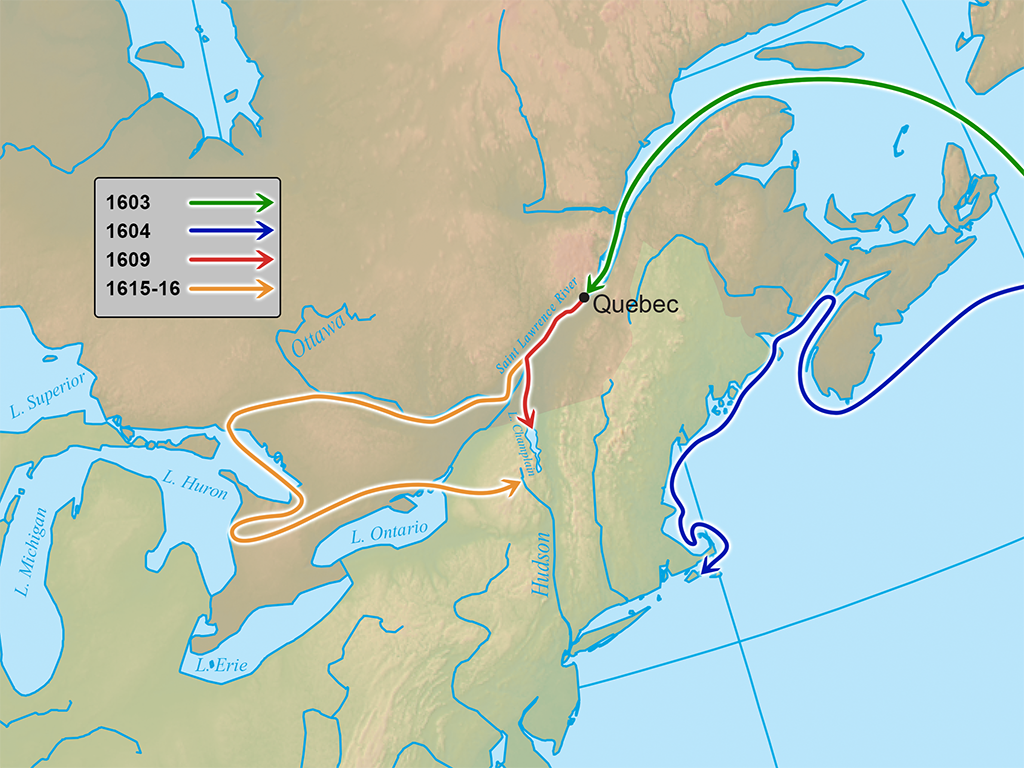
1. The St. Lawrence River (1603-1607): Champlain’s initial voyages focused on the St. Lawrence River, a crucial waterway for trade and exploration. He ascended the river, charting its course and documenting the indigenous communities he encountered along the way. His maps, including the renowned "Carte Geographique de la Nouvelle France" (1612), were groundbreaking for their accuracy and detail.
2. The Great Lakes (1615-1616): In a daring expedition, Champlain ventured into the Great Lakes region, exploring Lake Ontario, Lake Huron, and Lake Nipissing. He established diplomatic relations with the Algonquin and Huron First Nations, forging alliances that would prove vital for future trade and exploration. This expedition, documented in his "Voyages," provided valuable information about the geography, resources, and indigenous societies of the Great Lakes region.
3. The Atlantic Coast (1604-1613): Champlain also explored portions of the Atlantic coast, venturing into present-day Nova Scotia and Maine. He established Port Royal, the first permanent French settlement in North America, and his maps provided crucial information about the coastline and its potential for colonization.
4. The Interior of New France (1615-1632): Champlain’s later expeditions focused on expanding French influence further into the interior of what is now Canada. He explored the Ottawa River, the Richelieu River, and the Champlain Valley, establishing trading posts and forging alliances with indigenous communities. These expeditions solidified French control over key territories in the interior of North America.
