Navigating the Political Landscape of Sweden: A Comprehensive Guide to Its Map
Related Articles: Navigating the Political Landscape of Sweden: A Comprehensive Guide to Its Map
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Political Landscape of Sweden: A Comprehensive Guide to Its Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Navigating the Political Landscape of Sweden: A Comprehensive Guide to Its Map
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Navigating the Political Landscape of Sweden: A Comprehensive Guide to Its Map
- 3.1 Administrative Divisions: A Foundation for Governance
- 3.2 Political Parties: Shaping the Political Spectrum
- 3.3 Electoral System: Proportional Representation and Its Impact
- 3.4 Key Historical Events: Shaping the Political Landscape
- 3.5 FAQs: Understanding the Political Map
- 3.6 Tips: Navigating the Political Map
- 3.7 Conclusion: A Dynamic and Evolving Political Landscape
- 4 Closure
Navigating the Political Landscape of Sweden: A Comprehensive Guide to Its Map
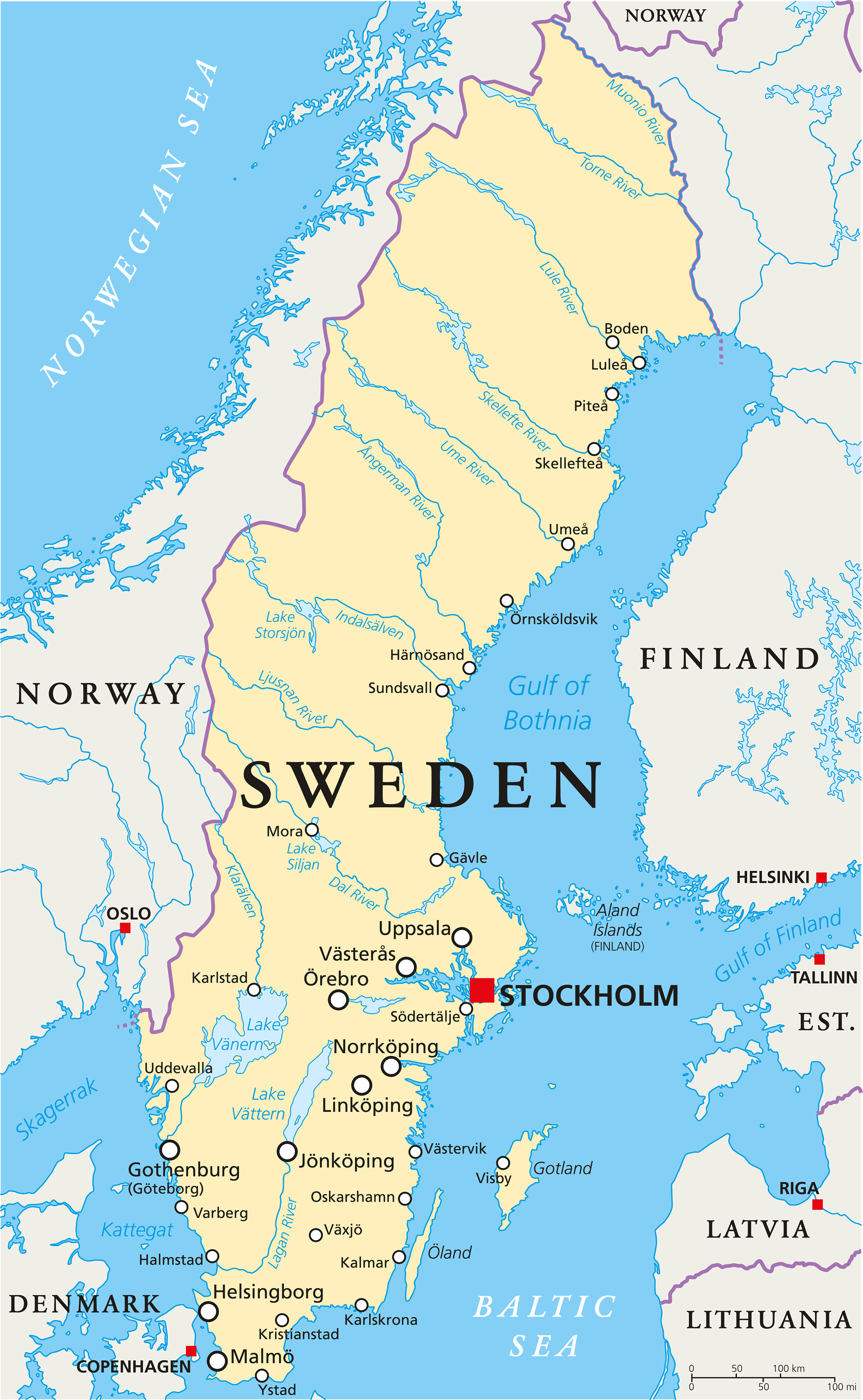
