Navigating the Winds: Identifying Low Wind Speed Regions on Weather Maps
Related Articles: Navigating the Winds: Identifying Low Wind Speed Regions on Weather Maps
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Winds: Identifying Low Wind Speed Regions on Weather Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Winds: Identifying Low Wind Speed Regions on Weather Maps

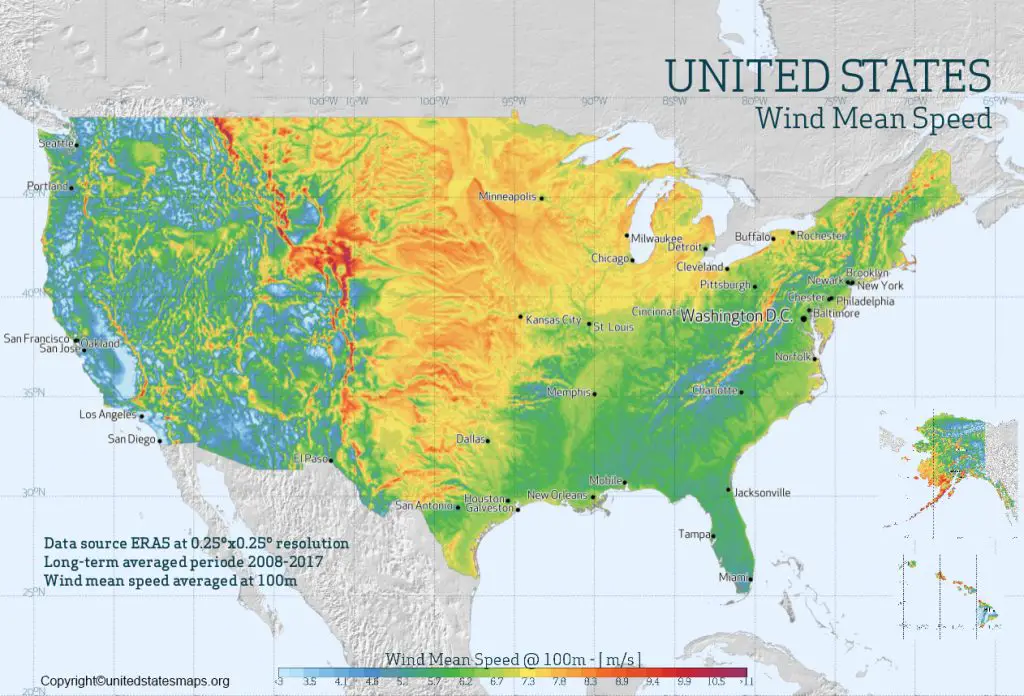
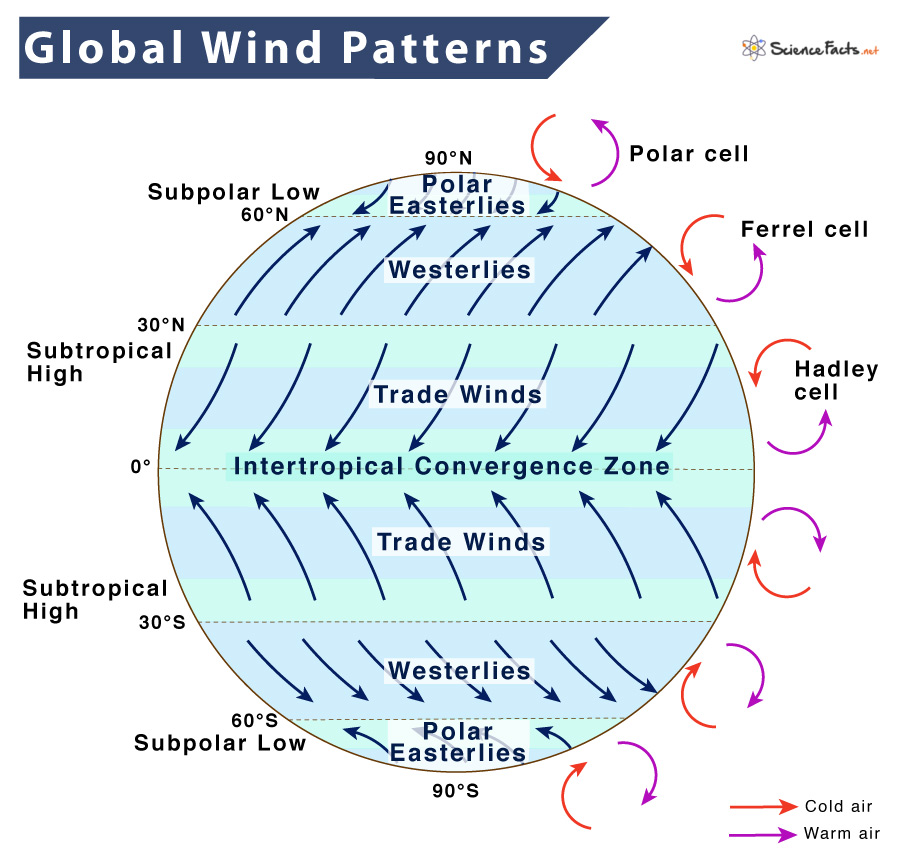
The wind, a seemingly ubiquitous force of nature, plays a crucial role in shaping our environment and influencing our daily lives. From its impact on weather patterns and energy generation to its influence on aviation and outdoor activities, understanding wind speed and direction is essential. Weather maps, with their intricate tapestry of symbols and data, provide a visual representation of wind conditions, enabling us to discern areas of low wind speed – a valuable insight for various purposes.
