Navigating the Divide: A Comprehensive Exploration of the Guatemala-Mexico Border
Related Articles: Navigating the Divide: A Comprehensive Exploration of the Guatemala-Mexico Border
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Divide: A Comprehensive Exploration of the Guatemala-Mexico Border. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Divide: A Comprehensive Exploration of the Guatemala-Mexico Border

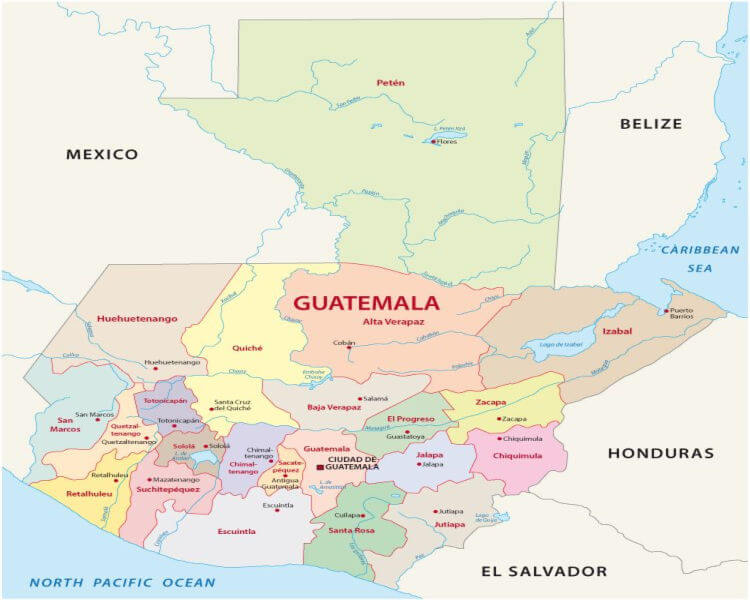
The Guatemala-Mexico border, a physical manifestation of a shared history and complex present, stretches for over 960 kilometers (600 miles) across diverse landscapes. This intricate boundary, a defining feature of Central America, is a vital artery for trade, migration, and cultural exchange. Understanding its geography, history, and current significance provides a crucial lens through which to view the interconnectedness of these two nations.
A Tapestry of Landscapes:
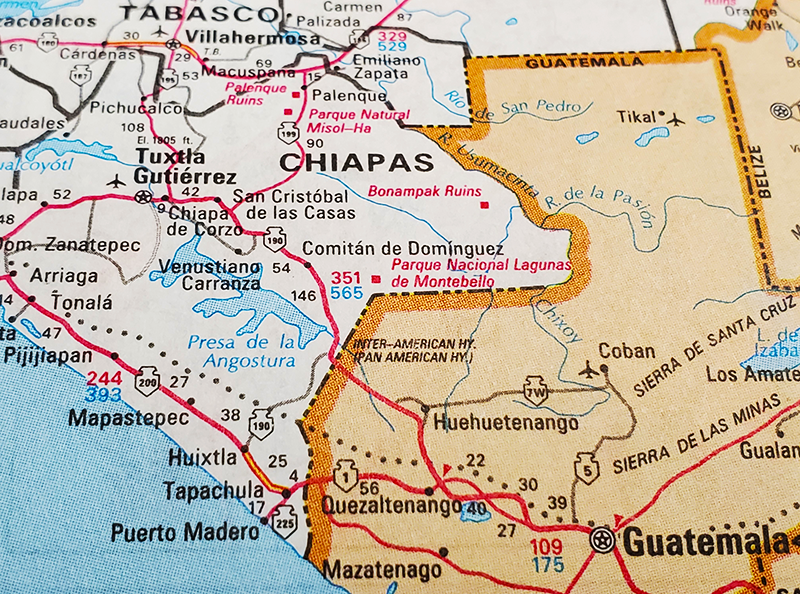
The Guatemala-Mexico border traverses a variety of geographical features, reflecting the distinct identities of both countries. In the north, the boundary runs along the Usumacinta River, a major waterway that serves as a natural barrier. This region is characterized by dense rainforests, home to diverse flora and fauna, including the iconic Mayan ruins of Tikal in Guatemala and Palenque in Mexico.
Further south, the border traverses the Sierra Madre de Chiapas, a rugged mountain range that presents significant challenges for transportation and communication. This mountainous region is home to indigenous communities with rich cultural traditions, many of whom straddle the border, maintaining strong ties on both sides.
The border also includes a section along the Pacific coast, where coastal lowlands and mangrove swamps provide a stark contrast to the mountainous terrain. This region is marked by fishing communities and agricultural lands, contributing significantly to the economies of both Guatemala and Mexico.
A Historical Tapestry:
The Guatemala-Mexico border has a long and complex history, shaped by pre-Columbian civilizations, colonial rule, and modern political developments. The Mayan civilization, which flourished in this region for centuries, left behind a legacy of intricate archaeological sites and cultural traditions that continue to influence both sides of the border.
