The Political Landscape of Syria: A Complex and Shifting Geography
Related Articles: The Political Landscape of Syria: A Complex and Shifting Geography
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Political Landscape of Syria: A Complex and Shifting Geography. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: The Political Landscape of Syria: A Complex and Shifting Geography
- 2 Introduction
- 3 The Political Landscape of Syria: A Complex and Shifting Geography
- 3.1 A Brief Historical Overview
- 3.2 The Syrian Civil War and its Impact on the Political Map
- 3.3 Key Political Divisions and Territories
- 3.4 The Future of Syria’s Political Map
- 3.5 FAQs about the Political Map of Syria
- 3.6 Tips for Understanding the Political Map of Syria
- 3.7 Conclusion
- 4 Closure
The Political Landscape of Syria: A Complex and Shifting Geography
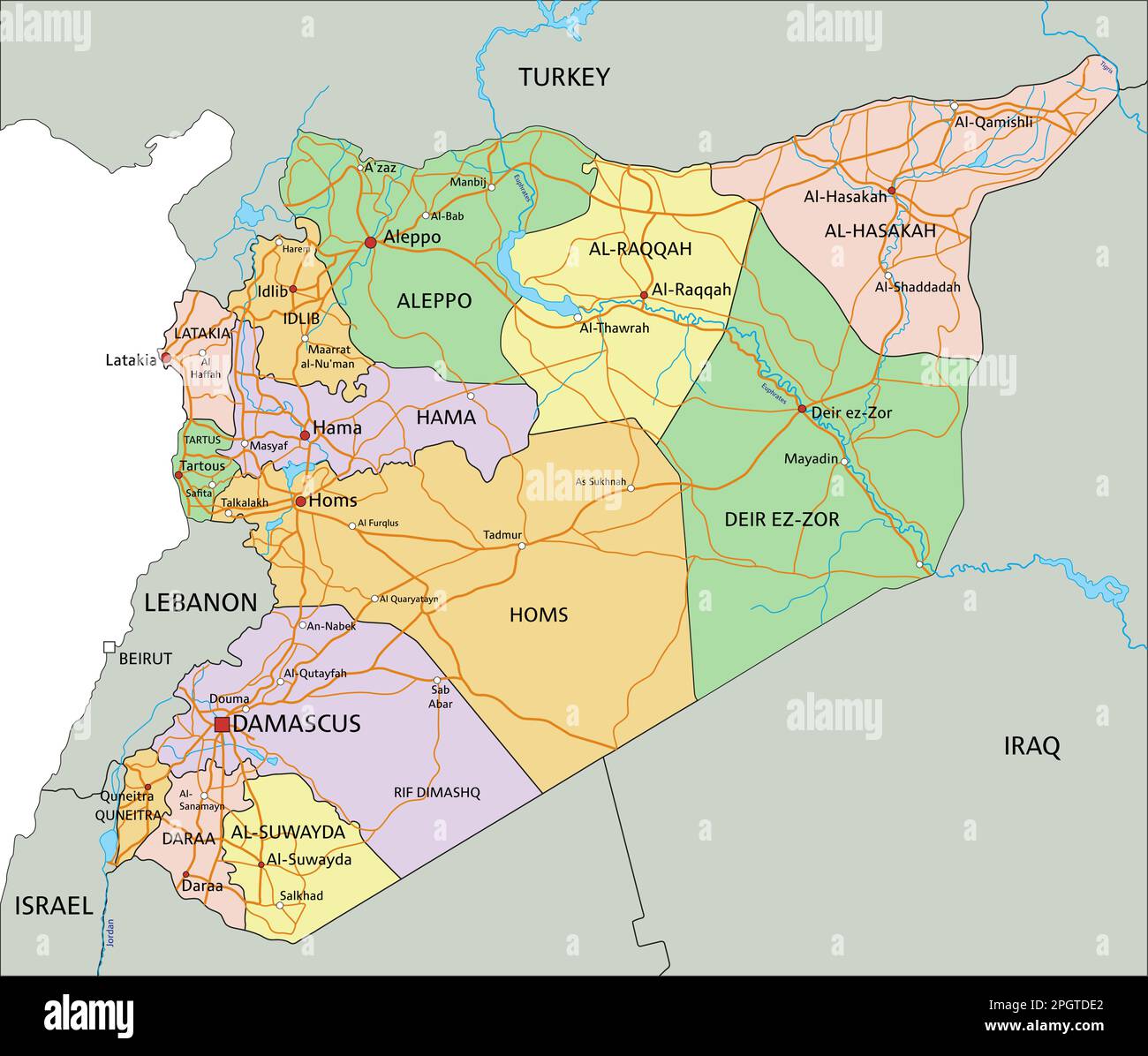
