Transforming Spatial Data: Converting Maps to Lists for Enhanced Analysis and Organization
Related Articles: Transforming Spatial Data: Converting Maps to Lists for Enhanced Analysis and Organization
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Transforming Spatial Data: Converting Maps to Lists for Enhanced Analysis and Organization. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Transforming Spatial Data: Converting Maps to Lists for Enhanced Analysis and Organization

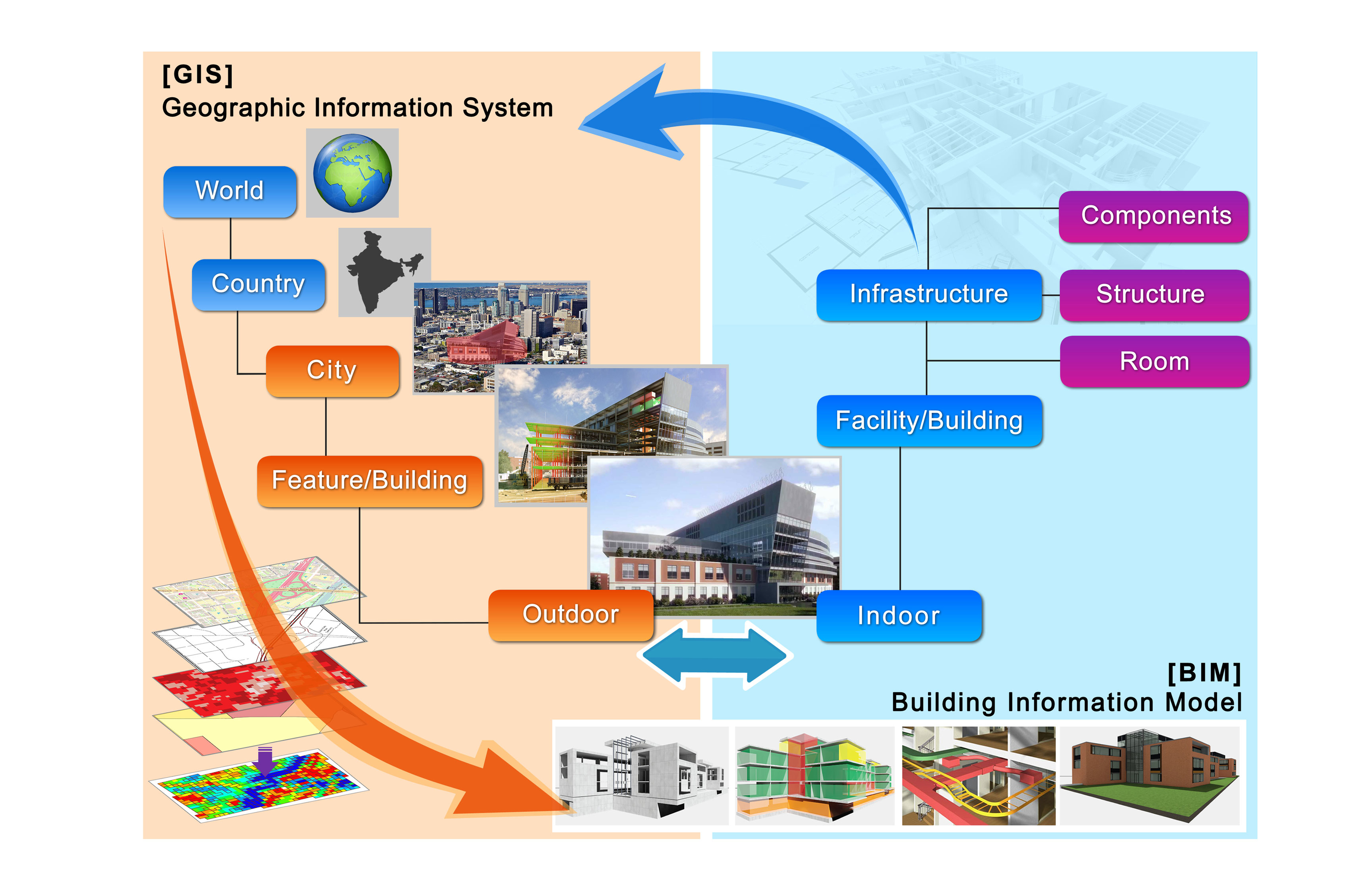
In the digital age, information is often presented in a variety of formats, with maps serving as a powerful visual representation of spatial data. While maps excel at conveying geographical relationships and overall spatial patterns, converting them to lists can unlock a wealth of analytical possibilities and offer a more structured approach to data management. This process, often referred to as "map to list conversion," involves extracting key information from a map and organizing it into a tabular format.
Benefits of Converting Maps to Lists
Transforming maps into lists provides numerous advantages, significantly enhancing data analysis, organization, and utilization:
-
Structured Data: Maps present data visually, but converting them into lists creates a structured format, making data easier to manipulate, analyze, and interpret. This structured approach simplifies data exploration and comparison, enabling more efficient insights.
