The Political Landscape of Iraq: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: The Political Landscape of Iraq: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to The Political Landscape of Iraq: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Political Landscape of Iraq: A Comprehensive Guide
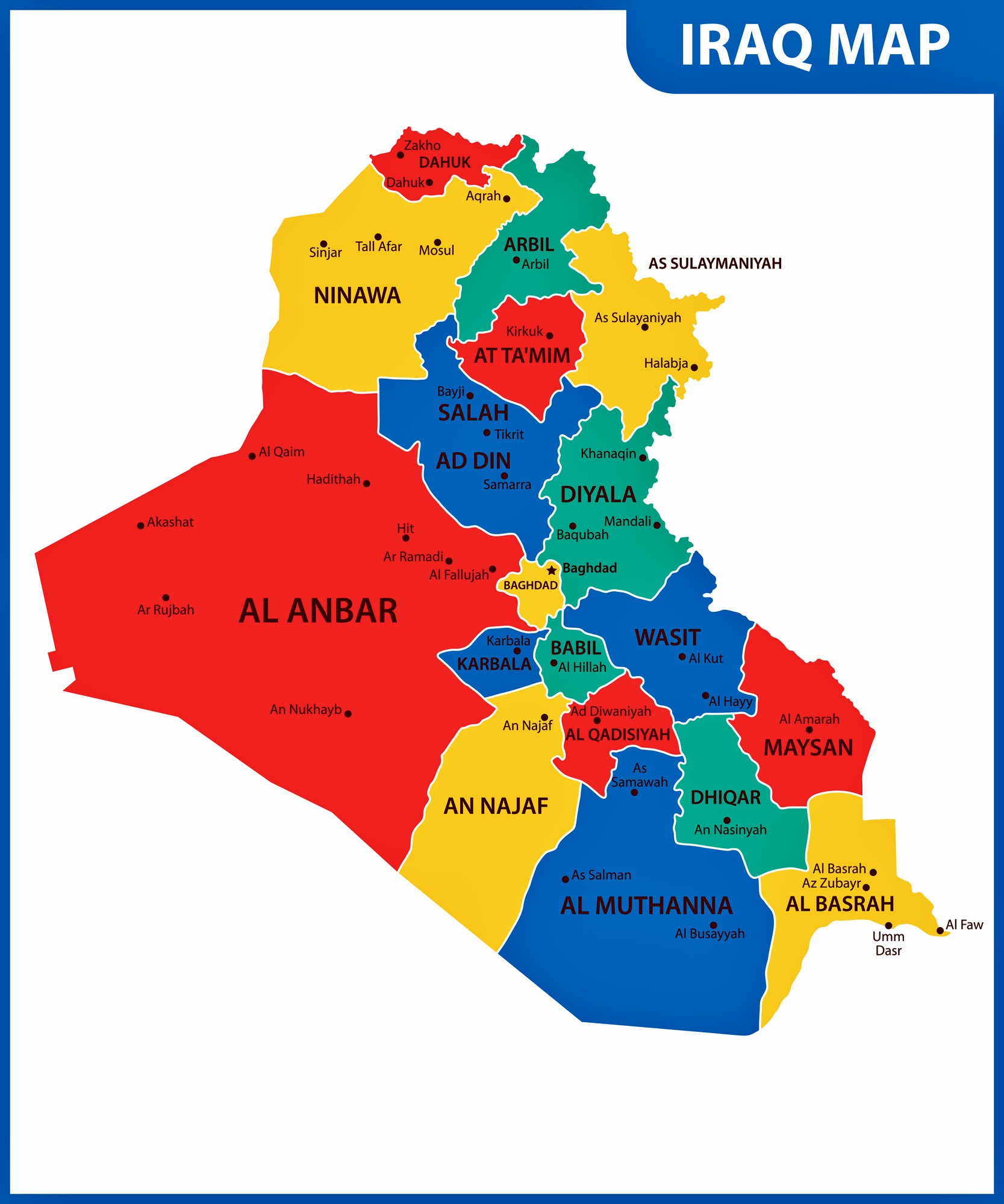
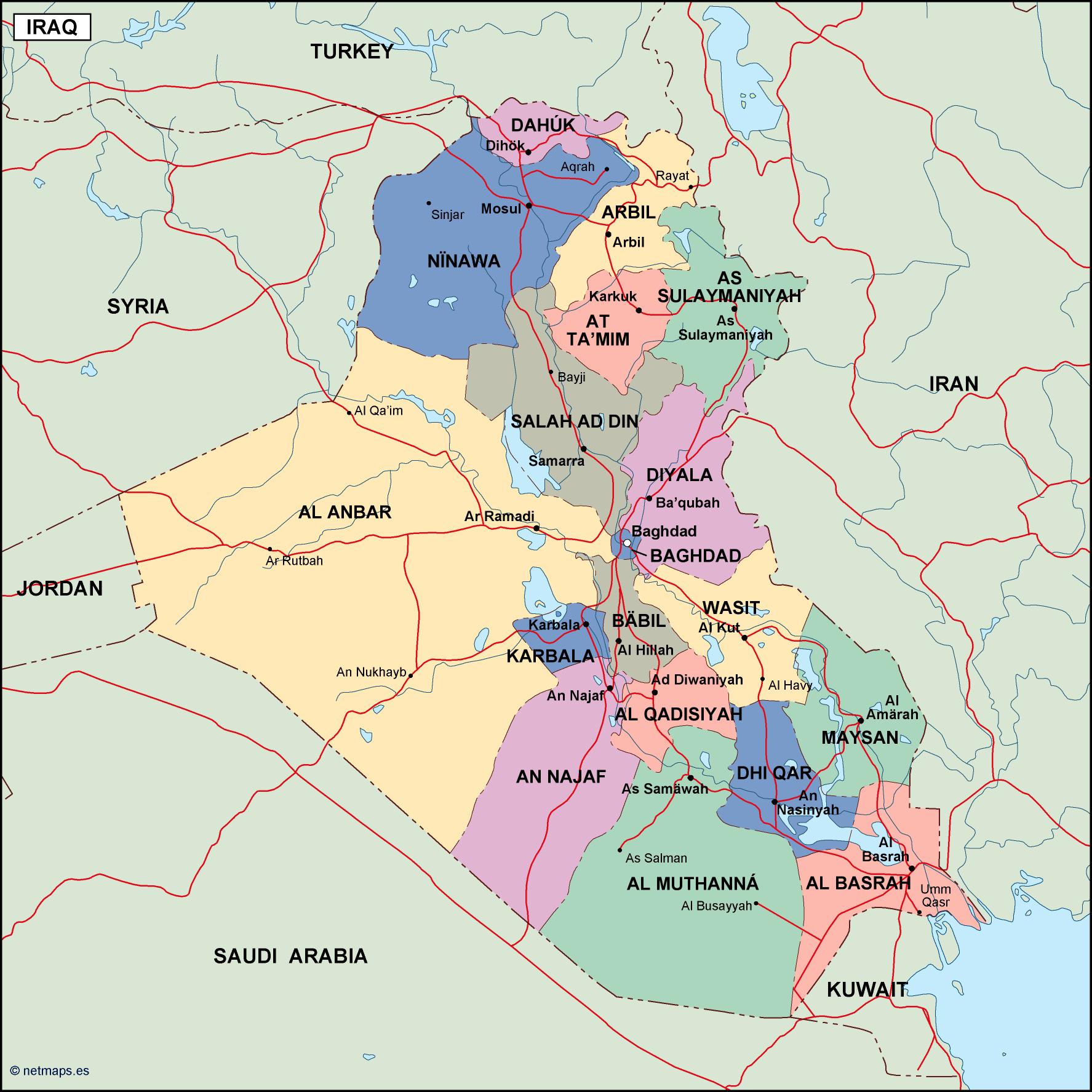