Understanding Wind Depiction on Weather Maps
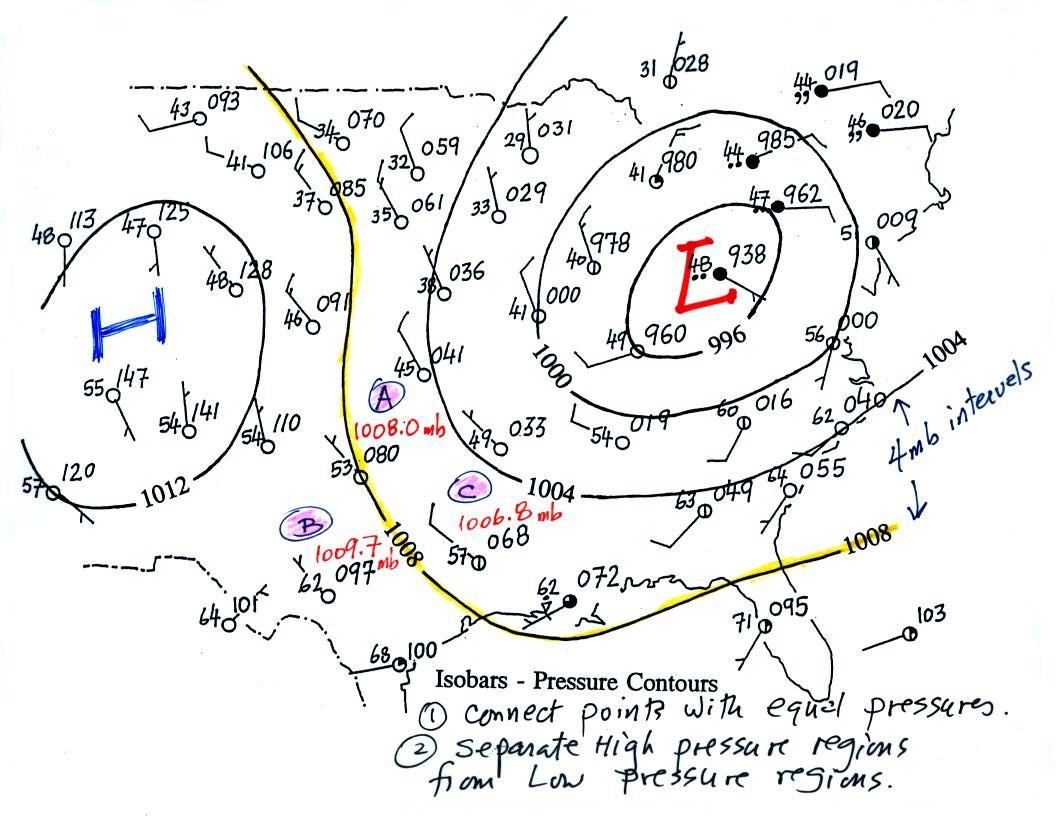
Weather maps typically employ wind barbs to illustrate wind direction and speed. These barbs, resembling small flags, are positioned at specific locations on the map, representing weather stations or grid points. The direction of the barb indicates the wind’s direction, while the number and length of its "tails" represent its speed.
