Navigating the Terrain: Understanding and Utilizing Peak-to-Peak Mapping for Enhanced Decision-Making
Related Articles: Navigating the Terrain: Understanding and Utilizing Peak-to-Peak Mapping for Enhanced Decision-Making
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Terrain: Understanding and Utilizing Peak-to-Peak Mapping for Enhanced Decision-Making. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Navigating the Terrain: Understanding and Utilizing Peak-to-Peak Mapping for Enhanced Decision-Making
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Navigating the Terrain: Understanding and Utilizing Peak-to-Peak Mapping for Enhanced Decision-Making
- 3.1 What is Peak-to-Peak Mapping?
- 3.2 The Importance of Peak-to-Peak Mapping
- 3.3 Applications of Peak-to-Peak Mapping
- 3.4 Creating a Peak-to-Peak Map
- 3.5 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- 3.6 Tips for Utilizing Peak-to-Peak Mapping Effectively
- 3.7 Conclusion
- 4 Closure
Navigating the Terrain: Understanding and Utilizing Peak-to-Peak Mapping for Enhanced Decision-Making

Peak-to-peak mapping, a powerful visualization tool in the realm of data analysis, allows for a clear and insightful understanding of data trends over time. This technique, also known as "peak-to-peak analysis" or "peak-to-peak comparison," focuses on identifying and comparing the highest and lowest points within a data set, providing valuable insights into growth, decline, volatility, and cyclical patterns.
What is Peak-to-Peak Mapping?
Peak-to-peak mapping involves plotting data points on a graph, with the vertical axis representing the data values and the horizontal axis representing time. The highest points (peaks) and lowest points (troughs) within the data set are then identified and connected, creating a visual representation of the data’s extreme values. This visual representation allows for a quick and intuitive understanding of the data’s overall trend and its fluctuations.
The Importance of Peak-to-Peak Mapping
Peak-to-peak mapping offers a range of benefits for various disciplines, including:
- Identifying Trends and Cycles: By connecting the peaks and troughs, the map reveals potential trends, cyclical patterns, and periods of growth or decline. This information can be crucial for forecasting future performance, identifying seasonal variations, and understanding long-term patterns within the data.
- Analyzing Volatility: The distance between peaks and troughs highlights the degree of fluctuation within the data. This information is particularly valuable for understanding risk and identifying periods of instability or uncertainty.
- Comparing Different Data Sets: Peak-to-peak mapping can be used to compare multiple data sets, allowing for a side-by-side analysis of their peaks and troughs. This comparison can reveal similarities and differences in trends, volatility, and overall performance.
- Facilitating Decision-Making: The insights gained from peak-to-peak mapping can inform strategic decision-making in various fields. For example, businesses can use it to optimize production, marketing, or pricing strategies based on identified trends and cycles.
Applications of Peak-to-Peak Mapping
The versatility of peak-to-peak mapping makes it applicable across diverse industries and domains:
- Finance: Identifying market trends, understanding volatility, and predicting future stock prices.
- Marketing: Analyzing customer behavior, identifying peak seasons, and optimizing advertising campaigns.
- Sales: Forecasting sales performance, identifying peak sales periods, and managing inventory levels.
- Healthcare: Tracking disease outbreaks, identifying seasonal trends, and optimizing resource allocation.
- Climate Science: Analyzing climate data, identifying extreme weather events, and understanding climate change patterns.
Creating a Peak-to-Peak Map
Creating a peak-to-peak map involves the following steps:
- Data Collection: Gather the relevant data for the analysis. This could include sales figures, stock prices, temperature readings, or any other data set relevant to the specific application.
- Data Preparation: Clean and organize the data, ensuring accuracy and consistency. This may involve removing outliers, handling missing data, and standardizing units of measurement.
- Plotting the Data: Plot the data points on a graph, with the vertical axis representing the data values and the horizontal axis representing time.
- Identifying Peaks and Troughs: Identify the highest points (peaks) and lowest points (troughs) within the data set.
- Connecting Peaks and Troughs: Connect the peaks and troughs with lines, creating a visual representation of the data’s extreme values.
- Interpretation and Analysis: Analyze the resulting map to identify trends, cycles, volatility, and other insights relevant to the specific application.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: What are the limitations of peak-to-peak mapping?
A: While peak-to-peak mapping is a valuable tool, it is important to note its limitations:
- Focus on Extremes: The method primarily focuses on extreme values, potentially overlooking other important data points or nuances within the data set.
- Sensitivity to Outliers: Outliers, or extreme data points that deviate significantly from the overall trend, can disproportionately influence the map’s interpretation.
- Limited Predictive Power: While peak-to-peak mapping can identify trends and cycles, it does not guarantee future performance or provide definitive predictions.
Q: What are some alternative methods for analyzing data trends?
A: While peak-to-peak mapping offers a valuable perspective, other methods can complement or provide alternative insights:
- Moving Average Analysis: Calculates a series of averages over time, smoothing out data fluctuations and revealing underlying trends.
- Trendline Analysis: Fits a line to the data, highlighting the overall trend and its direction.
- Regression Analysis: Identifies relationships between variables, allowing for prediction and forecasting.
Q: How can I improve the accuracy of peak-to-peak mapping?
A: Several strategies can enhance the accuracy and reliability of peak-to-peak mapping:
- Data Quality: Ensure data accuracy and completeness to minimize the impact of errors or missing values.
- Outlier Detection: Identify and address outliers, either by removing them or adjusting their influence on the analysis.
- Time Scale: Choose an appropriate time scale for the analysis, ensuring it captures the relevant trends and cycles.
- Data Transformation: Consider transforming the data, such as using logarithmic scales, to better visualize certain trends or patterns.
