Navigating the World: A Comprehensive Guide to GPS Mapping Systems
Related Articles: Navigating the World: A Comprehensive Guide to GPS Mapping Systems
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Navigating the World: A Comprehensive Guide to GPS Mapping Systems. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the World: A Comprehensive Guide to GPS Mapping Systems

The ability to pinpoint one’s location and navigate unfamiliar terrain has been a driving force behind human exploration for centuries. From rudimentary maps etched on stone to the intricate globes of the Renaissance, the desire to understand and control our spatial environment has remained constant. Today, this pursuit finds its zenith in the realm of Global Positioning Systems (GPS), a technology that has revolutionized our understanding of space and transformed the way we interact with the world around us.
This guide delves into the intricate workings of GPS mapping systems, exploring their fundamental principles, diverse applications, and the transformative impact they have had on various aspects of modern life. We will examine the core components that enable GPS to function, understand the different types of GPS maps available, and delve into the myriad ways these systems enhance our daily lives.
Understanding the Fundamentals of GPS
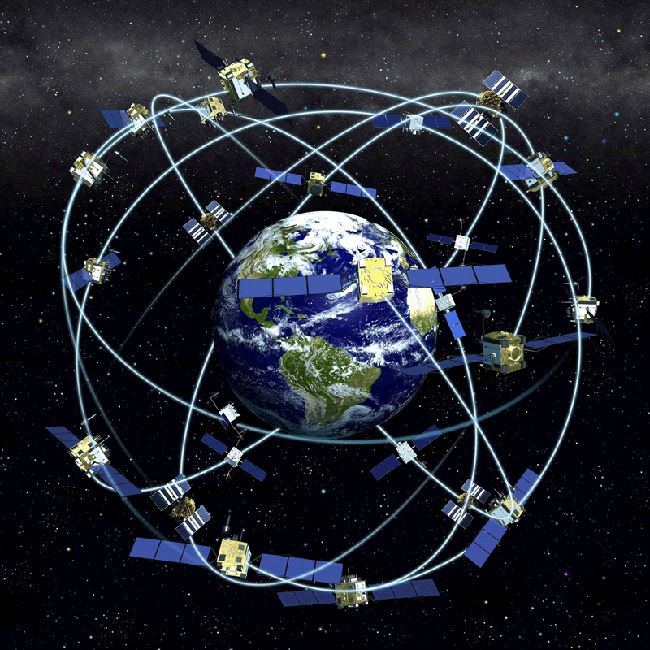
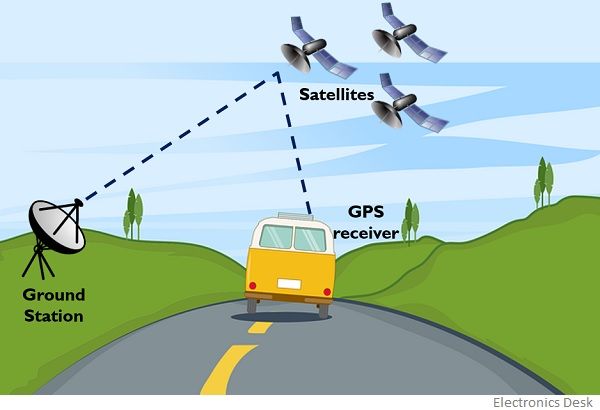
GPS, or Global Positioning System, is a satellite-based navigation system that provides precise location and time information anywhere on Earth. It relies on a network of 31 satellites orbiting the planet, continuously transmitting radio signals. These signals are received by GPS receivers, typically found in smartphones, cars, and dedicated navigation devices.
Here’s how GPS works:
-
Satellite Network: The constellation of GPS satellites orbits the Earth at an altitude of approximately 12,550 miles, completing two orbits every day. Each satellite transmits a unique signal containing information about its position and the current time.