- Direction: The wind barb points in the direction from which the wind is blowing. For example, a barb pointing west indicates that the wind is blowing from the west.
-
Speed: The speed is represented by the number of "tails" on the barb:
- One "tail" represents 5 knots (approximately 5.7 mph).
- Two "tails" represent 10 knots.
- Three "tails" represent 15 knots.
- A pennant (a triangular flag) represents 50 knots.
Identifying Low Wind Speed Regions
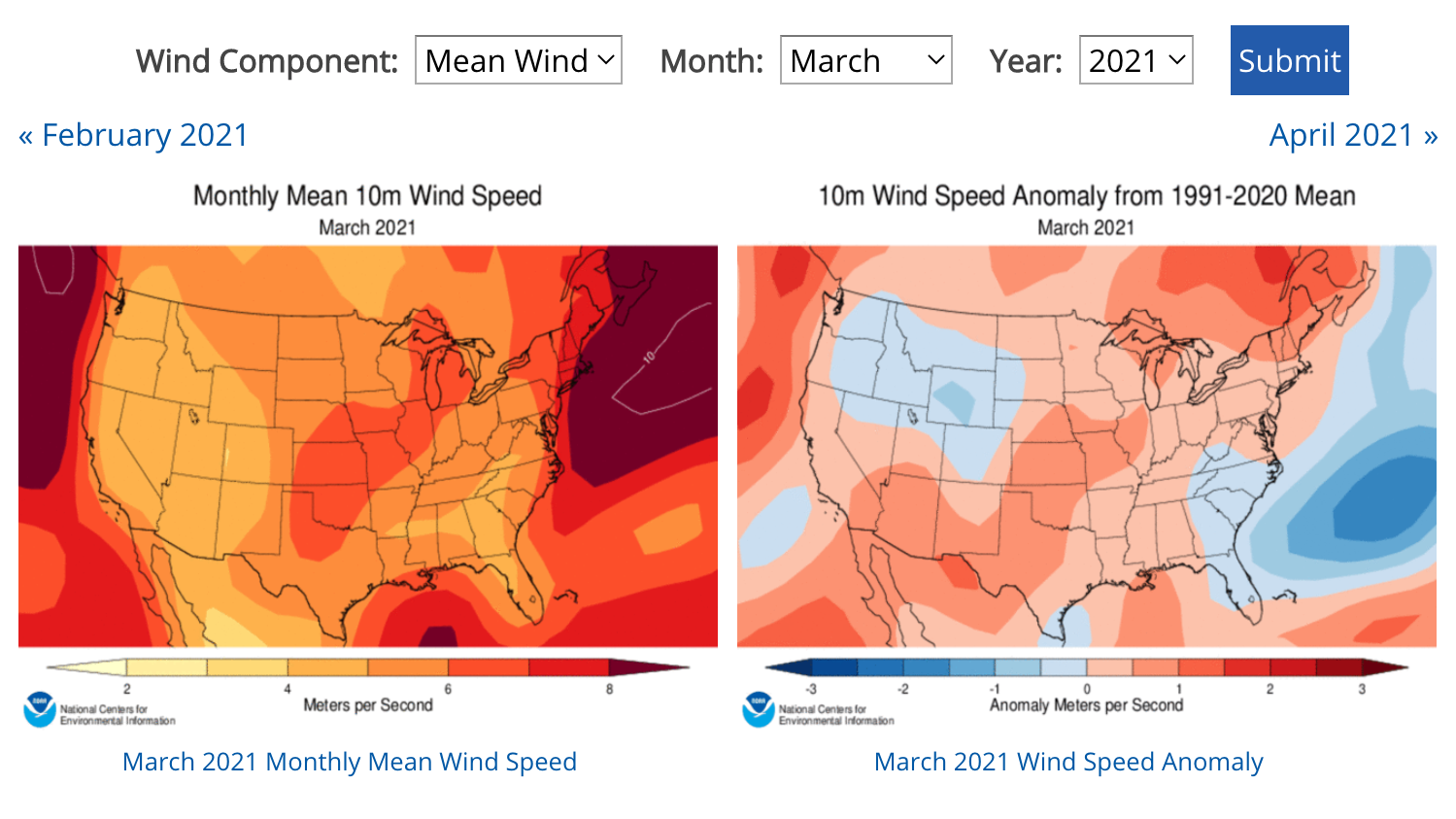
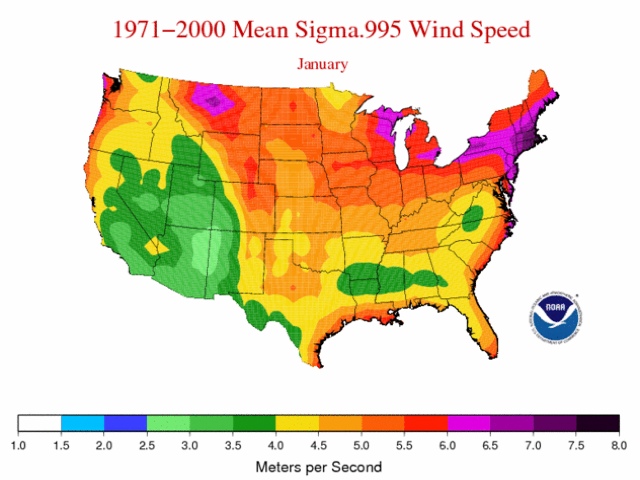
While the specific criteria for "low wind speed" may vary depending on the context, generally, wind speeds below 10 knots (approximately 11.5 mph) are considered low. To locate regions of low wind speed on a weather map, focus on areas where:
- Wind barbs have fewer or no tails: This indicates wind speeds of 5 knots or less.
- Wind barbs are clustered closely together: This suggests a lack of significant wind variations within the area.
- Isotachs (lines of equal wind speed) are closely spaced: This indicates a gradual change in wind speed, often associated with low wind speeds.
- Areas of high pressure: High-pressure systems are typically associated with calm or light winds. Look for areas marked with "H" on the weather map.
Importance of Identifying Low Wind Speed Regions
The ability to identify low wind speed regions holds significance across various domains:
- Aviation: Pilots rely on wind information to optimize flight paths and fuel efficiency. Low wind conditions are favorable for takeoffs and landings, reducing turbulence and increasing safety.
- Renewable Energy: Wind turbines require consistent wind speeds for efficient energy generation. Identifying low wind speed regions helps optimize turbine placement and operation, maximizing energy output.
- Outdoor Activities: Activities like kite flying, sailing, and paragliding are heavily influenced by wind conditions. Knowledge of low wind areas allows enthusiasts to plan activities accordingly, ensuring a safe and enjoyable experience.
- Weather Forecasting: Low wind speeds can be an indicator of stable atmospheric conditions, potentially leading to clear skies and favorable weather for outdoor events and activities.
