Tracing the Roots of Faith: A Journey Through the Early Christian Map
Related Articles: Tracing the Roots of Faith: A Journey Through the Early Christian Map
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Tracing the Roots of Faith: A Journey Through the Early Christian Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Tracing the Roots of Faith: A Journey Through the Early Christian Map
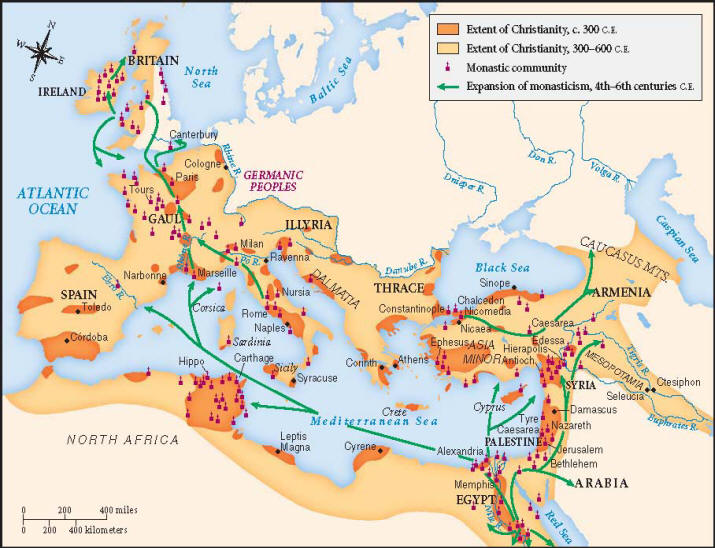
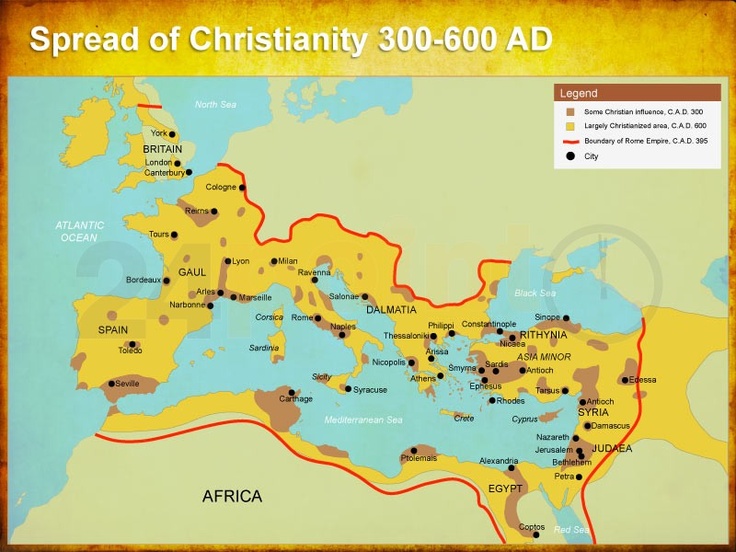
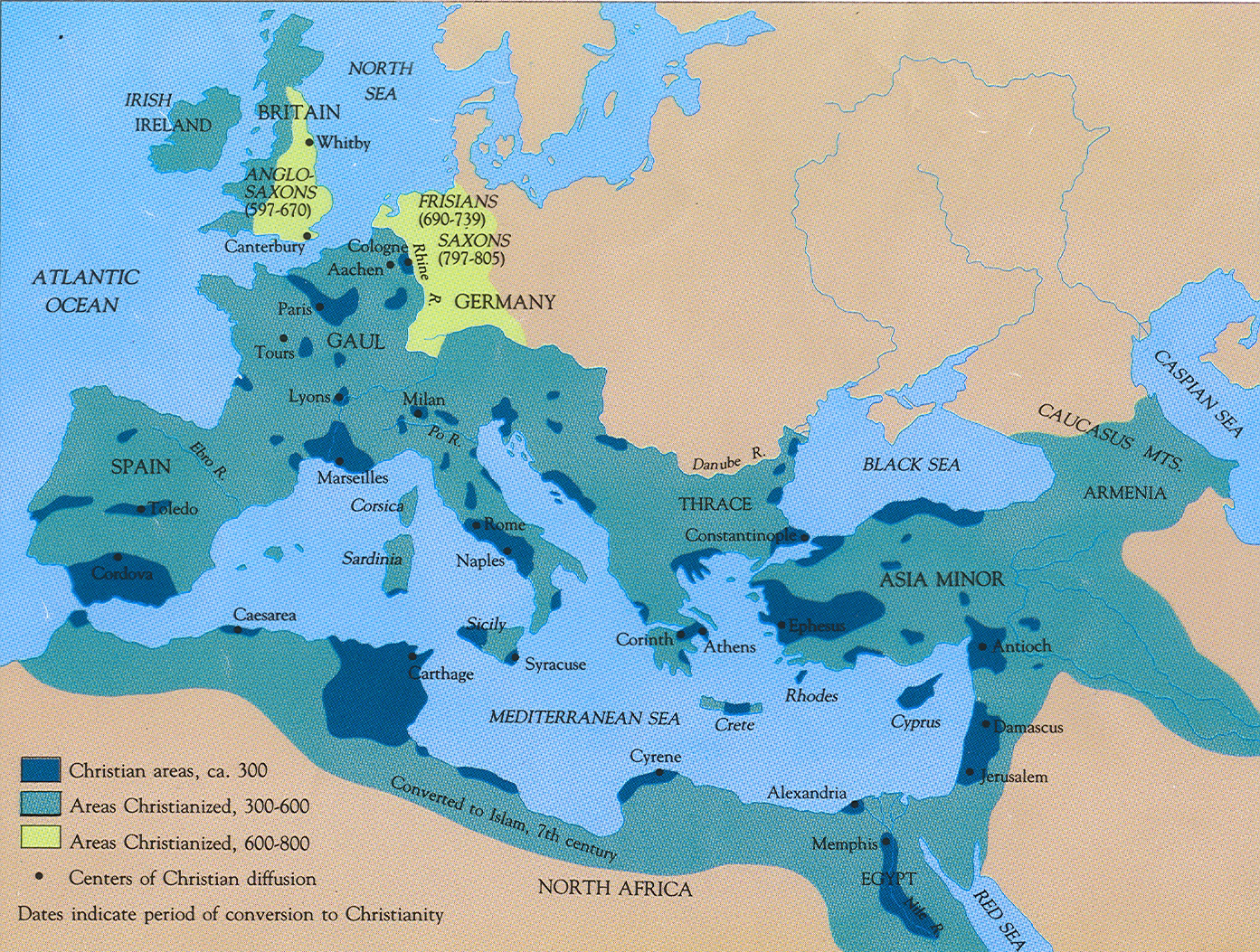
The early Christian map is not merely a collection of dots on a parchment, but a vibrant tapestry woven with the threads of faith, persecution, and cultural exchange. It charts the spread of Christianity from its humble origins in Judea to its eventual establishment as a dominant force in the Roman Empire. Understanding this map is essential for appreciating the evolution of Christian thought, practice, and influence on Western civilization.
The Cradle of Christianity: Judea and the Levant