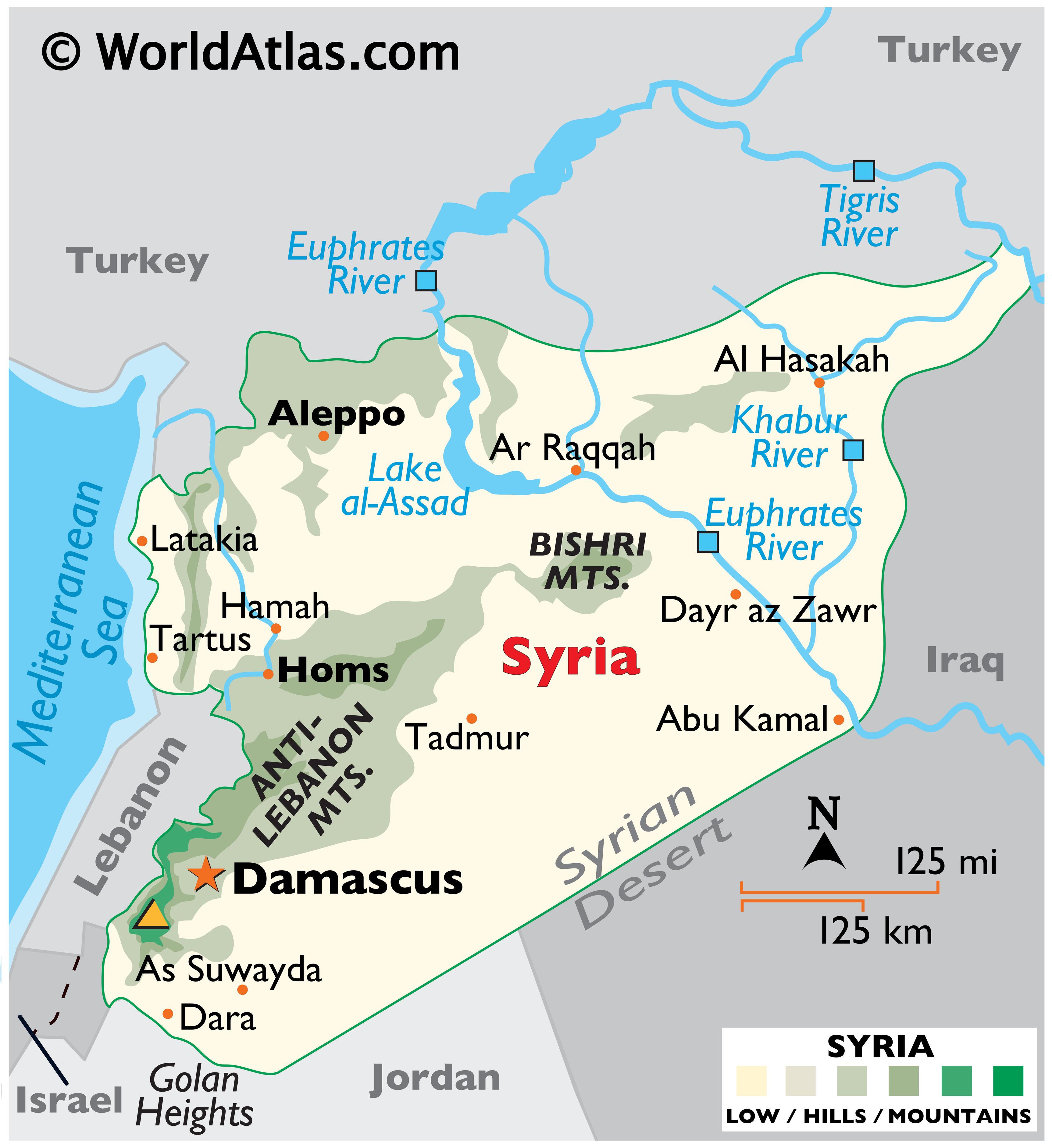
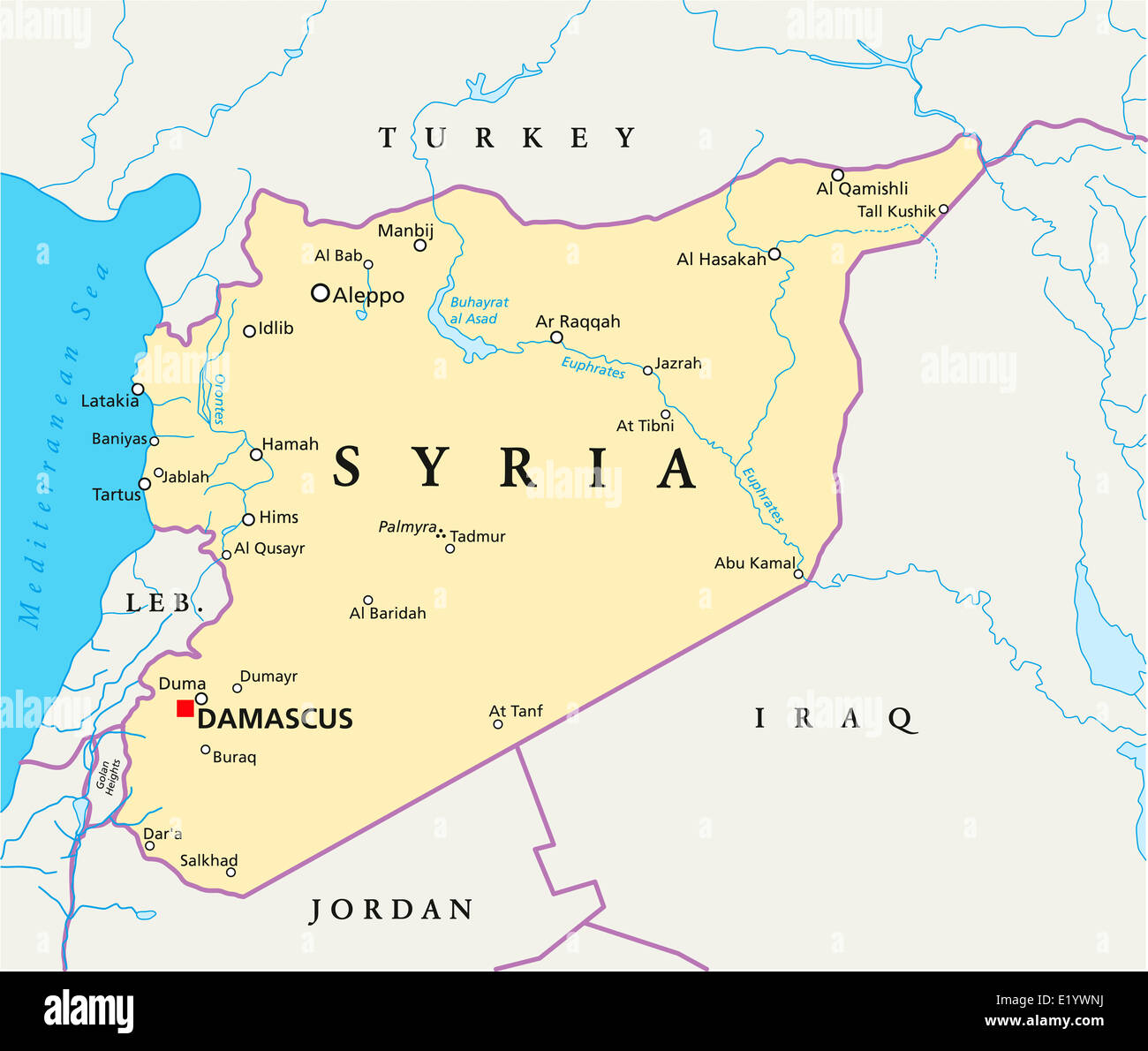
The political map of Syria is a testament to the country’s tumultuous history and ongoing conflict. Understanding its intricate divisions and evolving boundaries is crucial for comprehending the current political landscape and the challenges that lie ahead.
A Brief Historical Overview
Syria’s modern political map emerged from the collapse of the Ottoman Empire in the aftermath of World War I. The French Mandate for Syria and Lebanon, established in 1920, carved out a new political entity, encompassing present-day Syria, Lebanon, and parts of Turkey. The mandate period was characterized by internal conflict and political instability, culminating in Syria’s independence in 1946.
The newly independent Syria witnessed a series of coups and political upheavals, with the Ba’ath Party, a socialist Arab nationalist party, gaining power in 1963. Under the leadership of Hafez al-Assad, the Ba’ath Party consolidated its control, establishing a one-party state and implementing a centralized political system.
The Syrian Civil War and its Impact on the Political Map
The Syrian Civil War, which began in 2011, fundamentally altered the political map of the country. The uprising, initially fueled by demands for democratic reforms, quickly devolved into a complex and multifaceted conflict, with various factions vying for power.
The conflict has witnessed the emergence of several key players, including:
- The Syrian Government: The Syrian government, led by President Bashar al-Assad, has been supported by Russia, Iran, and Hezbollah. It has retained control of major cities, including Damascus, Aleppo, and Homs, but its authority remains contested.