Tips for Utilizing Peak-to-Peak Mapping Effectively
- Clear Objectives: Define clear objectives for the analysis, ensuring the chosen data set and time scale align with the desired insights.
- Contextualization: Consider the context of the data and the potential factors influencing the observed peaks and troughs.
- Multiple Perspectives: Combine peak-to-peak mapping with other analytical methods to gain a comprehensive understanding of the data.
- Visualization Tools: Utilize appropriate software and tools for creating and interpreting peak-to-peak maps, ensuring clear visualization and accurate analysis.
Conclusion
Peak-to-peak mapping is a powerful and versatile tool for analyzing data trends and identifying key insights. By focusing on extreme values, it provides a clear and intuitive representation of data fluctuations, revealing patterns, cycles, and potential areas of concern. While it is essential to consider its limitations and complement it with other analytical methods, peak-to-peak mapping remains a valuable asset for decision-making in various fields, offering a unique perspective on data trends and informing strategic choices.
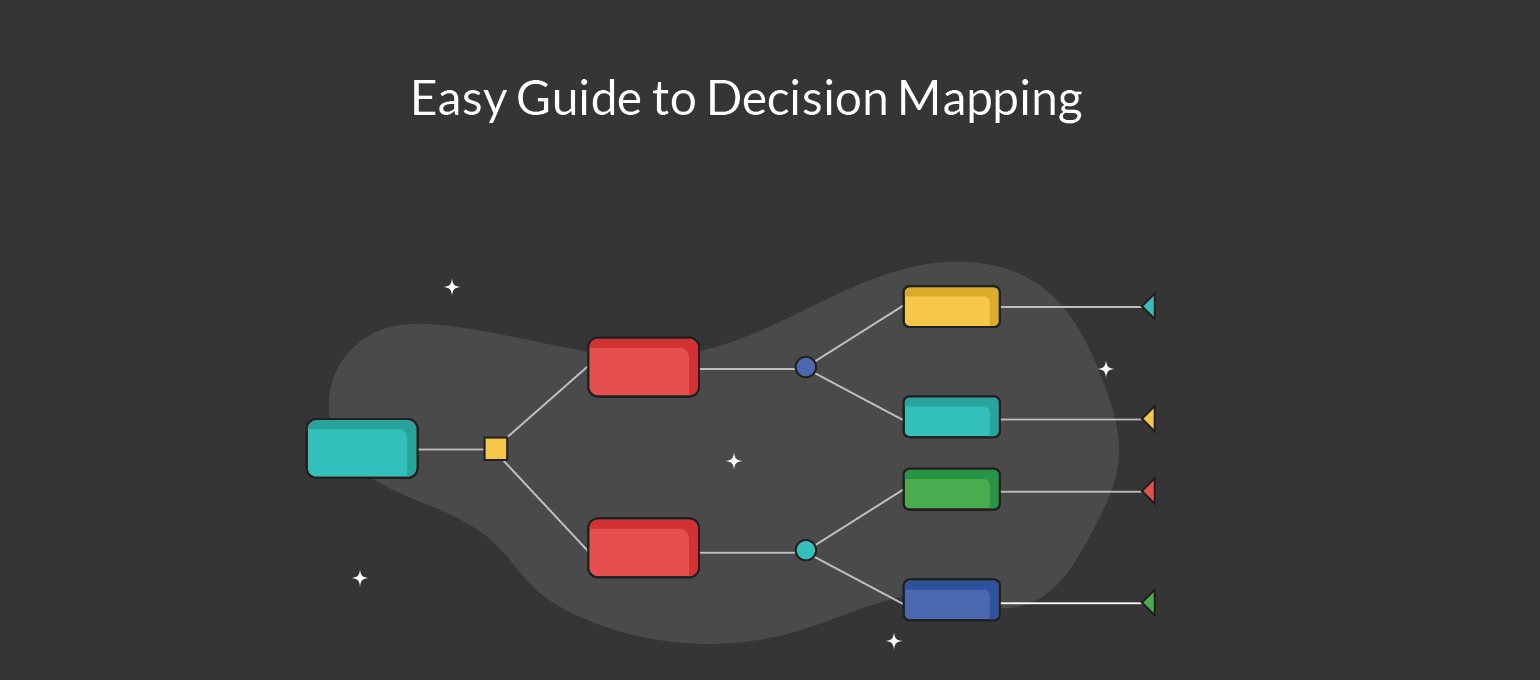




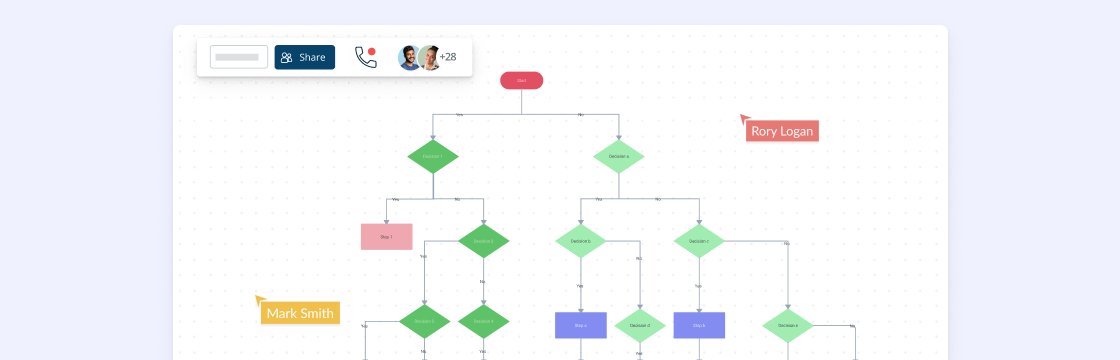
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Terrain: Understanding and Utilizing Peak-to-Peak Mapping for Enhanced Decision-Making. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!