Tips for Identifying Low Wind Speed Regions
- Consult multiple weather sources: Utilize various online weather websites and apps to obtain a comprehensive view of wind conditions.
- Pay attention to weather forecasts: Weather forecasts often include wind speed and direction predictions, providing valuable insights into potential low wind areas.
- Consider local topography: Mountain ranges, valleys, and bodies of water can significantly influence wind patterns. Understanding the local topography helps refine your analysis.
- Utilize online wind visualization tools: Several online tools offer interactive wind maps, providing detailed information on wind speed and direction at various altitudes.
FAQs
Q: What are the units used to measure wind speed on weather maps?
A: Wind speed is typically measured in knots (nautical miles per hour) or meters per second.
Q: How do I interpret the wind direction indicated on a weather map?
A: The wind barb points in the direction from which the wind is blowing. For example, a barb pointing west indicates that the wind is blowing from the west.
Q: Can low wind speed regions change quickly?
A: Yes, wind conditions can fluctuate rapidly, particularly in areas prone to thunderstorms or other weather disturbances. It’s essential to monitor wind conditions regularly.
Q: Is it possible to predict low wind speed regions in advance?
A: To some extent, yes. Weather forecasts often provide wind speed and direction predictions, offering insights into potential low wind areas. However, predicting wind conditions accurately remains challenging due to the complex dynamics of the atmosphere.
Conclusion
Navigating the complexities of weather maps and understanding the nuances of wind depiction empowers us to identify regions of low wind speed. This knowledge is invaluable for various applications, from aviation and renewable energy to outdoor activities and weather forecasting. By carefully examining wind barbs, isotachs, and other weather map indicators, we can gain insights into wind conditions and make informed decisions based on the prevailing winds.


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Winds: Identifying Low Wind Speed Regions on Weather Maps. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!