-
Enhanced Analysis: Converting maps to lists unlocks the power of data analysis tools and techniques. Data can be sorted, filtered, and grouped based on specific criteria, revealing hidden patterns and trends that might not be readily apparent in a map format.
-
Improved Data Management: Lists facilitate efficient data management and storage. Data can be easily organized, searched, and retrieved, streamlining workflows and minimizing the risk of data loss or duplication.
-
Data Integration: Converting maps to lists allows for seamless integration with other data sources. This integration facilitates cross-referencing and analysis, enriching the overall understanding of the data.
-
Automated Processes: Converting maps to lists can be automated, saving time and effort. This automation streamlines data extraction and analysis, allowing users to focus on higher-level tasks.
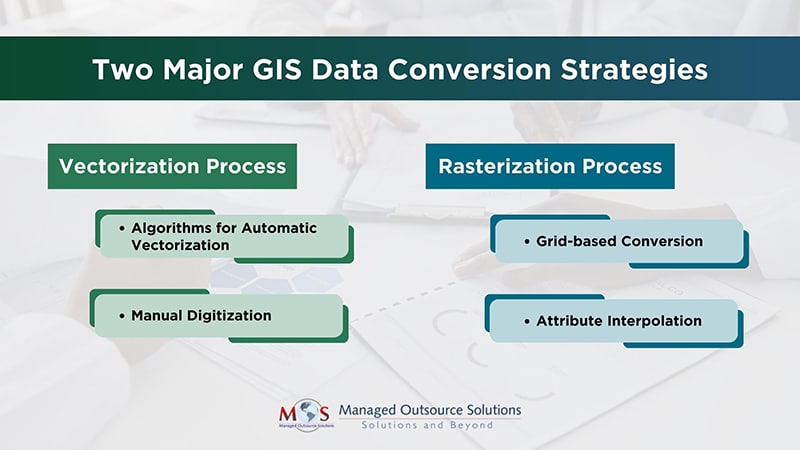
Methods for Converting Maps to Lists
Several methods can be employed to convert maps to lists, each with its own strengths and limitations:
-
Manual Extraction: This method involves manually extracting data points from a map and entering them into a spreadsheet or database. While simple, it is time-consuming and prone to errors, especially for large datasets.
-
Geocoding Tools: Geocoding tools utilize geographic coordinates (latitude and longitude) to convert addresses or place names into points on a map. This process can be reversed, extracting coordinates from map points and converting them into a list format.
-
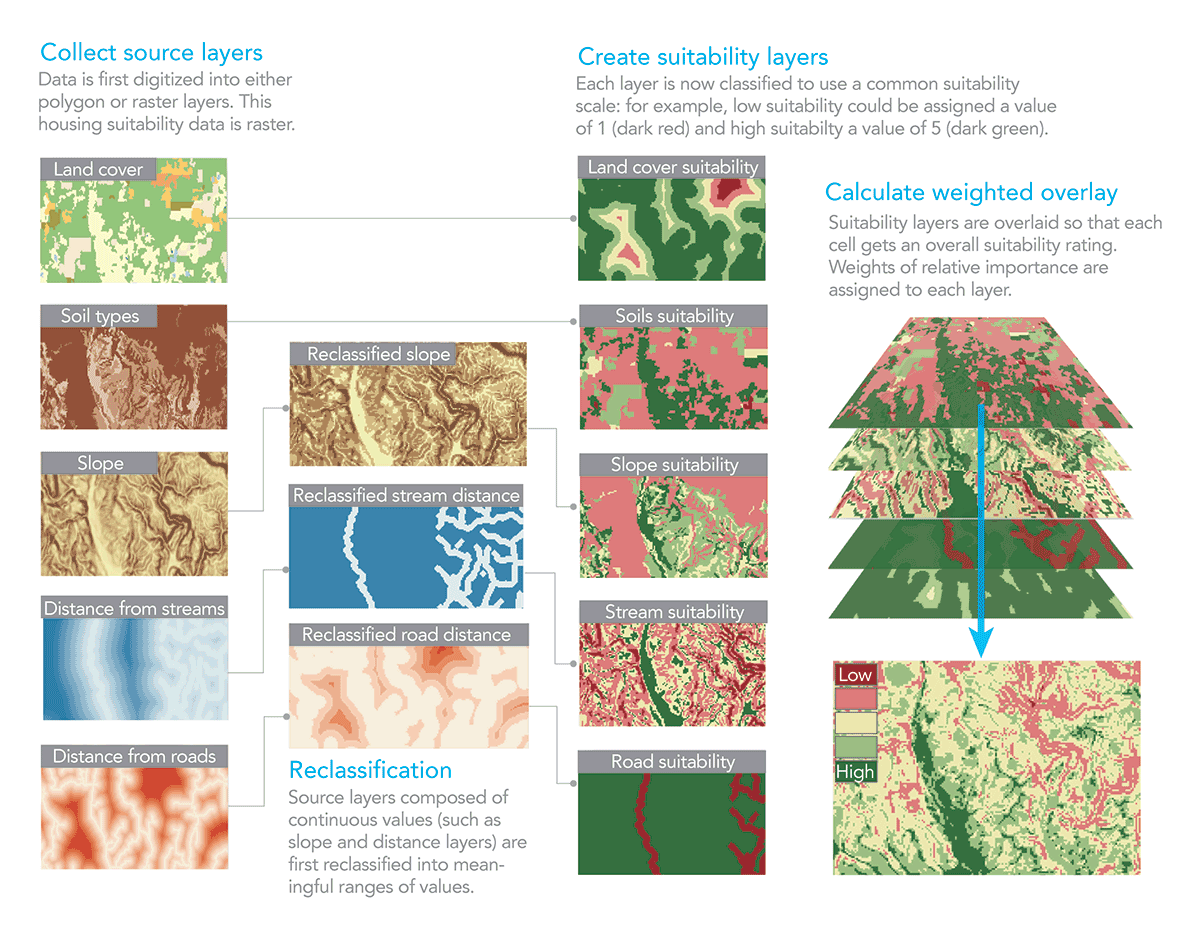
GIS Software: Geographic Information Systems (GIS) software offers advanced capabilities for converting maps to lists. Users can select specific features on a map, extract their attributes, and export them into a table format. GIS software provides powerful tools for manipulating spatial data and offers flexibility in defining the output format.