- The Syrian Opposition: The Syrian opposition is a diverse group comprising various political and military factions, ranging from moderate groups seeking democratic reforms to Islamist and jihadist organizations.
- Kurdish Groups: The Syrian Kurds, represented by the Democratic Union Party (PYD), have established autonomous regions in northern Syria. The PYD’s control over these areas has been challenged by both the Syrian government and Turkish forces.
- Islamic State of Iraq and Syria (ISIS): At its peak, ISIS controlled vast swathes of territory in both Syria and Iraq. While it has been significantly weakened, its remnants continue to pose a security threat.
The Syrian Civil War has led to the creation of de facto autonomous regions, fragmented control over territory, and the emergence of new political entities. This complex political landscape has made it difficult to achieve a lasting peace and has created a humanitarian crisis of unprecedented proportions.
Key Political Divisions and Territories
- Government-Controlled Areas: The Syrian government maintains control over major cities and key infrastructure, but its authority is limited in some areas.
- Opposition-Controlled Areas: The Syrian opposition controls territory in the north and south of the country, but its control is fragmented and its influence varies across different regions.
- Kurdish-Controlled Areas: The Syrian Kurds have established autonomous regions in northern Syria, including the Afrin region, which was captured by Turkish forces in 2018.
- ISIS-Controlled Areas: While ISIS has been significantly weakened, it still retains pockets of influence in the Syrian desert.
- UN-Buffer Zones: The United Nations has established buffer zones in southern Syria, with the aim of protecting civilians and promoting peace.
The Future of Syria’s Political Map
The future of Syria’s political map remains uncertain. The conflict has deeply divided the country, and there is no clear path towards a lasting peace. The international community has struggled to find a solution, and the humanitarian crisis continues to worsen.
Several factors will influence the future of Syria’s political map, including:
- The outcome of the conflict: The outcome of the Syrian Civil War will determine the future of the country’s political landscape.
- The role of external actors: The involvement of foreign powers, such as Russia, Iran, and Turkey, will continue to shape the political landscape.
- The aspirations of the Syrian people: The Syrian people’s desire for peace, stability, and a democratic future will play a crucial role in shaping the country’s political trajectory.
FAQs about the Political Map of Syria
Q: What is the current status of the Syrian government?
A: The Syrian government, led by President Bashar al-Assad, retains control over major cities and key infrastructure, but its authority is limited in some areas. The government has been supported by Russia, Iran, and Hezbollah, but its legitimacy remains contested.
Q: What are the main factions within the Syrian opposition?
A: The Syrian opposition is a diverse group comprising various political and military factions. Some factions are moderate and seek democratic reforms, while others are more radical and have links to Islamist or jihadist groups.
Q: What is the status of the Kurdish-controlled areas in Syria?
A: The Syrian Kurds have established autonomous regions in northern Syria, but their control over these areas has been challenged by both the Syrian government and Turkish forces. The PYD, the main Kurdish political party, has sought to establish a federal system within Syria.
Q: What is the current threat posed by ISIS?
A: While ISIS has been significantly weakened, it still retains pockets of influence in the Syrian desert and continues to pose a security threat. The group has been responsible for terrorist attacks in both Syria and Iraq.
Q: What is the role of the United Nations in Syria?
A: The United Nations has been actively involved in efforts to resolve the Syrian conflict, including providing humanitarian aid and facilitating peace talks. The UN has also established buffer zones in southern Syria, with the aim of protecting civilians and promoting peace.
Tips for Understanding the Political Map of Syria
- Focus on the key players: Identify the main factions involved in the conflict, including the Syrian government, the Syrian opposition, Kurdish groups, and ISIS.
- Understand the motivations and objectives of each faction: Analyze the goals and interests of each group to better understand their actions and strategies.
- Pay attention to the dynamics of external actors: Consider the role of foreign powers, such as Russia, Iran, and Turkey, in shaping the conflict and influencing the political landscape.
- Recognize the complexities of the situation: Acknowledge the multifaceted nature of the conflict and the diverse range of actors involved.
- Stay informed about current events: Keep up with news reports and analysis to stay abreast of the evolving political situation in Syria.
Conclusion
The political map of Syria is a dynamic and complex landscape, shaped by a tumultuous history and an ongoing conflict. Understanding the intricate divisions and evolving boundaries is essential for comprehending the current situation and the challenges that lie ahead. The future of Syria’s political map remains uncertain, but the aspirations of the Syrian people for peace, stability, and a democratic future offer a glimmer of hope for a brighter future.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Political Landscape of Syria: A Complex and Shifting Geography. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!