-
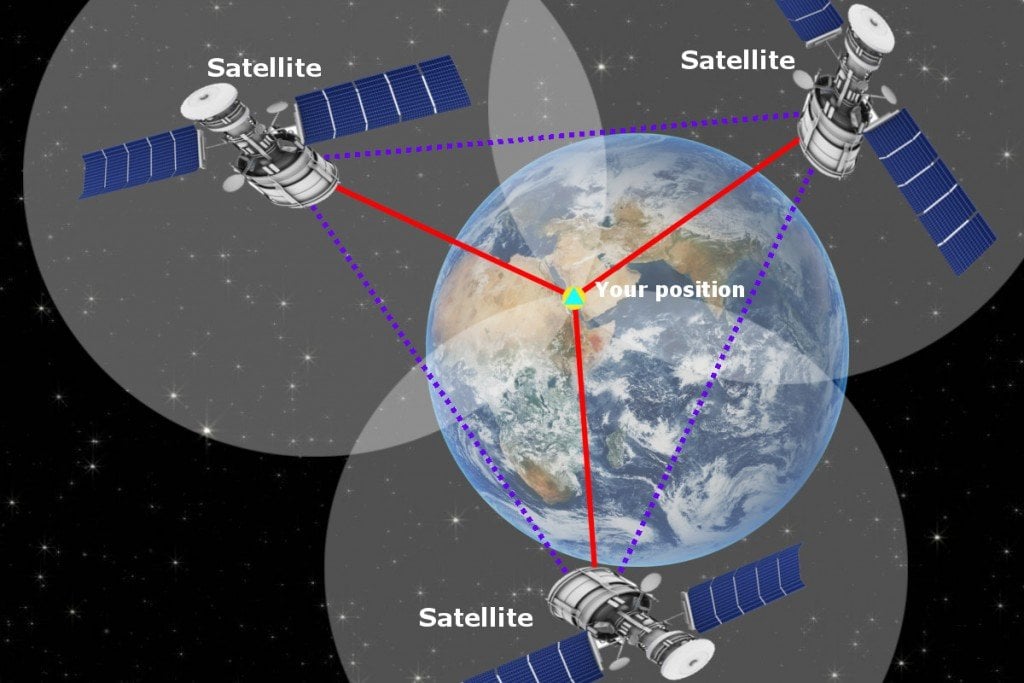
Signal Reception: A GPS receiver, such as a smartphone or a navigation device, picks up these signals from multiple satellites. The receiver then calculates the distance to each satellite by measuring the time it takes for the signal to travel from the satellite to the receiver.
-
Triangulation: Using the distances to at least four satellites, the receiver can triangulate its precise location on Earth. This is achieved by determining the intersection point of multiple spheres centered on the satellites, with radii corresponding to the calculated distances.
-
Time Synchronization: To ensure accuracy, GPS relies on highly precise atomic clocks onboard the satellites and in the receiver. These clocks synchronize the timing of the signals, enabling accurate distance measurements and location determination.
Types of GPS Maps:
The world of GPS maps is diverse, encompassing a wide array of specialized applications tailored to specific needs. These maps can be broadly categorized into:
1. Road Maps:
- Standard Road Maps: These are the most common type of GPS map, offering detailed information about roads, highways, and major landmarks. They often include points of interest (POIs) such as restaurants, gas stations, and hotels.
- Traffic Maps: These maps incorporate real-time traffic data, displaying traffic congestion and suggesting alternative routes to avoid delays.
- Navigation Maps: These maps are designed for turn-by-turn navigation, providing voice guidance and visual cues to guide users through unfamiliar routes.
2. Topographic Maps:
- Outdoor Maps: These maps focus on terrain features, including elevation, contours, trails, and natural landmarks. They are indispensable for hiking, camping, and other outdoor activities.
- Marine Maps: These maps provide detailed information about waterways, including depths, hazards, and navigational aids. They are essential for marine navigation and safety.
- Aviation Maps: These maps are specifically designed for pilots, featuring airspace restrictions, airfields, and other aviation-related information.
3. Specialized Maps:
- City Maps: These maps offer detailed information about urban areas, including street networks, public transportation routes, and points of interest.
- Historical Maps: These maps showcase the evolution of geographic features over time, providing insights into historical events and land use patterns.
- Satellite Imagery Maps: These maps use high-resolution satellite imagery to provide a realistic view of the Earth’s surface, revealing features like buildings, forests, and water bodies.
Applications of GPS Mapping Systems:
The transformative power of GPS extends far beyond navigation, influencing numerous industries and aspects of modern life:
1. Transportation:
- Vehicle Navigation: GPS is ubiquitous in modern vehicles, providing drivers with turn-by-turn directions, traffic updates, and point-of-interest information.
- Fleet Management: Businesses use GPS to track their vehicles, optimize routes, and improve efficiency.
- Public Transportation: GPS enables real-time tracking of buses, trains, and other public transportation vehicles, providing passengers with accurate arrival times and route information.