Sweden, a Nordic nation renowned for its social welfare system, innovative industries, and captivating landscapes, also boasts a rich and dynamic political structure. Understanding the intricate web of its political map is crucial for grasping its history, current affairs, and future trajectory. This comprehensive guide delves into the complexities of Sweden’s political landscape, exploring its administrative divisions, political parties, electoral system, and key historical events that have shaped its current political framework.
Administrative Divisions: A Foundation for Governance
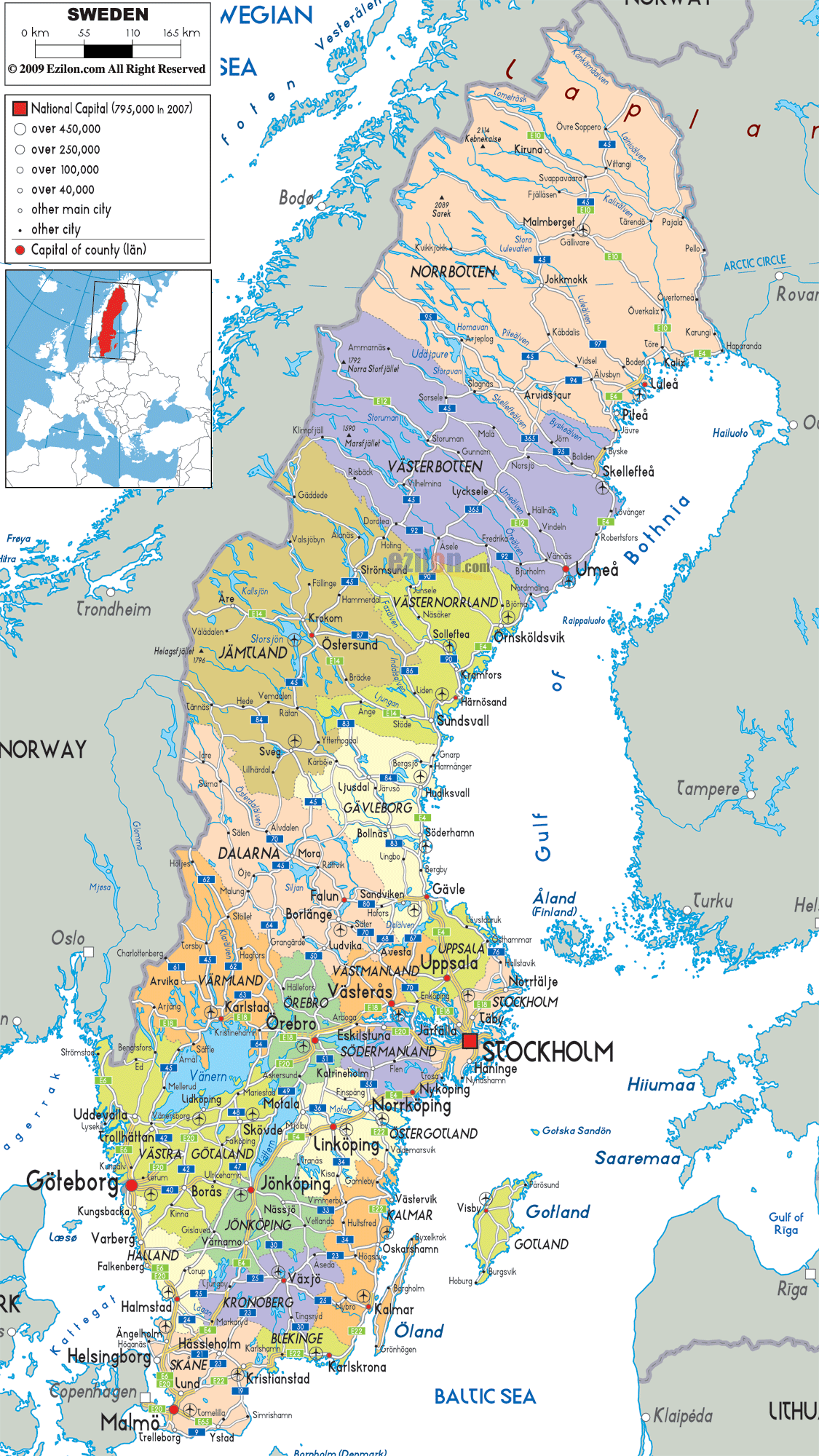
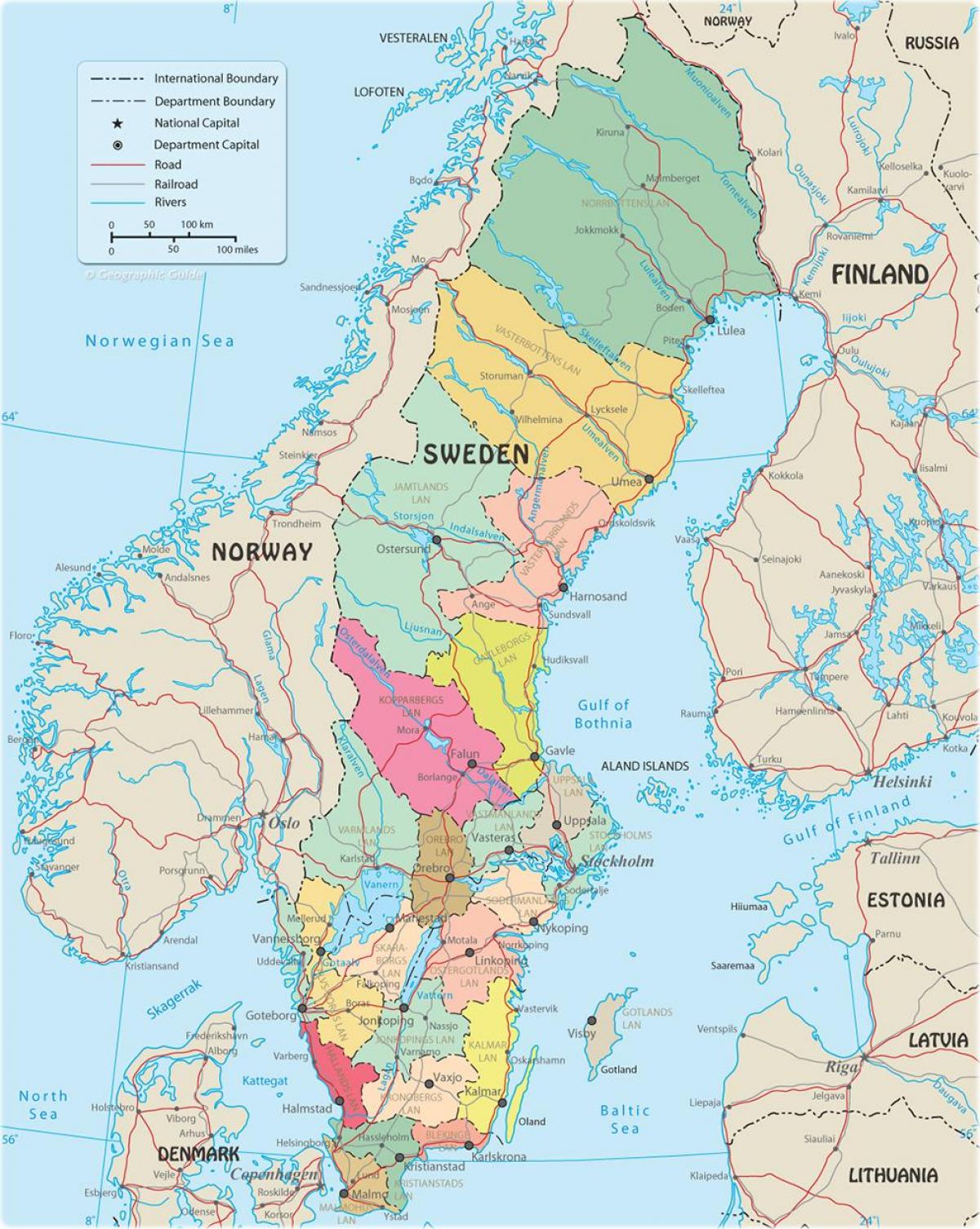
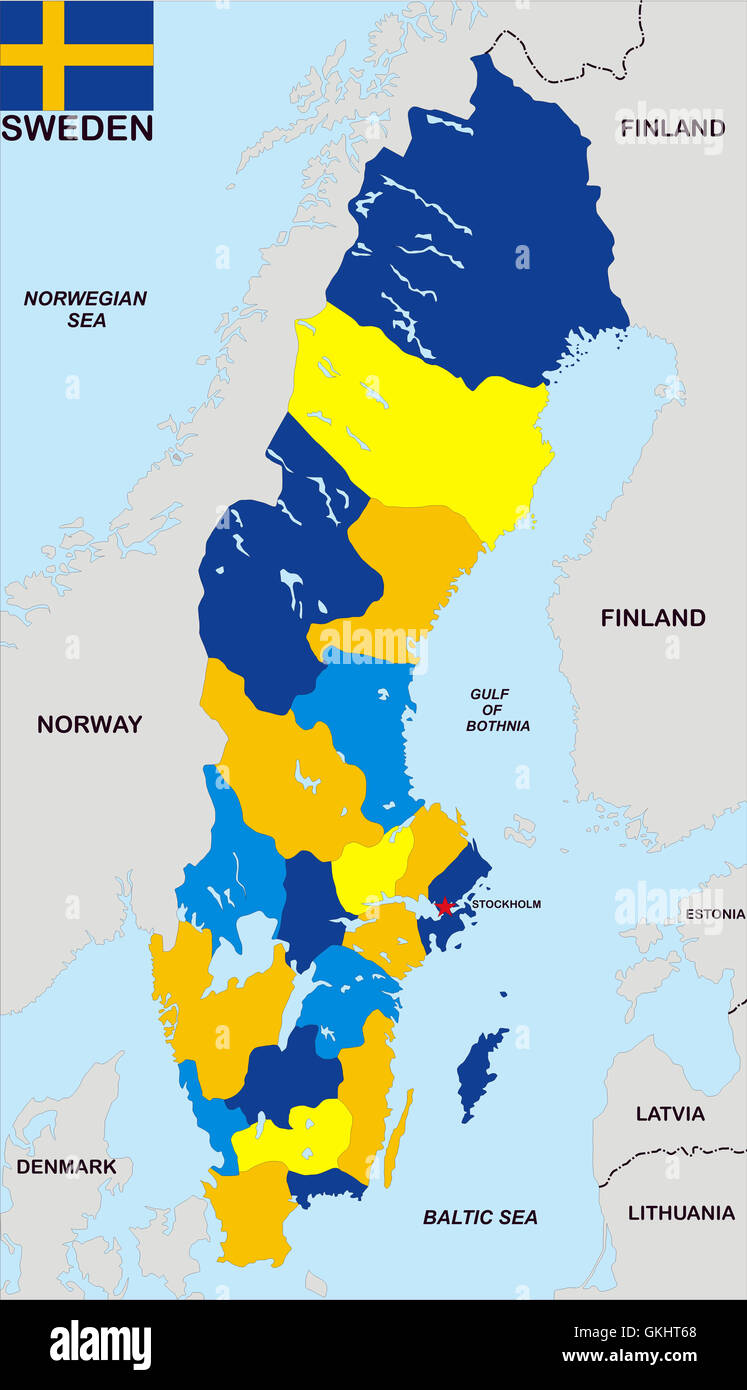
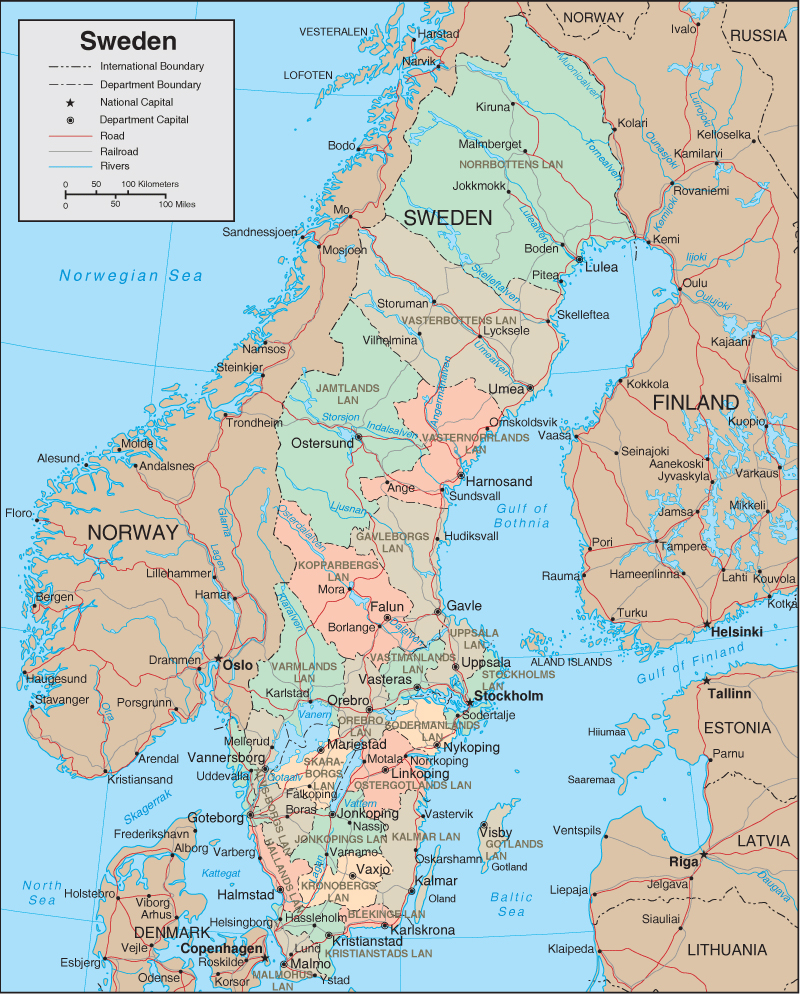
Sweden’s political map is characterized by a tiered administrative structure, encompassing national, regional, and local levels. At the national level, the country is governed by a parliamentary democracy with a unicameral legislature, the Riksdag. This national parliament comprises 349 members, elected every four years through a proportional representation system.
The regional level is represented by 21 counties (län), each with a county council (landsting) responsible for regional healthcare, public transport, and cultural initiatives. These councils are elected by the residents of each county.
At the local level, Sweden is further divided into 290 municipalities (kommuner), each with its own elected council responsible for local services such as schools, childcare, and social care. This decentralized system allows for localized decision-making and responsiveness to specific community needs.