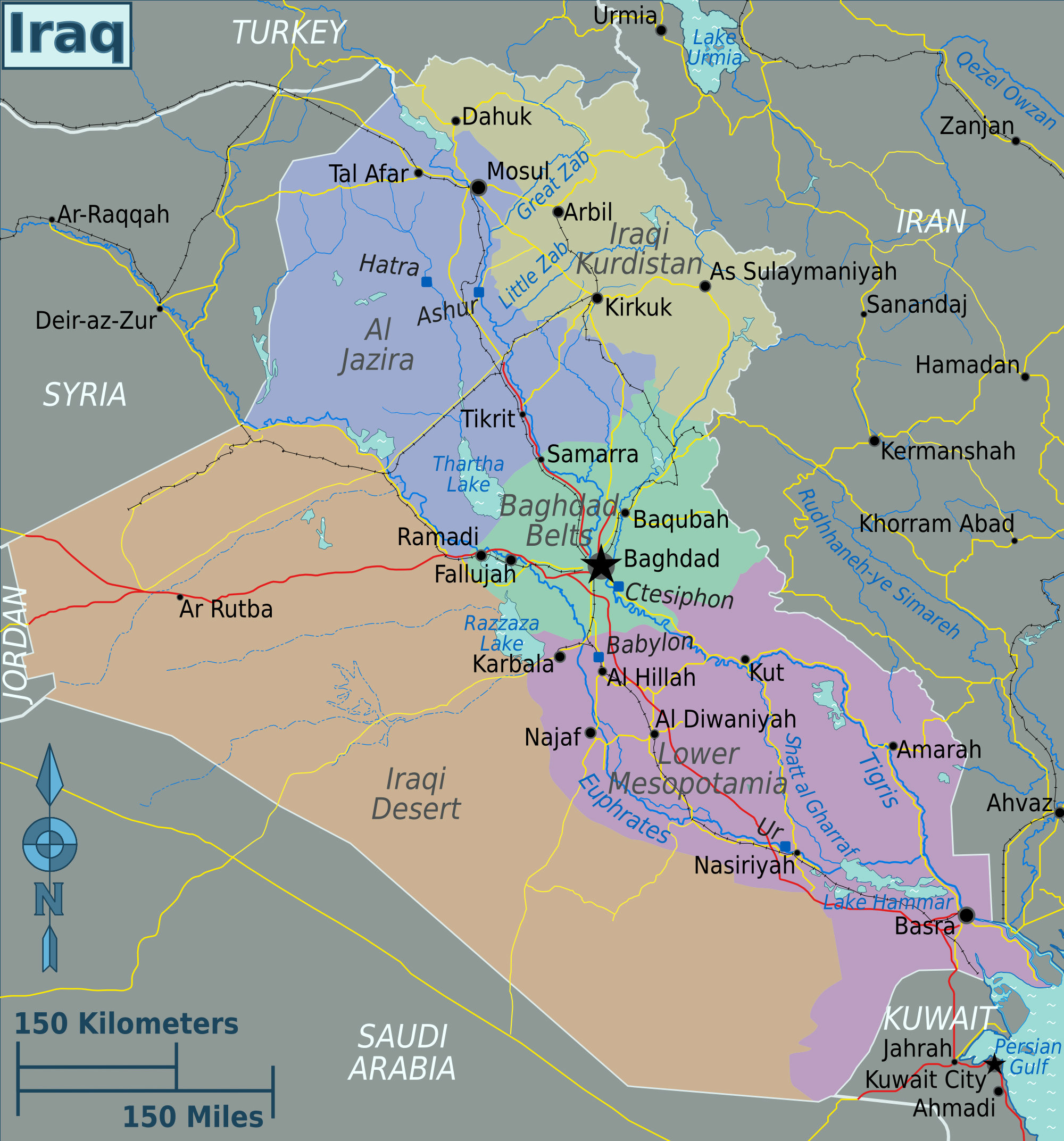
The political map of Iraq, a nation in the Middle East, is a complex tapestry woven from historical, cultural, and geopolitical threads. Understanding its intricate design is crucial for comprehending the region’s current dynamics and navigating the challenges it faces. This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of Iraq’s political map, examining its historical evolution, key players, and contemporary issues.
Historical Context: A Legacy of Division and Conflict
Iraq’s political landscape is deeply rooted in its history. The country’s borders, drawn by colonial powers in the early 20th century, failed to account for the diverse ethnic and religious groups inhabiting the region. This artificial division laid the groundwork for future conflicts and political instability.