2. Emergency Services:
- Emergency Response: GPS is crucial for emergency services, allowing first responders to quickly locate incidents and optimize their response times.
- Search and Rescue: GPS assists in locating missing persons, providing coordinates and facilitating search efforts.
3. Surveying and Mapping:
- Land Surveying: GPS technology enables precise land surveying, facilitating accurate property measurements and boundary determination.
- Geographic Information Systems (GIS): GPS data feeds into GIS systems, creating detailed maps and spatial analyses used for planning, resource management, and environmental monitoring.
4. Agriculture and Forestry:
- Precision Agriculture: GPS enables farmers to optimize fertilizer application, irrigation, and other agricultural practices, maximizing yields and minimizing waste.
- Forest Management: GPS helps in mapping forest resources, tracking logging operations, and monitoring forest health.
5. Personal Safety and Security:
- Personal Tracking: GPS devices can be used to track individuals, providing peace of mind for parents, caregivers, and individuals with medical conditions.
- Asset Tracking: GPS enables tracking of valuable assets, such as laptops, phones, and vehicles, deterring theft and facilitating recovery.
6. Tourism and Recreation:
- Travel Planning: GPS maps help travelers plan their trips, discover points of interest, and navigate unfamiliar destinations.
- Outdoor Activities: GPS devices are essential for hikers, campers, and other outdoor enthusiasts, providing navigation, location tracking, and emergency communication.
FAQs about GPS Mapping Systems:
1. What are the different types of GPS receivers?
GPS receivers come in various forms, including:
- Standalone GPS Receivers: These are dedicated devices designed specifically for navigation.
- Smartphone GPS Receivers: Most modern smartphones are equipped with built-in GPS receivers.
- Automotive GPS Receivers: These receivers are integrated into car navigation systems.
- Portable GPS Receivers: These compact devices are ideal for outdoor activities and travel.
2. What are the benefits of using GPS maps?
GPS maps offer numerous benefits, including:
- Improved Navigation: GPS maps provide accurate directions and help users navigate unfamiliar areas.
- Enhanced Safety: GPS can help drivers avoid traffic congestion and find safer routes.
- Increased Efficiency: GPS optimizes routes and reduces travel time.
- Real-Time Information: GPS maps provide real-time traffic updates, weather information, and other valuable data.
- Personal Safety: GPS tracking devices can help locate individuals and enhance personal safety.
3. What are the limitations of GPS mapping systems?
Despite their numerous advantages, GPS systems have limitations:
- Signal Blockage: GPS signals can be blocked by tall buildings, dense foliage, and other obstacles.
- Accuracy Issues: GPS accuracy can be affected by atmospheric conditions, satellite availability, and receiver quality.
- Privacy Concerns: GPS tracking raises privacy concerns, as it can be used to monitor individuals’ movements without their consent.
- Dependence on Technology: GPS systems require a working receiver and satellite connection, making them vulnerable to technological failures.
4. How can I improve GPS accuracy?
To enhance GPS accuracy, consider these tips:
- Use a High-Quality Receiver: Invest in a GPS receiver with a good antenna and signal processing capabilities.
- Ensure Clear Line of Sight: Position your receiver in an open area with a clear view of the sky.
- Calibrate Your Receiver: Regularly calibrate your GPS receiver to ensure accurate positioning.
- Avoid Interference: Keep your receiver away from sources of electromagnetic interference, such as power lines and radio transmitters.
5. What are the future trends in GPS mapping systems?
GPS technology continues to evolve, with several emerging trends:
- Augmented Reality (AR) Integration: GPS maps are being integrated with AR technology, overlaying digital information onto the real world.
- Improved Accuracy: GPS systems are becoming more accurate, with the development of new technologies like Precise Point Positioning (PPP).
- Increased Connectivity: GPS is being integrated with other technologies, such as the Internet of Things (IoT), enabling smarter and more connected navigation experiences.
Conclusion:
GPS mapping systems have fundamentally transformed our understanding of space and revolutionized the way we navigate the world. From providing turn-by-turn directions to enhancing emergency response and revolutionizing agriculture, GPS has become an indispensable tool in various aspects of modern life.
As GPS technology continues to evolve, we can expect even more innovative applications and transformative impacts in the future. By understanding the principles behind GPS and its diverse applications, we can harness its power to navigate the world more efficiently, safely, and intelligently.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the World: A Comprehensive Guide to GPS Mapping Systems. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!