During the colonial era, the border was established by Spanish authorities, dividing the territories of Guatemala and Chiapas, then part of the Captaincy General of Guatemala. This division, often arbitrary and insensitive to existing cultural and ethnic boundaries, sowed the seeds of future conflict.
In the 19th century, both countries experienced independence, leading to further border disputes. The final demarcation of the border was agreed upon in 1882, but ongoing disagreements over the interpretation of the treaty continue to this day.
A Border in Flux:
The Guatemala-Mexico border is not merely a geographical line; it is a dynamic space where social, economic, and political forces converge. The border region is a significant hub for trade, with goods and services flowing freely across the boundary. However, this trade is often characterized by informal networks and limited regulation, raising concerns about smuggling and illicit activities.
The border is also a major route for migration, with many Guatemalans seeking economic opportunities or fleeing violence and poverty in their homeland. This migration flow has created a complex and sensitive situation, with both countries struggling to manage the influx of migrants and address the underlying causes of migration.
Moreover, the border is a focal point for drug trafficking and organized crime, posing challenges to law enforcement on both sides. The porous nature of the border, combined with limited resources and coordination, makes it difficult to control illicit activities and protect communities from violence.
The Importance of Cooperation:
The Guatemala-Mexico border presents both opportunities and challenges. To maximize the benefits of this shared space, both countries must engage in constructive cooperation. This cooperation should encompass a range of initiatives, including:
- Strengthening border security: Implementing joint patrols, information sharing, and capacity building to combat cross-border crime and ensure the safety of communities.
- Promoting economic development: Fostering trade and investment opportunities, creating jobs, and promoting sustainable economic growth in the border region.
- Addressing migration challenges: Developing humane and effective policies to manage migration flows, protect the rights of migrants, and address the root causes of migration.
- Promoting cultural exchange: Encouraging cultural exchange programs, fostering understanding between communities on both sides of the border, and preserving shared cultural heritage.
FAQs about the Guatemala-Mexico Border:
Q: What are the main border crossings between Guatemala and Mexico?
A: Some of the main border crossings include:
- Ciudad Hidalgo, Chiapas, Mexico – Tecún Umán, Guatemala: This is the busiest border crossing, connecting the Mexican state of Chiapas with the Guatemalan department of San Marcos.
- El Carmen, Chiapas, Mexico – La Mesilla, Guatemala: This crossing connects the Mexican state of Chiapas with the Guatemalan department of Huehuetenango.
- Benemérito de las Américas, Chiapas, Mexico – Melchor de Mencos, Guatemala: This crossing connects the Mexican state of Chiapas with the Guatemalan department of Petén.
Q: What are the key challenges facing the Guatemala-Mexico border region?
A: The border region faces a number of challenges, including:
- Drug trafficking and organized crime: The porous nature of the border makes it difficult to control illicit activities and protect communities from violence.
- Migration: The influx of migrants from Guatemala seeking economic opportunities or fleeing violence and poverty in their homeland creates a complex and sensitive situation.
- Poverty and inequality: The border region is home to many marginalized communities, struggling with poverty, lack of access to education and healthcare, and limited economic opportunities.
- Environmental degradation: Deforestation, pollution, and unsustainable resource extraction threaten the delicate ecosystems of the border region.
Q: What are the potential benefits of cooperation between Guatemala and Mexico?
A: Cooperation between Guatemala and Mexico can bring a range of benefits, including:
- Enhanced border security: Joint efforts can combat cross-border crime, protect communities, and facilitate the flow of legitimate trade.
- Increased economic opportunities: Cooperation can foster trade and investment, create jobs, and promote sustainable economic development in the border region.
- Improved migration management: Collaboration can address the root causes of migration, protect the rights of migrants, and ensure humane and effective migration management.
- Cultural enrichment: Exchange programs and cultural initiatives can foster understanding and promote the shared heritage of both countries.
Tips for Travelers Crossing the Guatemala-Mexico Border:
- Check visa requirements: Ensure that you have the necessary travel documents and visas for both countries.
- Be aware of security risks: Stay vigilant, avoid traveling alone at night, and be aware of your surroundings.
- Respect local customs: Dress modestly, be mindful of local customs and traditions, and avoid offensive behavior.
- Carry essential documents: Keep your passport, visa, and other important documents safe and readily accessible.
- Exchange currency: Exchange currency at reputable exchange bureaus and be aware of exchange rates.
- Be prepared for delays: Border crossings can be crowded and subject to delays, so plan accordingly.
Conclusion:
The Guatemala-Mexico border is a complex and dynamic space that reflects the shared history, interconnected economies, and cultural ties between these two nations. Understanding the complexities of this border, its history, and its challenges is crucial for fostering cooperation, promoting development, and ensuring the well-being of communities on both sides. By working together, Guatemala and Mexico can harness the potential of this shared space and build a brighter future for the border region and its inhabitants.
![]()




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Divide: A Comprehensive Exploration of the Guatemala-Mexico Border. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!