-
The Ottoman Empire: Before the rise of modern Iraq, the region was part of the vast Ottoman Empire. While the Ottomans implemented a centralized administration, their rule was marked by a degree of local autonomy, allowing various ethnic and religious groups to maintain their identities.
-
The British Mandate: Following World War I, the Ottoman Empire collapsed, and Iraq fell under British control. The British sought to create a unified state, but their efforts were hampered by the existing ethnic and sectarian divisions.
-
The Birth of Modern Iraq: In 1932, Iraq gained independence from British rule, becoming a constitutional monarchy. However, the new state remained fragile, with tensions between different groups escalating into regular conflicts.
The Rise and Fall of Ba’athist Rule:
The 1968 coup led by the Ba’ath Party, a secular Arab nationalist movement, ushered in a period of centralized control and political repression. The Ba’ath regime, under Saddam Hussein, sought to create a unified Iraqi identity, suppressing Kurdish and Shi’a aspirations for autonomy.
-
The Iran-Iraq War: The 1980-1988 war with Iran further solidified the Ba’ath regime’s power and fueled a nationalist sentiment. However, the war also left Iraq economically devastated and burdened by a massive debt.
-
The Gulf War: The 1991 Gulf War, which followed Iraq’s invasion of Kuwait, marked a turning point in Iraq’s political landscape. The war weakened the Ba’ath regime, leading to the imposition of international sanctions and the rise of Kurdish and Shi’a opposition groups.
The US-led Invasion and its Aftermath:
The 2003 US-led invasion of Iraq toppled Saddam Hussein’s regime, ushering in a new era of instability and political fragmentation. The subsequent occupation and the emergence of sectarian violence further complicated the political landscape.
-
The Rise of Sectarianism: The post-invasion period witnessed a surge in sectarian violence, primarily between Shi’a and Sunni Muslims. This conflict was fueled by the disbanding of the Iraqi military and the emergence of extremist groups like al-Qaeda in Iraq.
-
The Formation of a New Political System: Following the US withdrawal in 2011, Iraq adopted a parliamentary democracy based on a power-sharing agreement among its diverse ethnic and religious groups. However, this system has been plagued by political deadlock and instability, leading to frequent government changes and a lack of effective governance.
The Current Political Landscape: A Complex and Fragile System
Iraq’s current political map is characterized by a complex web of alliances and rivalries among various political factions. The country’s political system is based on a power-sharing arrangement between the three main ethnic groups:
-
Kurds: The Kurds are the largest ethnic group in Iraq, primarily residing in the northern region. They have long sought autonomy and have their own regional government.
-
Sunni Arabs: The Sunni Arabs are concentrated in the central and western regions of Iraq. They were historically dominant under the Ba’ath regime, but their influence has waned since the US invasion.
-
Shi’a Arabs: The Shi’a Arabs constitute the majority of the Iraqi population and are concentrated in the south and southeast. They have gained significant political power since the fall of Saddam Hussein.
Key Players and Political Factions:
-
The Kurdistan Regional Government (KRG): The KRG is the semi-autonomous government of the Kurdistan Region in northern Iraq. It has its own parliament, president, and prime minister.
-
The Iraqi National Alliance (INA): The INA is a coalition of Shi’a political parties, led by the Supreme Islamic Iraqi Council (SIIC). It is the largest bloc in the Iraqi parliament.
-
The State of Law Coalition: This coalition is led by former Prime Minister Nouri al-Maliki and represents a significant faction within the Shi’a community.
-
The Sunni Political Bloc: This bloc comprises various Sunni political parties, including the Iraqi Islamic Party and the Iraqi Accord Front.
Challenges and Prospects:
Iraq faces numerous challenges that threaten its political stability and future prospects. These include:
-
Sectarian Violence: Despite a decline in recent years, sectarian violence remains a significant threat to national unity and stability.
-
Political Deadlock: The power-sharing system has often resulted in political deadlock, hampering the government’s ability to address critical issues.
-
Corruption: Corruption is widespread in Iraq, undermining trust in the government and hindering economic development.
