Navigating the Waters: Understanding the USGS Water Map
Related Articles: Navigating the Waters: Understanding the USGS Water Map
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Waters: Understanding the USGS Water Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Waters: Understanding the USGS Water Map
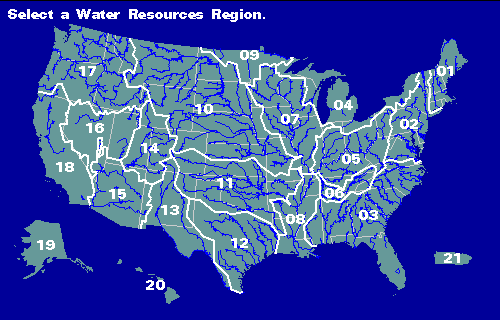
The United States Geological Survey (USGS) plays a crucial role in understanding and managing the nation’s water resources. A key tool in this effort is the USGS Water Map, a comprehensive online platform providing access to a vast repository of water-related data. This map serves as a central hub for information on water availability, quality, and usage across the United States, empowering researchers, policymakers, and the public alike to make informed decisions regarding water management.
Unveiling the Layers of Information:
The USGS Water Map is more than just a static map; it’s a dynamic portal that integrates various datasets and tools. Its core features include:
-
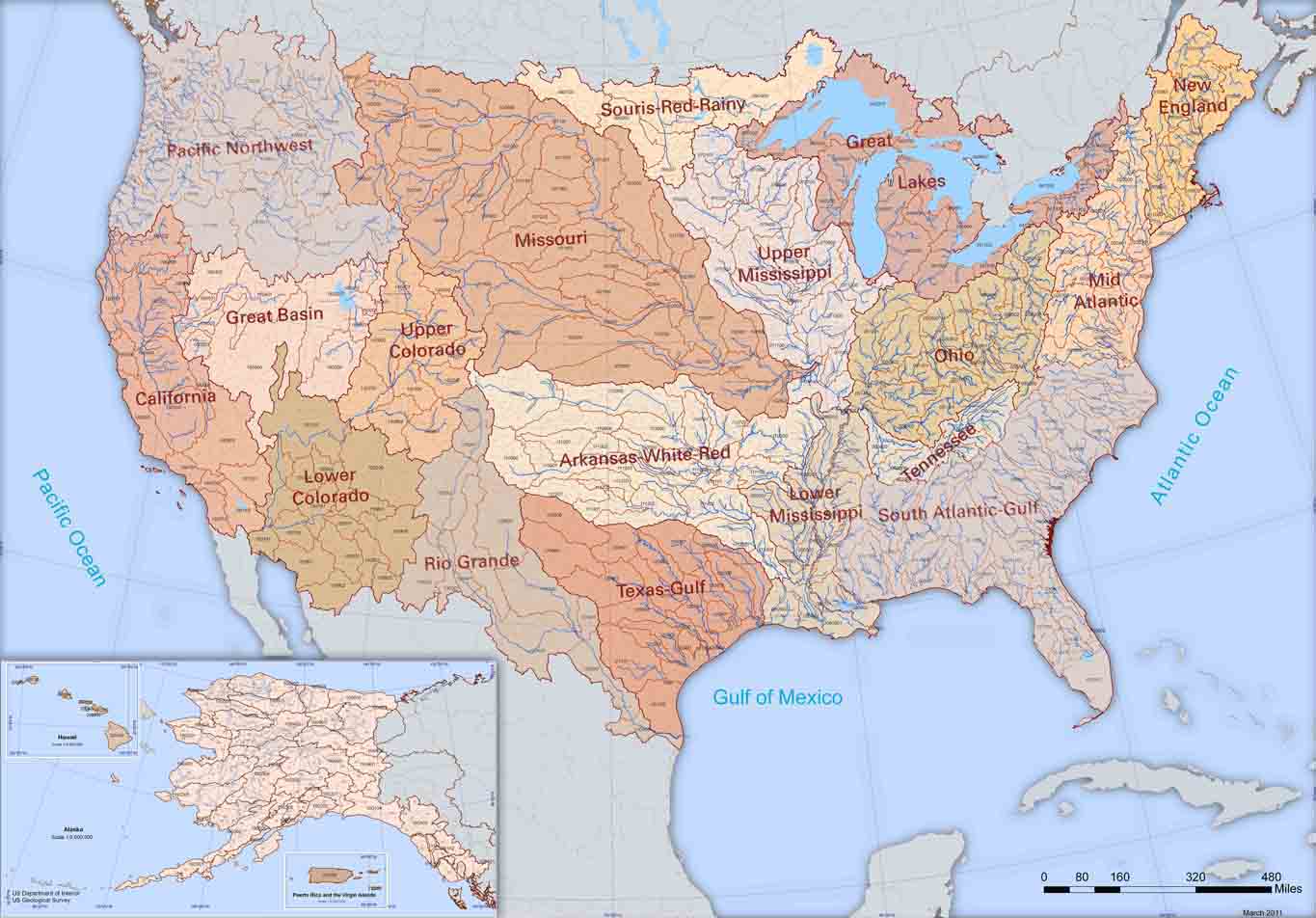
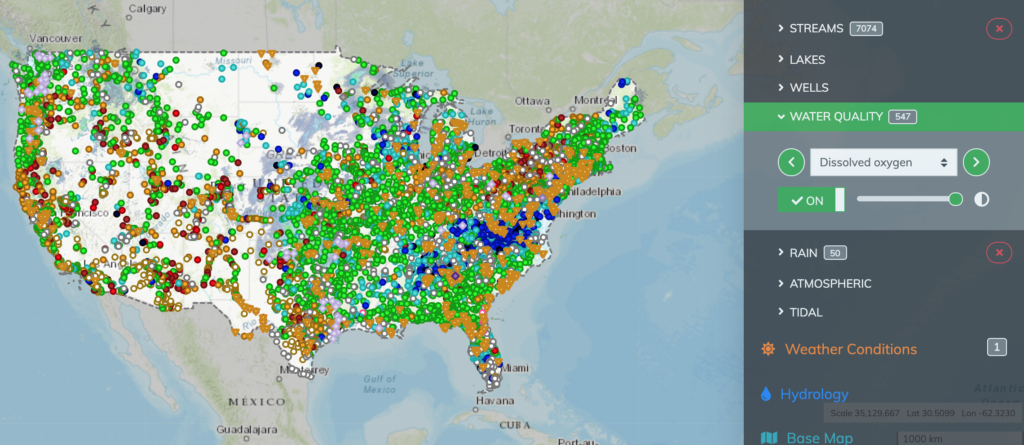
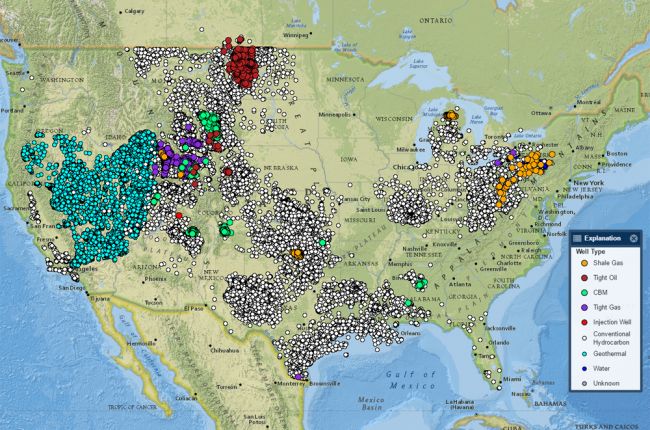
Interactive Maps: Users can explore a range of map layers, each representing a specific aspect of water resources. These layers encompass surface water features, groundwater information, water quality data, streamflow measurements, and more. Users can select, combine, and analyze these layers to gain insights into water conditions in specific areas.
-
Data Downloads: The platform allows users to download raw data in various formats, including shapefiles, spreadsheets, and web services. This enables researchers and analysts to conduct in-depth studies and build their own custom analyses.
-
Water Data Explorer: This powerful tool provides access to a vast database of water-related data, including streamflow, water quality, groundwater levels, and precipitation. Users can query the database based on location, time period, and other parameters to retrieve specific information.
