Navigating Nigeria: A Comprehensive Guide to Its 36 States
Related Articles: Navigating Nigeria: A Comprehensive Guide to Its 36 States
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Navigating Nigeria: A Comprehensive Guide to Its 36 States. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating Nigeria: A Comprehensive Guide to Its 36 States
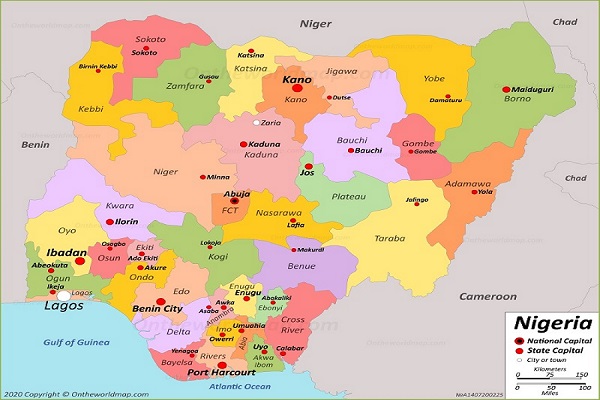
Nigeria, the giant of Africa, boasts a rich tapestry of cultures, languages, and landscapes. Its diverse geography is reflected in its administrative structure, encompassing 36 states, each with its unique identity and contribution to the nation. Understanding the spatial arrangement of these states is crucial for comprehending Nigeria’s political, economic, and social dynamics. This guide delves into the intricate geography of Nigeria, providing a detailed explanation of its 36 states and their significance.
A Visual Journey: The Map of Nigeria’s 36 States
The map of Nigeria, showcasing its 36 states, is an invaluable tool for understanding the country’s administrative framework. It visually represents the intricate division of the nation, highlighting the geographical distribution of its diverse populations and resources.
Key Features of the Map:
- State Boundaries: The map clearly delineates the boundaries of each state, allowing for easy identification and differentiation.
- State Capitals: The location of each state’s capital city is marked, offering a crucial reference point for understanding the administrative center of each state.
- Major Cities: Significant urban centers beyond the state capitals are also indicated, providing insights into the distribution of population and economic activity.
- Landforms: The map often incorporates geographical features like mountains, rivers, and lakes, providing a comprehensive understanding of the country’s diverse landscapes.
- Geographic Zones: Nigeria is broadly divided into six geopolitical zones, often depicted on the map, highlighting regional groupings based on shared cultural and historical influences.
Navigating the States: A Detailed Exploration
Understanding each state’s location and its unique characteristics is essential for appreciating the complexity and dynamism of Nigeria. Here’s a detailed exploration of the 36 states, categorized by their respective geopolitical zones:
1. South-South Zone:
- Akwa Ibom: Renowned for its oil and gas reserves, Akwa Ibom is a major economic powerhouse in the region. Its capital, Uyo, is a thriving commercial hub.
- Bayelsa: Situated in the Niger Delta, Bayelsa is another state with significant oil and gas resources. Its capital, Yenagoa, is a vital center for the petroleum industry.
- Cross River: Known for its stunning scenery, Cross River is a state rich in biodiversity and tourism potential. Its capital, Calabar, is a historic city with a vibrant cultural scene.
- Delta: Delta State is another major oil-producing state, with its capital, Asaba, serving as a major administrative and commercial center.
- Edo: Edo State, home to the historic city of Benin City, boasts a rich cultural heritage and is a significant agricultural producer.
- Rivers: Rivers State is a major industrial hub, with its capital, Port Harcourt, being a key center for the oil and gas industry.
2. South-East Zone:
- Abia: Abia State is a significant commercial center, known for its bustling markets and thriving manufacturing sector. Its capital, Umuahia, is a major administrative hub.
- Anambra: Anambra State is renowned for its entrepreneurial spirit and its role as a key player in the commercial and industrial sectors. Its capital, Awka, is a center for education and commerce.
- Ebonyi: Ebonyi State is a predominantly agricultural state, known for its production of crops like yam and cassava. Its capital, Abakaliki, is a growing administrative center.