-
Economic Challenges: Iraq’s economy is heavily reliant on oil exports, making it vulnerable to global market fluctuations.
FAQs
1. What are the major ethnic and religious groups in Iraq?
The main ethnic groups in Iraq are Kurds, Sunni Arabs, and Shi’a Arabs. The country is also home to various religious communities, including Muslims (both Sunni and Shi’a), Christians, Yazidis, and others.
2. What is the current political system in Iraq?
Iraq has a parliamentary democracy based on a power-sharing agreement among its diverse ethnic and religious groups. The country has a president, a prime minister, and a parliament.
3. What are the main political parties in Iraq?
Some of the main political parties in Iraq include the Kurdistan Democratic Party (KDP), the Patriotic Union of Kurdistan (PUK), the Supreme Islamic Iraqi Council (SIIC), the State of Law Coalition, and the Iraqi Islamic Party.
4. What are the major challenges facing Iraq today?
Iraq faces numerous challenges, including sectarian violence, political deadlock, corruption, economic instability, and the threat of terrorism.
5. What is the future of Iraq?
The future of Iraq remains uncertain. The country faces significant challenges, but it also has the potential to overcome them. The success of Iraq’s political transition will depend on the ability of its leaders to build a stable and inclusive government that can address the needs of all its citizens.
Tips
- Stay informed about current events in Iraq through reputable news sources.
- Engage in constructive dialogue about the challenges and opportunities facing Iraq.
- Support organizations working to promote peace and stability in Iraq.
- Advocate for policies that promote democracy, human rights, and economic development in Iraq.