-
Web-based Tools: Several online tools and services allow for map to list conversion. These tools often offer user-friendly interfaces and can handle various map formats. However, they may have limitations in terms of customization and data processing capabilities.
Applications of Map to List Conversion
The process of converting maps to lists finds wide application across various domains:
-
Urban Planning: Urban planners utilize map to list conversion to analyze land use patterns, identify areas for development, and assess infrastructure needs. This data can be used to optimize resource allocation and create sustainable urban environments.
-
Environmental Management: Environmental scientists use map to list conversion to analyze environmental data, such as air quality, water pollution, and biodiversity. This information helps in identifying environmental hazards and developing strategies for mitigation and conservation.
-
Business Analytics: Businesses leverage map to list conversion to analyze customer demographics, optimize delivery routes, and identify market opportunities. This data-driven approach enables businesses to make informed decisions and improve operational efficiency.
-
Transportation Planning: Transportation planners use map to list conversion to analyze traffic patterns, identify congestion points, and plan infrastructure improvements. This data helps in optimizing transportation networks and improving traffic flow.
-
Disaster Management: In emergency situations, map to list conversion is crucial for identifying affected areas, assessing damage, and coordinating relief efforts. This data-driven approach allows for efficient resource allocation and effective response to disasters.
FAQs about Converting Maps to Lists
1. What types of maps can be converted to lists?
Almost any type of map can be converted to a list, including digital maps, paper maps, and satellite imagery. The specific format and data content will determine the suitability of a particular conversion method.
2. What data can be extracted from a map?
The data extracted from a map depends on the map’s content and the specific features selected for conversion. Common data elements include:
- Location: Coordinates (latitude and longitude), addresses, place names
- Attributes: Feature type (e.g., road, building, park), size, elevation, population density
- Relationships: Proximity to other features, connectivity, spatial patterns
3. What are the challenges associated with converting maps to lists?
Challenges can arise during map to list conversion, particularly with complex datasets:
- Data Accuracy: The accuracy of the converted data depends on the quality and resolution of the original map.
- Data Consistency: Ensuring data consistency across different sources and formats can be challenging.
- Data Interpretation: Interpreting the extracted data and drawing meaningful insights requires careful analysis and domain expertise.
4. How can I ensure the accuracy of the converted data?
To ensure data accuracy, it is essential to:
- Use reliable source maps: Choose maps from reputable sources with accurate data.
- Verify data: Cross-check the extracted data against the original map and other sources.
- Employ appropriate tools: Utilize software and tools designed for accurate data extraction and conversion.
5. What are some best practices for converting maps to lists?
- Define clear objectives: Determine the specific data requirements and the intended use of the converted list.
- Select appropriate methods: Choose the conversion method that best suits the map format and data content.
- Ensure data quality: Validate the extracted data for accuracy and consistency.
- Document the process: Maintain records of the conversion steps and the data sources used.
Tips for Converting Maps to Lists
- Start with a clear objective: Define the specific data you need and how you intend to use it.
- Choose the right tools: Select tools that are suitable for the map format and data content.
- Focus on data quality: Ensure that the extracted data is accurate and consistent.
- Test and refine: Test the conversion process and refine it based on the results.
- Document your work: Keep a record of the conversion steps and data sources used.
Conclusion
Converting maps to lists offers a powerful approach to enhancing data analysis, organization, and utilization. By transforming spatial data into a structured format, users can unlock a wealth of insights, streamline data management, and facilitate integration with other data sources. The process of map to list conversion finds broad application across various domains, from urban planning and environmental management to business analytics and disaster management. By understanding the benefits, methods, and challenges associated with this process, users can leverage its power to extract valuable information and make informed decisions based on spatial data.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Transforming Spatial Data: Converting Maps to Lists for Enhanced Analysis and Organization. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!