- Enugu: Enugu State, known for its coal deposits, is a major industrial and commercial center. Its capital, Enugu, is a significant transportation hub.
- Imo: Imo State is a major agricultural producer, with its capital, Owerri, serving as a vital center for commerce and transportation.
3. South-West Zone:
- Ekiti: Ekiti State is known for its rich cultural heritage and its role as a major producer of cocoa and other agricultural products. Its capital, Ado Ekiti, is a center for education and administration.
- Lagos: Lagos State, the commercial and financial hub of Nigeria, is a bustling metropolis and a key player in the nation’s economy.
- Ondo: Ondo State is a major producer of cocoa, oil palm, and other agricultural products. Its capital, Akure, is a growing commercial and administrative center.
- Osun: Osun State is known for its rich cultural heritage and its role as a major producer of cocoa and other agricultural products. Its capital, Osogbo, is a center for traditional arts and crafts.
- Oyo: Oyo State, known for its historical significance and its role in the development of Yoruba culture, is a major agricultural producer. Its capital, Ibadan, is the second-largest city in Nigeria.
4. North-Central Zone:
- Benue: Benue State is a major agricultural producer, known for its production of crops like rice and yam. Its capital, Makurdi, is a vital center for commerce and transportation.
- FCT (Federal Capital Territory): The Federal Capital Territory, home to Abuja, the capital of Nigeria, serves as the seat of the federal government and is a major administrative center.
- Kogi: Kogi State is a major producer of gold, iron ore, and other mineral resources. Its capital, Lokoja, is a historical city with a strategic location.
- Kwara: Kwara State is known for its agricultural production, particularly of crops like rice and cassava. Its capital, Ilorin, is a major educational and commercial center.
- Nasarawa: Nasarawa State is a major agricultural producer, with its capital, Lafia, serving as a vital center for commerce and transportation.
- Niger: Niger State is a major producer of agricultural products, particularly of crops like rice and millet. Its capital, Minna, is a significant administrative and commercial center.
- Plateau: Plateau State is known for its scenic beauty, its role as a major producer of tin and columbite, and its diverse cultural heritage. Its capital, Jos, is a major commercial and industrial center.
5. North-East Zone:
- Adamawa: Adamawa State is a major agricultural producer, known for its production of crops like rice and cotton. Its capital, Yola, is a significant administrative and commercial center.
- Bauchi: Bauchi State is known for its rich cultural heritage and its role as a major producer of agricultural products. Its capital, Bauchi, is a significant administrative and commercial center.
- Borno: Borno State is a major agricultural producer, known for its production of crops like rice and millet. Its capital, Maiduguri, is a significant administrative and commercial center.
- Gombe: Gombe State is known for its agricultural production, particularly of crops like rice and cassava. Its capital, Gombe, is a growing administrative and commercial center.
- Taraba: Taraba State is known for its scenic beauty and its role as a major producer of agricultural products. Its capital, Jalingo, is a significant administrative and commercial center.
- Yobe: Yobe State is a major agricultural producer, known for its production of crops like rice and millet. Its capital, Damaturu, is a significant administrative and commercial center.
6. North-West Zone:
- Jigawa: Jigawa State is a major agricultural producer, known for its production of crops like rice and millet. Its capital, Dutse, is a significant administrative and commercial center.
- Kaduna: Kaduna State is known for its industrial production, particularly of textiles and leather goods. Its capital, Kaduna, is a major commercial and administrative center.
- Kano: Kano State is a major commercial and industrial center, known for its traditional industries and its role as a key player in the nation’s economy. Its capital, Kano, is one of the largest cities in Nigeria.
- Kebbi: Kebbi State is a major agricultural producer, known for its production of crops like rice and millet. Its capital, Birnin Kebbi, is a significant administrative and commercial center.
- Katsina: Katsina State is a major agricultural producer, known for its production of crops like rice and millet. Its capital, Katsina, is a significant administrative and commercial center.
- Sokoto: Sokoto State is known for its historical significance and its role as a major producer of agricultural products. Its capital, Sokoto, is a significant administrative and commercial center.