The birthplace of Christianity is firmly rooted in the Levant, specifically Judea, a region encompassing modern-day Israel, Palestine, Lebanon, and Syria. It was here, in the bustling city of Jerusalem, that Jesus of Nazareth preached his message of love, forgiveness, and the coming Kingdom of God. His teachings resonated with a diverse audience, attracting followers from different social strata and backgrounds.
After Jesus’ crucifixion and resurrection, his disciples, led by the apostle Paul, began spreading his message beyond Judea. They ventured into the neighboring regions of Galilee, Samaria, and the Decapolis, establishing early Christian communities. These communities served as focal points for the dissemination of Christian teachings and the formation of new believers.
Expanding Horizons: The Roman Empire and Beyond
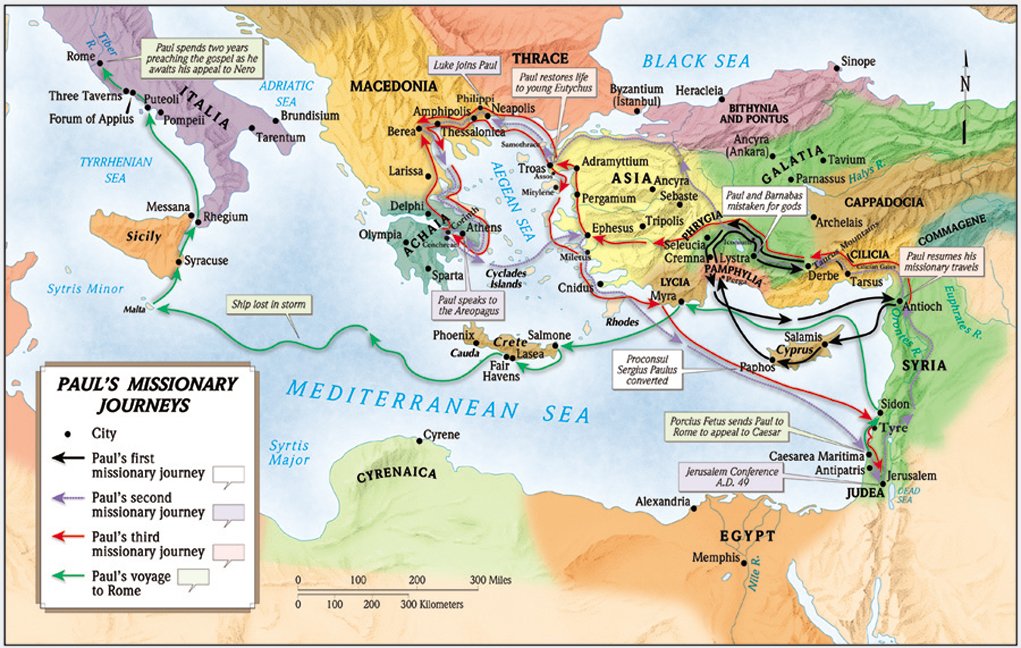
The Roman Empire, with its vast network of roads and bustling trade routes, provided the perfect conduit for the spread of Christianity. Paul, a Roman citizen, utilized the Roman infrastructure to travel extensively, establishing churches in major cities like Antioch, Ephesus, Corinth, and Rome.
