Demystifying the Landscape of Socioeconomic Disparities: Understanding Low- and Moderate-Income Census Tracts
Related Articles: Demystifying the Landscape of Socioeconomic Disparities: Understanding Low- and Moderate-Income Census Tracts
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Demystifying the Landscape of Socioeconomic Disparities: Understanding Low- and Moderate-Income Census Tracts. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Demystifying the Landscape of Socioeconomic Disparities: Understanding Low- and Moderate-Income Census Tracts

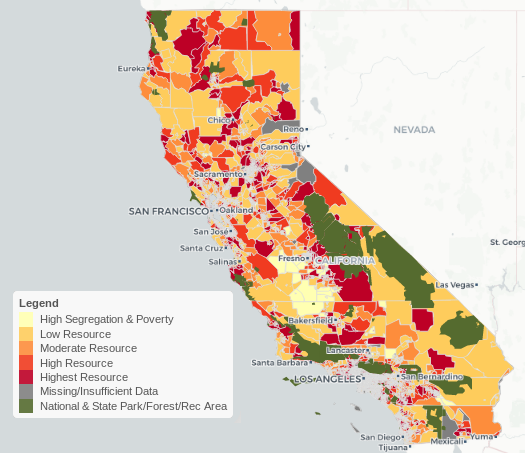
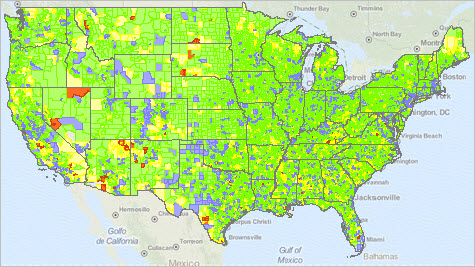
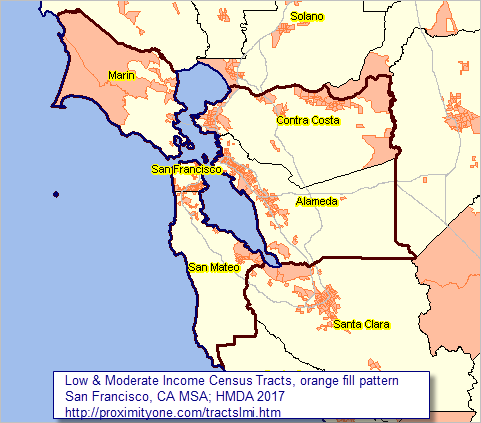
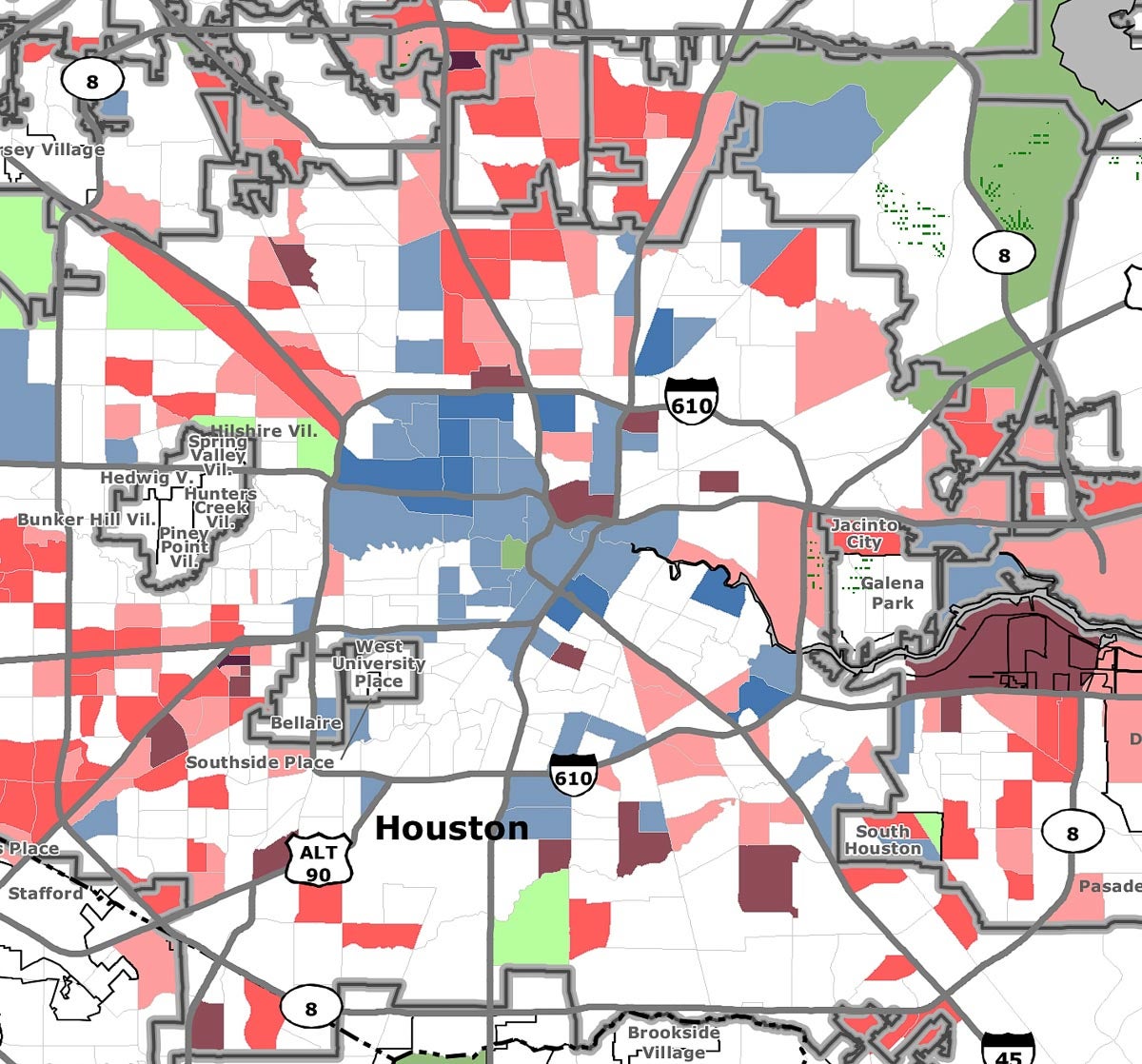
The United States Census Bureau, a vital source of demographic and socioeconomic data, plays a crucial role in understanding the intricate tapestry of American society. One of its most powerful tools is the census tract, a small geographic area used to collect and analyze data on a local level. Within this framework, low- and moderate-income census tracts stand out as critical indicators of economic disparities and social challenges. This article delves into the significance of these tracts, exploring their definition, usage, and implications for policy and community development.