Political Parties: Shaping the Political Spectrum
Sweden’s political landscape is characterized by a multi-party system, with numerous parties vying for political power. The two dominant parties, the Social Democratic Party (SAP) and the Moderate Party (M), have historically held significant influence, often forming coalition governments.
The Social Democratic Party, rooted in social democratic principles, advocates for a strong welfare state, social justice, and economic equality. The Moderate Party, aligned with liberal conservatism, emphasizes individual responsibility, economic freedom, and a more limited role for the state.
Other prominent parties include the Green Party (MP), advocating for environmental protection and sustainable development; the Left Party (V), promoting socialist ideals; the Center Party (C), focused on rural issues and regional development; the Liberal Party (FP), championing free market principles; and the Christian Democrats (KD), prioritizing family values and Christian ethics.
Electoral System: Proportional Representation and Its Impact
Sweden’s electoral system, based on proportional representation, ensures that all parties with sufficient support are represented in the Riksdag. This system, unlike first-past-the-post systems, minimizes wasted votes and fosters greater inclusivity.
While proportional representation promotes a more diverse representation of political views, it can also lead to coalition governments, requiring compromises and negotiations between parties to form a stable majority. This process can sometimes result in political instability and prolonged negotiations, particularly when no single party secures a clear majority.
Key Historical Events: Shaping the Political Landscape
Sweden’s political landscape has been shaped by a series of pivotal historical events that have significantly impacted its political system and social fabric.
-
The 1932 General Election: This election marked a turning point in Swedish politics, with the Social Democratic Party winning a landslide victory and ushering in a period of social reforms and expansion of the welfare state.
-
The 1970s and 1980s: These decades witnessed a shift in Swedish politics, with the rise of the Green Party and the emergence of new social movements advocating for environmental protection and social justice.
-
The 1990s: The collapse of the Soviet Union and the rise of globalization had a profound impact on Swedish politics, leading to a focus on economic liberalization and integration into the European Union.
-
The 2000s and 2010s: This period saw the emergence of new political parties, including the Sweden Democrats, a nationalist party that gained traction due to concerns about immigration and social cohesion.
FAQs: Understanding the Political Map
Q: What is the role of the Swedish monarchy in the political system?
A: Sweden is a constitutional monarchy, with a monarch as head of state. However, the monarch’s role is primarily ceremonial, and they do not hold any significant political power. The real power resides with the government, led by the Prime Minister and the Riksdag.
Q: How does the Swedish political system ensure accountability and transparency?
A: Sweden has a strong tradition of freedom of the press and freedom of information. The media plays a crucial role in holding the government accountable, and citizens have access to extensive information about government activities.
Q: What are the key challenges facing Swedish politics today?
A: Contemporary challenges include managing the influx of refugees and migrants, balancing social welfare with economic competitiveness, and addressing climate change.
Tips: Navigating the Political Map
-
Follow Swedish news outlets: Stay informed about current events and political developments by following reputable Swedish news sources, such as Sveriges Radio (SR) and Sveriges Television (SVT).
-
Explore political party websites: Visit the websites of major political parties to understand their policies, platforms, and key figures.
-
Engage with political discussions: Participate in online forums and discussions to gain insights into different perspectives and opinions on political issues.
Conclusion: A Dynamic and Evolving Political Landscape
Sweden’s political map is a complex tapestry woven from historical events, political ideologies, and societal values. The country’s decentralized administrative structure, multi-party system, and proportional representation electoral system contribute to a dynamic and evolving political landscape. Understanding this map is crucial for appreciating the complexities of Swedish politics and its impact on the nation’s social, economic, and cultural development. By engaging with current affairs, exploring the history of political events, and understanding the key players and their ideologies, one can gain a deeper appreciation for the intricacies of Sweden’s political landscape and its role in shaping the nation’s future.


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Political Landscape of Sweden: A Comprehensive Guide to Its Map. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!