-
Water Science Center Publications: The USGS Water Map connects to a library of scientific publications, reports, and datasets produced by USGS Water Science Centers across the country. This provides valuable context and analysis to the data presented on the map.
The Significance of the USGS Water Map:
The USGS Water Map is a vital resource for a multitude of stakeholders:
-
Water Managers: By providing access to real-time and historical data, the map empowers water managers to make informed decisions regarding water allocation, drought planning, and flood control. They can track water levels, assess water quality, and monitor changes in water availability, enabling proactive and effective management strategies.
-
Researchers and Scientists: The platform serves as a valuable tool for researchers studying various aspects of water resources. They can access data on streamflow, groundwater levels, water quality, and precipitation, facilitating in-depth analysis and scientific discovery.
-
Policymakers and Legislators: The USGS Water Map provides crucial information for developing water-related policies and regulations. It allows policymakers to understand water resource availability, identify areas of concern, and implement effective water management strategies.
-
The Public: The platform empowers the public to access information about water resources in their communities. Citizens can understand water availability, water quality, and potential risks associated with water scarcity or flooding. This fosters public awareness and engagement in water management issues.
Understanding the Data:
The USGS Water Map utilizes a variety of data sources, including:
-
Real-Time Data: The platform integrates real-time data from a network of sensors and monitoring stations across the country. This includes streamflow measurements, groundwater levels, water quality parameters, and precipitation data.
-
Historical Data: The USGS maintains extensive archives of water-related data, dating back decades. This historical data provides valuable context and insights into long-term trends and changes in water resources.
-
Modeling and Analysis: The USGS utilizes advanced modeling techniques to simulate water flow, predict water availability, and assess the impact of climate change on water resources. These models provide valuable information for water management and planning.
FAQs about the USGS Water Map:
1. How can I access the USGS Water Map?
The USGS Water Map is freely accessible online at [link to USGS Water Map].
2. What types of data are available on the map?
The USGS Water Map provides data on surface water, groundwater, water quality, streamflow, precipitation, and other water-related factors.
3. How can I find data for a specific location?
The USGS Water Map allows users to search for data by location, using either a search bar or by clicking on a specific area on the map.
4. What formats can I download data in?
Data can be downloaded in various formats, including shapefiles, spreadsheets, and web services.
5. Are there any limitations to the data available?
The USGS Water Map provides a vast repository of data, but there may be limitations in terms of temporal and spatial coverage depending on the specific data set.
6. How can I contribute to the USGS Water Map?
The USGS welcomes contributions from researchers and citizen scientists. Data can be submitted through the USGS Water Data Portal or by contacting the relevant USGS Water Science Center.
7. What are some of the benefits of using the USGS Water Map?
The USGS Water Map provides a comprehensive and accessible platform for understanding and managing water resources, empowering researchers, policymakers, and the public to make informed decisions regarding water management.
Tips for Using the USGS Water Map:
- Start with a clear objective: Define your research question or the information you need before exploring the map.
- Explore the map layers: Familiarize yourself with the available layers and their corresponding data types.
- Use the search tools: Utilize the search bar or map interface to locate specific areas or data sets.
- Combine map layers: Overlay different layers to analyze relationships between various water-related factors.
- Download data for in-depth analysis: Utilize the download feature to access raw data for further analysis.
- Consult USGS publications: Refer to relevant publications for context and analysis of the data presented on the map.
Conclusion:
The USGS Water Map is a powerful resource for understanding and managing water resources in the United States. It provides a comprehensive platform for accessing and analyzing data, empowering stakeholders to make informed decisions regarding water availability, quality, and usage. By leveraging this valuable tool, researchers, policymakers, and the public can work together to ensure the sustainable management of this vital resource for future generations.