Conclusion
The political map of Iraq is a complex and dynamic landscape shaped by historical forces, ethnic and religious identities, and geopolitical interests. The country’s political system is fragile and faces numerous challenges. However, Iraq also possesses a rich cultural heritage and a resilient people who are determined to build a better future. Understanding the complexities of Iraq’s political map is crucial for navigating the region’s challenges and promoting peace, stability, and prosperity in the years to come.
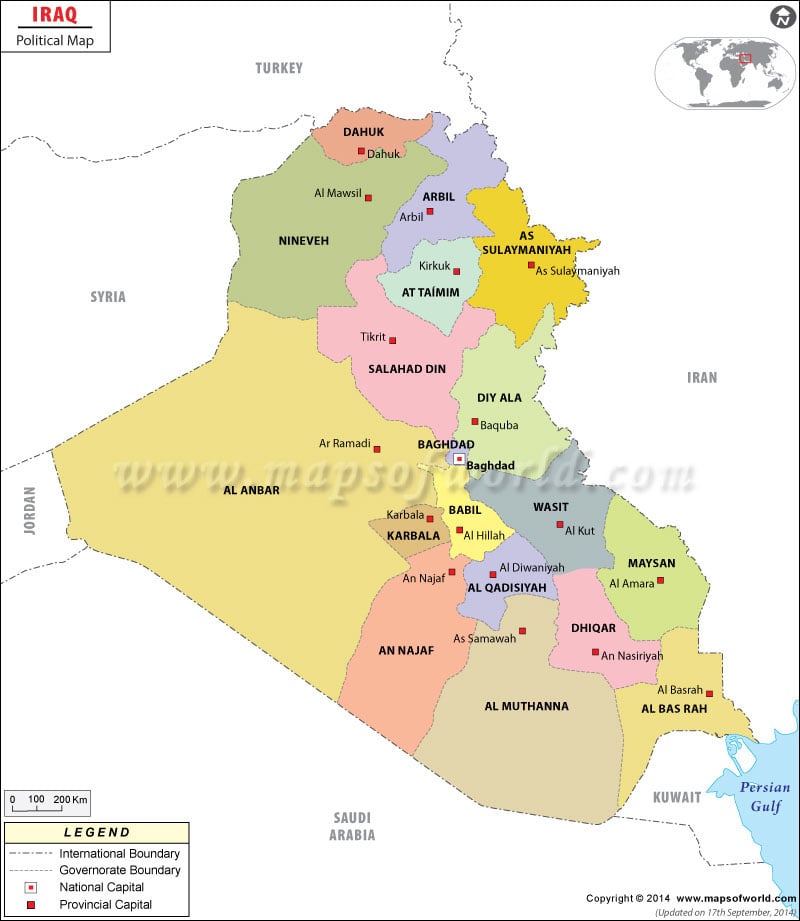
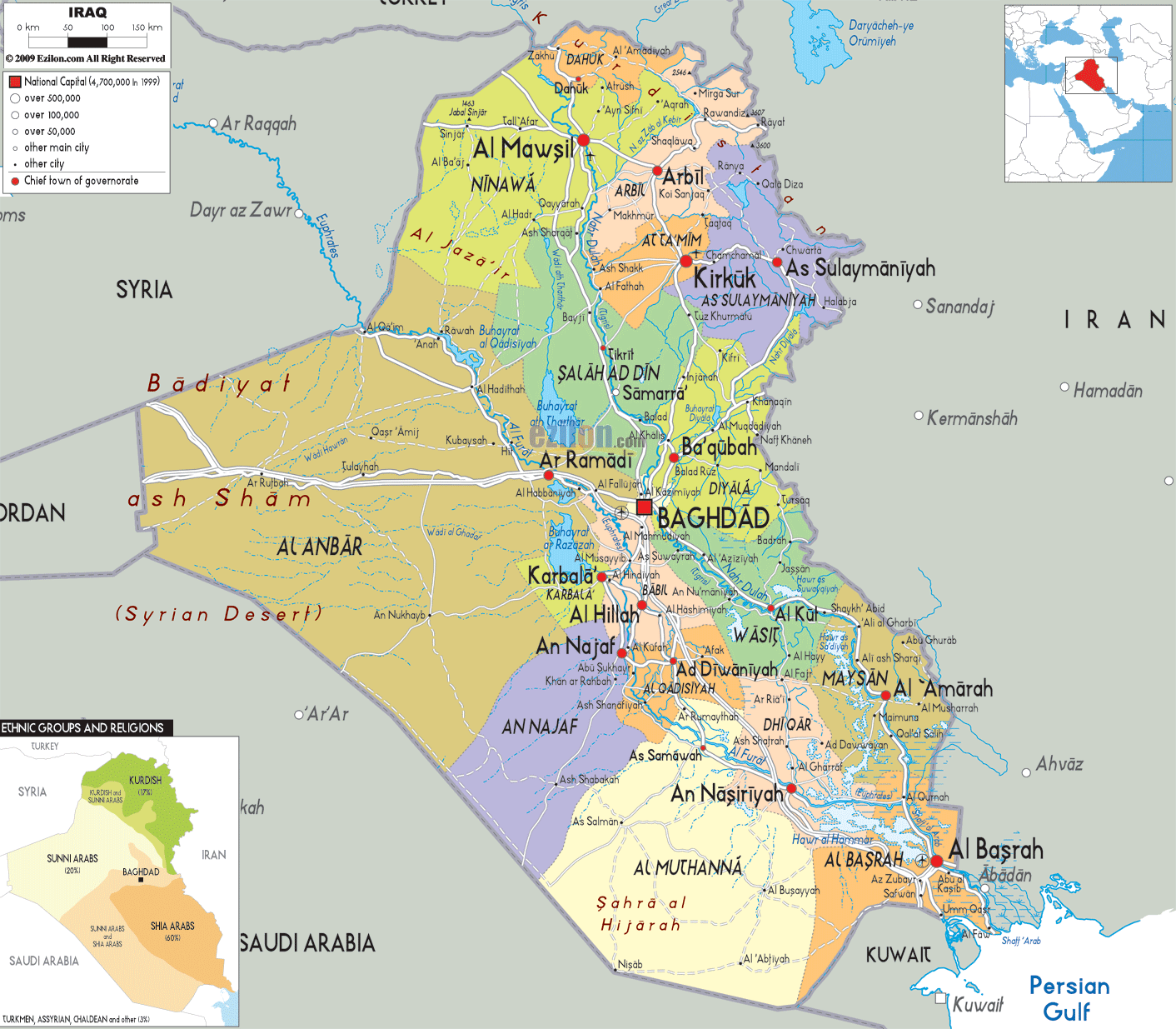
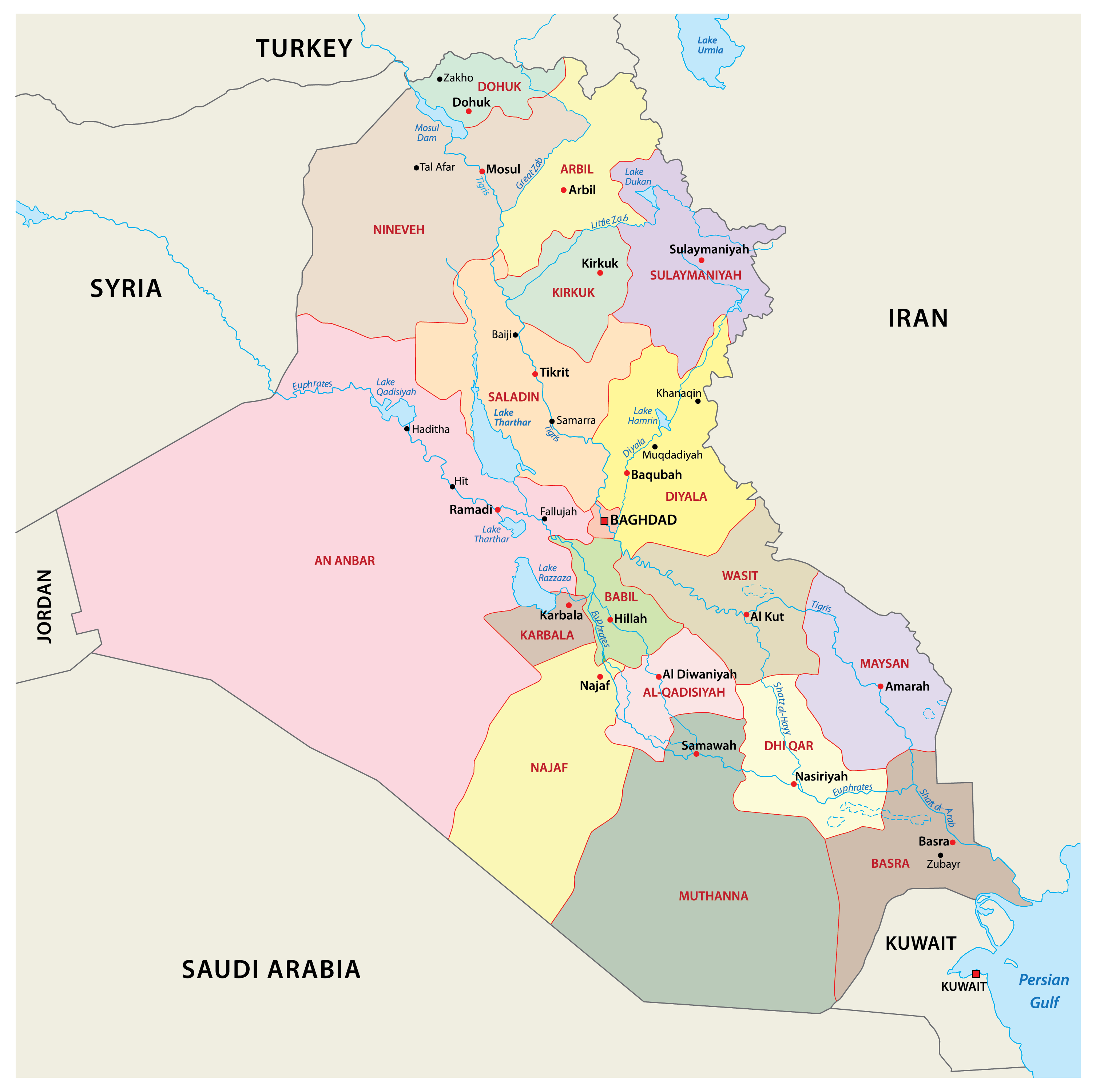



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Political Landscape of Iraq: A Comprehensive Guide. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!