Defining Low- and Moderate-Income Census Tracts:
The designation of a census tract as low- or moderate-income is determined by a combination of factors, primarily focusing on the median household income of its residents. The U.S. Department of Housing and Urban Development (HUD) defines low- and moderate-income households based on a percentage of the area median income (AMI). This threshold varies geographically, reflecting regional cost-of-living differences. For example, a household in a high-cost-of-living area like New York City may be considered low-income at a higher income level compared to a household in a rural area with a lower cost of living.
The Significance of Low- and Moderate-Income Census Tracts:
Understanding the distribution of low- and moderate-income census tracts is crucial for a variety of reasons:
-
Identifying Areas of Need: These tracts often experience higher rates of poverty, unemployment, and limited access to essential services like healthcare, education, and transportation. By mapping these areas, policymakers can identify communities in greatest need of targeted interventions and resource allocation.
-
Guiding Policy and Program Development: Data from low- and moderate-income census tracts informs the development of effective social programs and policies. For instance, understanding the specific needs and challenges of these communities allows for the tailoring of housing assistance programs, job training initiatives, and community development projects.
-
Promoting Equitable Development: By highlighting areas with concentrated poverty, these maps can guide urban planning and development strategies. This can help ensure that investments in infrastructure, housing, and public services are distributed equitably, promoting inclusive and sustainable growth.
-
Facilitating Community Engagement: These maps provide a valuable tool for community organizations, non-profits, and grassroots initiatives working to address social and economic issues. They can help identify areas where their services are most needed and facilitate collaboration with local stakeholders.
Applications and Uses of Low- and Moderate-Income Census Tracts:
The data gleaned from low- and moderate-income census tracts finds applications in a wide range of fields:
-
Community Development: Local governments, community development organizations, and non-profits utilize this data to target resources and programs towards areas with the greatest need. This includes initiatives focused on affordable housing, job training, financial literacy, and community infrastructure improvements.
-
Economic Development: Economic development agencies can leverage this data to identify areas with potential for revitalization and targeted investment. This can include initiatives to attract businesses, create jobs, and stimulate economic growth in low-income communities.
-
Healthcare and Social Services: Public health agencies and healthcare providers rely on this data to understand the distribution of health disparities and target resources towards areas with higher rates of chronic diseases, limited access to healthcare, and health inequities.
-
Education: School districts and educational organizations use this data to identify areas with high concentrations of low-income students and tailor educational programs and support services to address their unique needs.
-
Housing Policy: Housing authorities and affordable housing developers use this data to prioritize the allocation of housing resources and ensure that affordable housing options are available in areas with the highest need.
FAQs Regarding Low- and Moderate-Income Census Tracts:
Q: How frequently is this data updated?
A: The U.S. Census Bureau conducts a decennial census every ten years, providing the most comprehensive and up-to-date data. However, the American Community Survey (ACS), an ongoing survey, collects data annually and provides more frequent updates on a variety of socioeconomic indicators, including income levels.
Q: What are the limitations of using this data?
A: While valuable, it is important to acknowledge the limitations of census tract data. It is a snapshot in time, and changes in income levels and socioeconomic conditions can occur between census periods. Additionally, census tracts are relatively large geographic areas, and they may not accurately reflect the nuances and variations within a specific community.
Q: How can I access this data?
A: The U.S. Census Bureau provides free access to its data through its website and various data visualization tools. The American Community Survey (ACS) data is available on the Census Bureau’s website, and it can be downloaded and analyzed using various software programs.
Tips for Utilizing Low- and Moderate-Income Census Tract Data:
-
Contextualize the Data: Understand the historical and social context of the area being analyzed. Consider factors like local economic trends, housing market dynamics, and demographic shifts that may influence income levels.
-
Compare Data Across Time: Analyze trends in income levels and socioeconomic indicators over time to identify areas experiencing persistent poverty or significant changes in economic conditions.
-
Consider Geographic Scale: Explore data at different geographic scales, such as county, city, or neighborhood level, to understand the distribution of income levels and identify areas with specific needs.
-
Collaborate with Local Stakeholders: Engage with community organizations, local government officials, and residents to gain a deeper understanding of the social and economic challenges faced by low- and moderate-income communities.
Conclusion:
Low- and moderate-income census tracts serve as essential tools for understanding socioeconomic disparities and informing policy decisions. They provide a valuable framework for identifying areas of need, guiding resource allocation, and promoting equitable development. By leveraging this data responsibly and in collaboration with local stakeholders, policymakers, community organizations, and individuals can work towards building more inclusive, equitable, and prosperous communities.


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Demystifying the Landscape of Socioeconomic Disparities: Understanding Low- and Moderate-Income Census Tracts. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!