The Enduring Legacy of Champlain’s Maps
Champlain’s maps were more than mere geographical representations; they were powerful tools that shaped the course of history. Their accuracy and detail provided vital information for:
1. Trade and Commerce: Champlain’s maps facilitated trade between European settlers and indigenous communities. They revealed the location of valuable resources, such as furs, timber, and fish, and provided routes for navigating rivers and waterways, enabling efficient transportation and exchange.
2. Colonization and Settlement: Champlain’s maps guided the establishment of French settlements in North America. They identified suitable locations for agriculture, resource extraction, and defense, providing crucial information for the development of colonies.
3. Diplomacy and Relations: Champlain’s maps helped establish diplomatic relations with indigenous communities. By accurately representing their territories and cultural practices, his maps facilitated understanding and fostered alliances that were essential for the success of French colonization.
4. Scientific Knowledge: Champlain’s maps contributed to the growing body of scientific knowledge about North America. They provided detailed descriptions of the geography, flora, fauna, and indigenous cultures, advancing European understanding of the continent.
Beyond the Maps: The Lasting Impact of Champlain’s Legacy
Champlain’s legacy extends beyond his maps. His writings, meticulously documented accounts of his voyages, provide invaluable insights into the lives of the indigenous peoples he encountered, the challenges of early exploration, and the complexities of European colonization in North America. He was a pioneer of inter-cultural diplomacy, forging alliances and establishing trade partnerships with indigenous communities.
FAQs
1. What was the primary purpose of Samuel de Champlain’s voyages?
Champlain’s voyages were driven by a combination of motives: exploration, trade, and the establishment of French settlements in North America. His expeditions aimed to chart new territories, establish diplomatic relationships with indigenous communities, and secure resources for the burgeoning French fur trade.
2. How did Champlain’s maps contribute to the development of French settlements in North America?
Champlain’s maps provided crucial information for selecting suitable locations for settlements. They revealed the availability of resources, the suitability of land for agriculture, and the strategic importance of certain locations for defense.
3. How did Champlain’s maps influence the relationship between Europeans and indigenous peoples?
Champlain’s maps facilitated communication and understanding between Europeans and indigenous peoples. They provided a shared framework for navigating territories, identifying resources, and establishing trading partnerships.
4. What is the significance of Champlain’s "Carte Geographique de la Nouvelle France"?
This map, published in 1612, was one of the most accurate and detailed maps of North America at the time. It provided a comprehensive overview of the St. Lawrence River, the Great Lakes region, and the Atlantic coastline, significantly advancing European understanding of the geography of the continent.
Tips for Exploring Champlain’s Legacy
1. Visit Historic Sites: Explore historic sites associated with Champlain’s voyages, such as Port Royal in Nova Scotia, Quebec City, and the Champlain Valley in New York. These sites offer a glimpse into the era of exploration and colonization.
2. Study Champlain’s Writings: Read Champlain’s "Voyages" and other writings to gain a deeper understanding of his motivations, experiences, and observations. These firsthand accounts provide valuable insights into the history of early exploration and colonization.
3. Explore Maps and Charts: Examine Champlain’s maps and charts to appreciate the accuracy and detail of his work. These maps offer a visual representation of his voyages and the territories he explored.
4. Engage with Indigenous Cultures: Learn about the indigenous cultures that Champlain encountered during his voyages. Understand their perspectives on colonization, trade, and the impact of European arrival.
Conclusion
Samuel de Champlain’s map route was a testament to his spirit of exploration, his meticulous observations, and his dedication to charting new territories. His maps and writings provided invaluable insights into the geography, resources, and indigenous cultures of North America, shaping the course of European colonization and leaving an enduring legacy that continues to influence our understanding of the continent today.


![North America by Samuel de Champlain (1632) [4173×2542] : r/MapPorn](https://external-preview.redd.it/HSyIw0LvdN6VF_kx83iNGdoyoB1YsTBuIFYTj6_g3bU.jpg?auto=webpu0026s=75a6067a111b6ae80ccc95f545799b6e2fe472e1)


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Charting New Waters: Samuel de Champlain’s Exploration of North America. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!