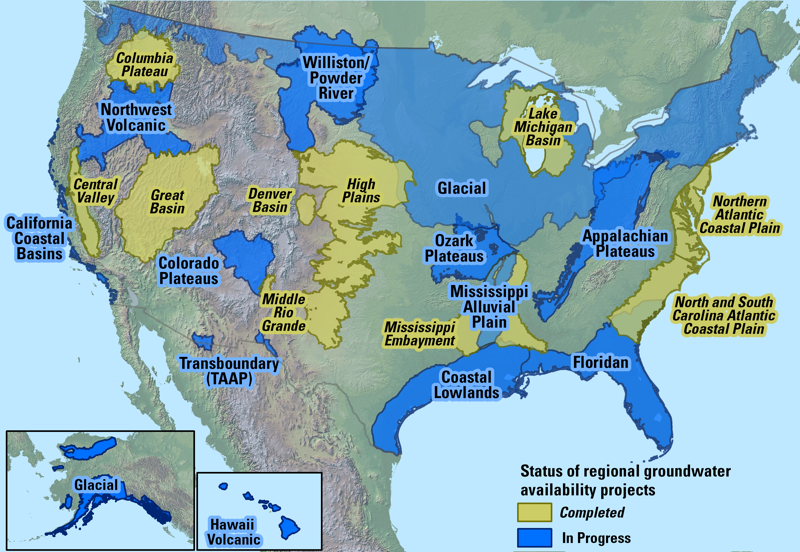
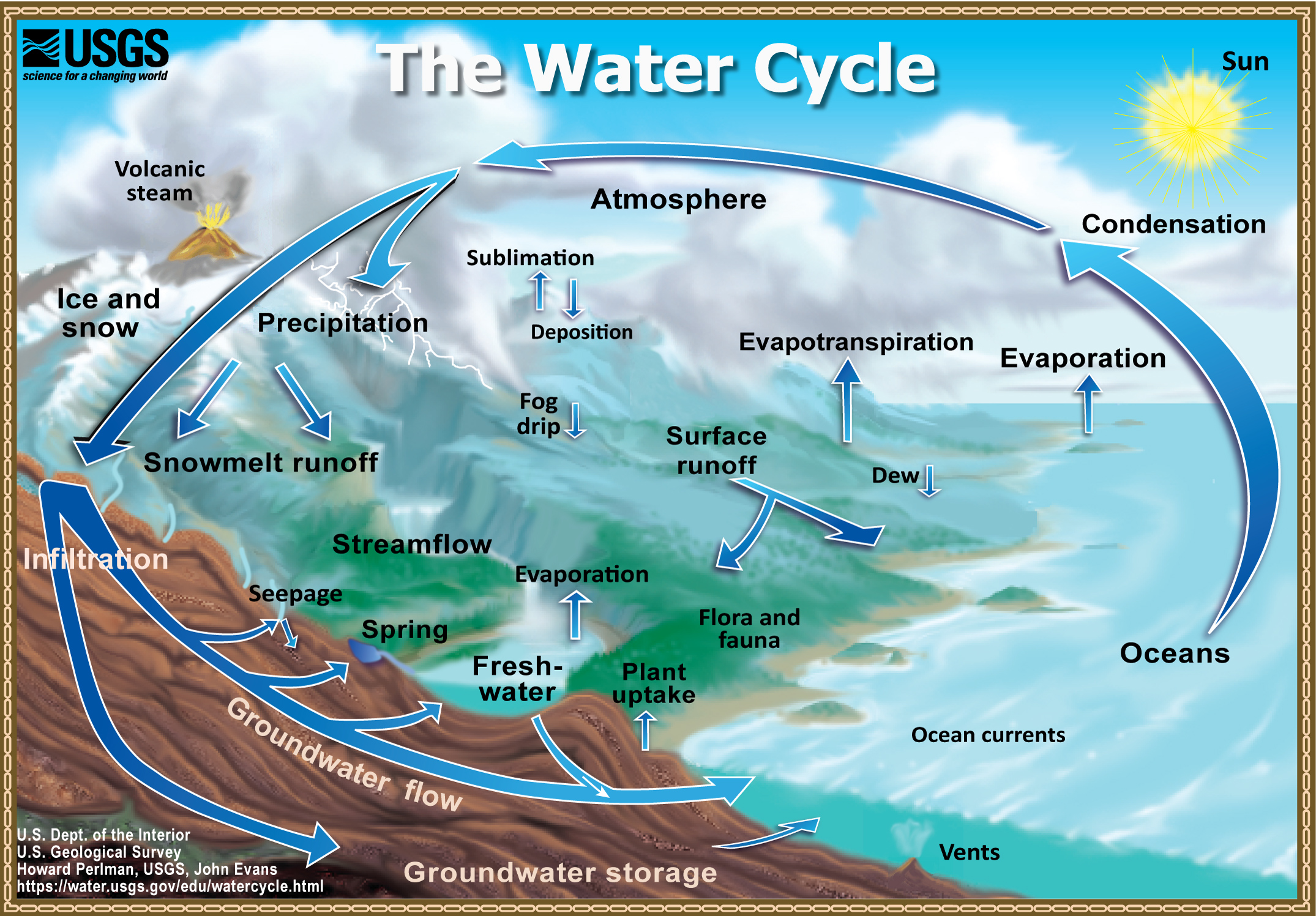
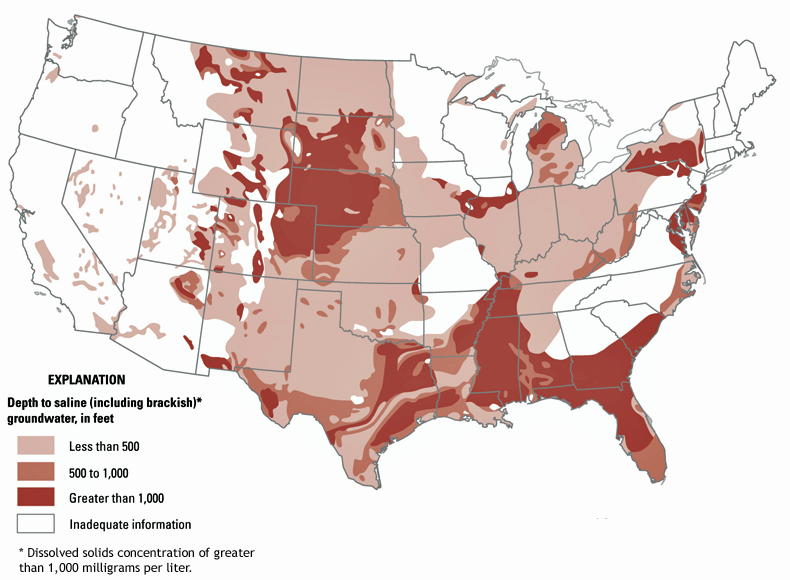
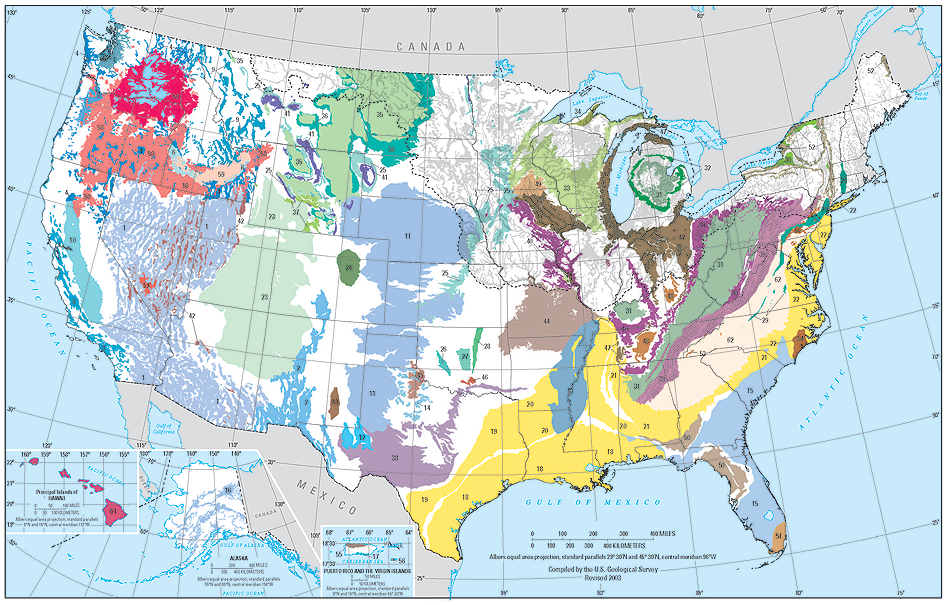

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Waters: Understanding the USGS Water Map. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!