Paul’s missionary journeys were crucial in shaping the early Christian movement. He articulated a universal message of salvation through faith in Jesus Christ, regardless of ethnicity or social status. This message resonated with many, attracting converts from diverse social backgrounds – slaves, soldiers, merchants, and even Roman officials.
The early Christians faced persecution from both Jewish and Roman authorities. However, their unwavering faith and commitment to their beliefs fueled their resilience and allowed them to spread their message further. The Roman Empire, despite its initial hostility, became the primary stage for the growth and development of Christianity.
From Persecution to Tolerance: The Evolving Relationship with the Roman Empire
The early centuries of Christianity witnessed a complex relationship with the Roman Empire. While persecution was a constant threat, the empire’s legal framework and administrative structure also provided opportunities for the faith to flourish.
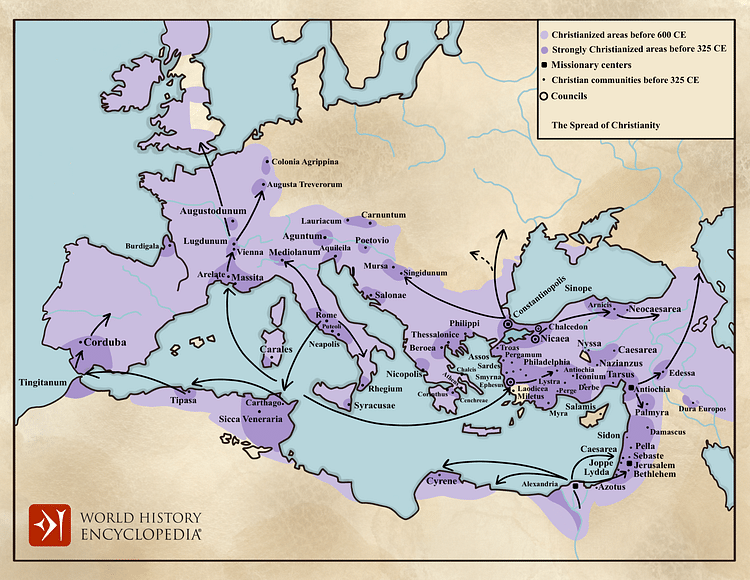
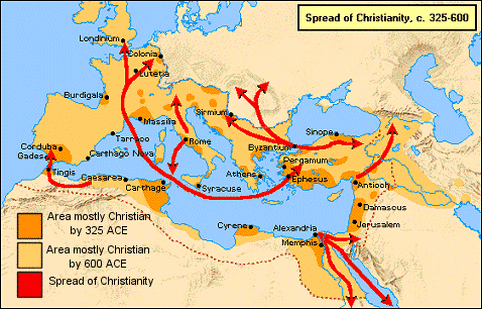
The conversion of Emperor Constantine in the 4th century marked a turning point in the relationship between Christianity and the Roman Empire. Constantine’s Edict of Milan in 313 AD granted religious freedom to Christians, ending centuries of persecution. This paved the way for the rapid expansion of Christianity, with churches and monasteries springing up throughout the empire.
The reign of Emperor Theodosius I further solidified Christianity’s position within the Roman Empire. In 380 AD, he declared Christianity the official religion of the empire, a landmark decision that ushered in a new era for the faith.
The Rise of Major Centers of Christianity: From Rome to Constantinople
As Christianity spread throughout the Roman Empire, major centers of faith emerged. Rome, the capital of the empire, naturally became a prominent hub for Christian activity. The city boasted numerous churches, including the Basilica of St. Peter, and was home to several influential early Christian leaders, such as Pope Clement I.
The establishment of Constantinople as the new capital of the Roman Empire in the 4th century also led to the emergence of a significant Christian community. The city’s strategic location and political importance made it a natural center for the dissemination of Christian teachings.