- Zamfara: Zamfara State is known for its gold deposits and its role as a major producer of agricultural products. Its capital, Gusau, is a significant administrative and commercial center.
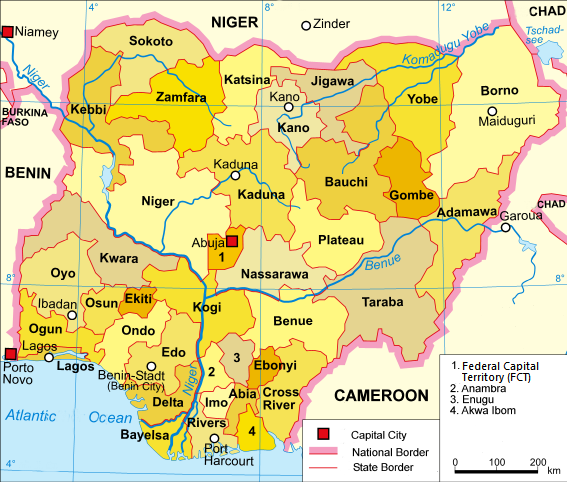
The Importance of Understanding the Map of Nigeria’s 36 States
The map of Nigeria, showcasing its 36 states, holds immense significance for various reasons:
- Political Understanding: It provides a visual representation of the country’s administrative structure, highlighting the distribution of power and authority.
- Economic Insights: The map helps identify key economic centers, resource-rich areas, and potential investment opportunities.
- Social Awareness: It facilitates understanding the distribution of diverse populations, cultural practices, and social challenges across the country.
- Resource Management: The map assists in planning for resource allocation, infrastructure development, and disaster response.
- Tourism and Travel: It serves as a valuable tool for planning trips, exploring different regions, and experiencing the diverse landscapes and cultures of Nigeria.
FAQs: Demystifying the Map of Nigeria’s 36 States
1. Why are there 36 states in Nigeria?
The creation of states in Nigeria is a complex process driven by political, social, and economic factors. The current number of 36 states reflects a balance between ensuring representation for diverse communities and maintaining administrative efficiency.
2. Are there any plans to create more states?
Discussions about creating new states in Nigeria are ongoing, with various political and social groups advocating for the division of existing states. However, any changes to the current structure would require significant political consensus and legislative approval.
3. How do the states relate to the geopolitical zones?
The geopolitical zones are broad regional groupings that reflect shared cultural, linguistic, and historical influences. The 36 states are distributed across these zones, further reflecting the diverse nature of Nigeria.
4. What is the significance of the state capitals?
Each state capital serves as the administrative center of its respective state, housing the state government and other key institutions. They are often major commercial and transportation hubs within their states.
5. How can I learn more about specific states?
Detailed information on each state, including its history, culture, economy, and tourism attractions, can be found through various online resources, academic journals, and government websites.
Tips for Using the Map of Nigeria’s 36 States Effectively
- Interactive Maps: Utilize interactive maps that allow for zooming, panning, and exploring specific areas in greater detail.
- Key References: Refer to the map alongside other resources like travel guides, historical accounts, and economic reports for a comprehensive understanding.
- Geographic Awareness: Pay attention to geographical features like mountains, rivers, and lakes, as they can influence the development and characteristics of each state.
- Cultural Exploration: Use the map to plan trips and explore the diverse cultures, traditions, and languages represented in each state.
- Stay Updated: Regularly check for updates to the map, as changes in administrative boundaries or the addition of new states can occur.
Conclusion: A Deeper Understanding of Nigeria’s Diverse Landscape
The map of Nigeria, showcasing its 36 states, is more than just a geographical representation. It serves as a window into the country’s rich history, cultural tapestry, and complex political and economic dynamics. By understanding the spatial distribution of these states, one gains a deeper appreciation for the diverse nature of Nigeria and its potential for growth and development. The map remains an essential tool for navigating this vast and dynamic nation, fostering a greater understanding of its people, resources, and challenges.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating Nigeria: A Comprehensive Guide to Its 36 States. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!