The Impact of Early Christianity on the Map
The early Christian map highlights the transformative impact of the faith on the ancient world. It demonstrates the intricate interplay of religious beliefs, political power, and social dynamics in shaping the course of history. The map provides a visual representation of how Christianity:
- Transcended geographical boundaries: It spread beyond its original confines in Judea, reaching the farthest corners of the Roman Empire and beyond.
- Promoted cultural exchange: The interaction between Christianity and other cultures led to the development of unique Christian traditions and expressions of faith.
- Influenced political landscapes: The conversion of emperors and the establishment of Christianity as the official religion of the Roman Empire profoundly impacted the political landscape of the ancient world.
- Shaped artistic and architectural expressions: The construction of churches, cathedrals, and monasteries, inspired by Christian themes and imagery, left a lasting legacy on the artistic and architectural heritage of Western civilization.
Understanding the Early Christian Map: A Guide to Key Features
To navigate the intricate tapestry of the early Christian map, it is crucial to understand its key features:
- Major Centers of Christianity: Identifying the key cities and regions where Christianity flourished in the early centuries is essential for understanding its spread and influence.
- Missionary Journeys: Tracing the routes of early Christian missionaries, such as Paul, provides insights into the strategies and challenges they faced in spreading the faith.
- Centers of Persecution: Recognizing areas where Christians faced persecution sheds light on the challenges and sacrifices made by early believers.
- Theological Developments: Understanding the development of key Christian doctrines, such as the Trinity and the nature of Christ, provides context for the evolution of Christian thought.
- Cultural Influences: Exploring the interaction between Christianity and other cultures, such as Roman, Greek, and Jewish, reveals the rich tapestry of early Christian traditions.
FAQs about the Early Christian Map
1. What were the primary factors that contributed to the spread of Christianity in the Roman Empire?
The spread of Christianity in the Roman Empire was driven by a combination of factors, including:
- The Roman road network: The extensive network of roads facilitated the movement of people and ideas, allowing the Christian message to reach distant regions.
- The Roman legal framework: The Roman legal system provided a framework for Christian communities to organize and operate, even amidst persecution.
- Paul’s missionary journeys: Paul’s extensive travels and eloquent preaching played a pivotal role in establishing churches and spreading the Christian message throughout the empire.
- The appeal of Christianity’s message: The universal message of salvation through faith in Jesus Christ resonated with a diverse audience, attracting converts from various social backgrounds.
2. How did the persecution of Christians impact the spread of the faith?
While persecution presented significant challenges for early Christians, it also paradoxically contributed to the spread of their faith. The stories of martyrs and the resilience of believers in the face of adversity inspired others and strengthened their commitment to the faith. Persecution also served as a catalyst for the development of Christian communities and networks of support.
3. What were the key theological developments in early Christianity?
Early Christianity witnessed significant theological debates and discussions, leading to the development of key doctrines, such as:
- The Trinity: The belief in the unity of God in three persons – Father, Son, and Holy Spirit – emerged as a central tenet of Christian faith.
- The nature of Christ: Debates surrounding the relationship between Jesus’ divine and human nature shaped early Christian thought and practice.
- Salvation: The concept of salvation through faith in Jesus Christ, as opposed to adherence to Jewish law, became a defining characteristic of early Christianity.
4. How did Christianity influence the art and architecture of the Roman Empire?
The rise of Christianity had a profound impact on the art and architecture of the Roman Empire. Churches and cathedrals were built throughout the empire, incorporating Christian themes and imagery. The development of Christian iconography, including depictions of Jesus, Mary, and saints, became an integral part of Christian art.
Tips for Exploring the Early Christian Map
- Utilize online resources: Numerous online maps and interactive resources provide detailed information about the spread of Christianity in the ancient world.
- Read historical accounts: Primary sources, such as the writings of early Christian authors and historical accounts of the period, provide valuable insights into the lives and beliefs of early Christians.
- Visit historical sites: Traveling to sites of early Christian significance, such as Jerusalem, Rome, and Constantinople, allows for a firsthand experience of the faith’s historical context.
- Engage in theological reflection: Reflecting on the theological developments and challenges faced by early Christians can deepen understanding and appreciation of the faith’s evolution.
Conclusion
The early Christian map is a testament to the transformative power of faith and its ability to transcend geographical boundaries and cultural barriers. It charts the journey of a nascent religion from its humble beginnings in Judea to its eventual establishment as a dominant force in the Roman Empire. Understanding this map allows us to appreciate the complex interplay of religious beliefs, political power, and social dynamics that shaped the course of Western civilization. It serves as a reminder of the enduring legacy of faith and its ability to inspire, challenge, and shape the world around us.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Tracing the Roots of Faith: A Journey Through the Early Christian Map. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!