Uncovering the Earth’s Black Gold: A Comprehensive Guide to Coal Maps
Related Articles: Uncovering the Earth’s Black Gold: A Comprehensive Guide to Coal Maps
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Uncovering the Earth’s Black Gold: A Comprehensive Guide to Coal Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Uncovering the Earth’s Black Gold: A Comprehensive Guide to Coal Maps
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Uncovering the Earth’s Black Gold: A Comprehensive Guide to Coal Maps
- 3.1 What are Coal Maps?
- 3.2 Types of Coal Maps
- 3.3 Importance of Coal Maps
- 3.4 Data Sources and Technologies for Coal Mapping
- 3.5 FAQs about Coal Maps
- 3.6 Tips for Using Coal Maps Effectively
- 3.7 Conclusion
- 4 Closure
Uncovering the Earth’s Black Gold: A Comprehensive Guide to Coal Maps
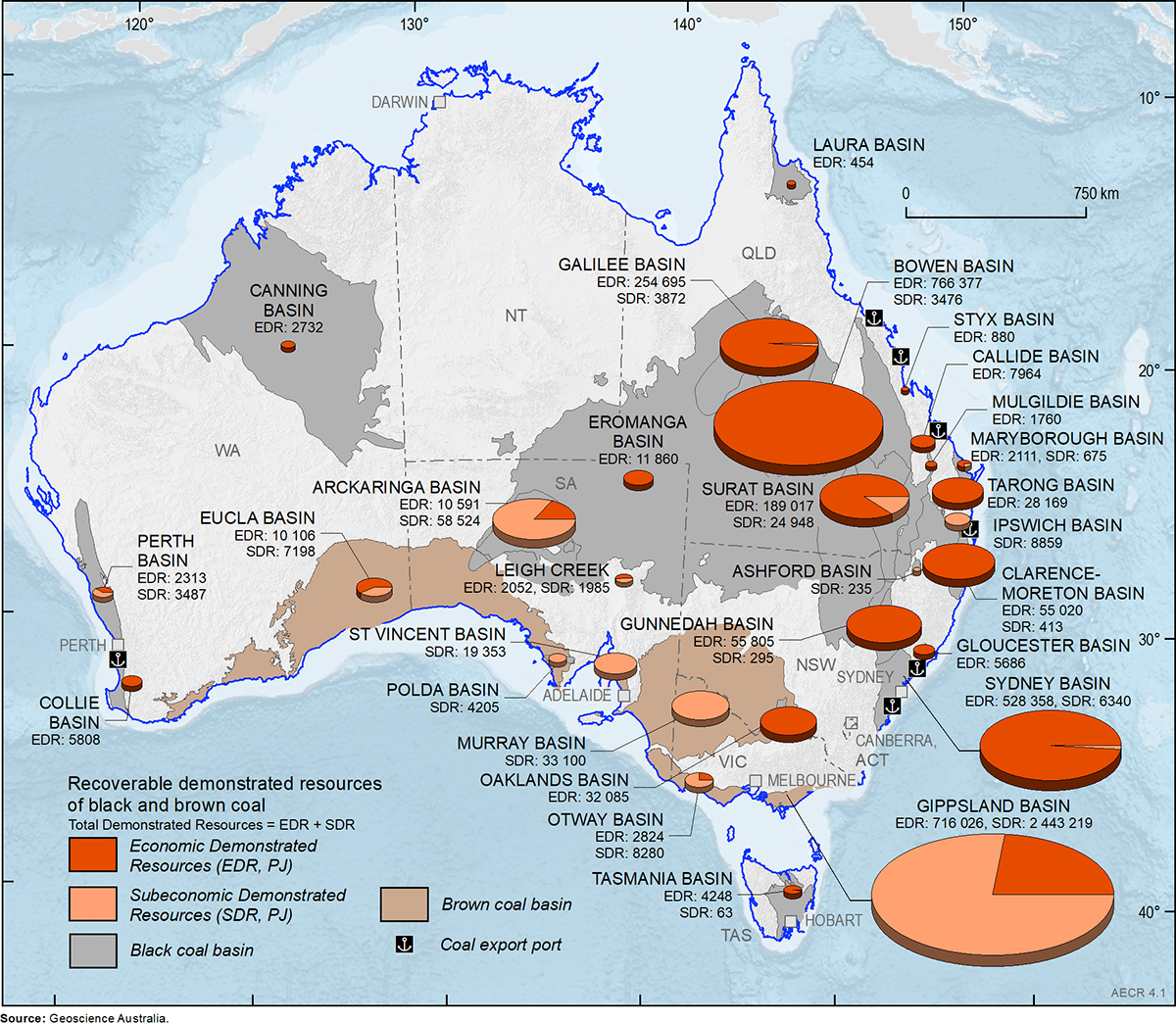
Coal, a fossil fuel formed over millions of years from ancient plant matter, has played a pivotal role in shaping human civilization. From powering industrial revolutions to providing electricity to homes, coal remains a significant energy source globally. Understanding the distribution and characteristics of this resource is crucial for efficient extraction, responsible utilization, and informed policy decisions. This is where coal maps come into play.
What are Coal Maps?
Coal maps are specialized geographical representations that depict the location, extent, and characteristics of coal deposits. They serve as invaluable tools for various stakeholders, including:
- Mining Companies: Coal maps help identify potential mining sites, assess the quality and quantity of coal reserves, and plan efficient extraction strategies.
- Government Agencies: These maps aid in regulating coal mining activities, ensuring environmental protection, and establishing land-use policies.
- Researchers: Coal maps are essential for understanding the geological history of coal formation, analyzing environmental impacts, and developing sustainable energy strategies.
- Energy Companies: These maps assist in determining coal reserves, assessing transportation logistics, and planning power plant operations.
Types of Coal Maps
Coal maps can be broadly categorized based on their purpose and level of detail:
1. Regional Coal Maps: These maps depict the overall distribution of coal deposits across a large geographical area, such as a state or country. They provide a general overview of coal resources and their geological context.
2. Local Coal Maps: Focusing on specific mining areas, these maps provide detailed information about coal seams, their thickness, quality, and geological structure. They are crucial for planning mining operations and assessing the economic viability of a site.
3. Geological Coal Maps: These maps emphasize the geological aspects of coal deposits, including the age, formation process, and structural features. They are essential for understanding the geological context of coal deposits and predicting potential challenges during mining.
4. Resource Coal Maps: These maps primarily focus on the quantity and quality of coal reserves. They are used to assess the economic potential of coal deposits and inform energy policy decisions.
5. Environmental Coal Maps: These maps highlight the environmental impacts of coal mining, such as land disturbance, water pollution, and greenhouse gas emissions. They are used to assess the environmental risks associated with coal extraction and inform sustainable mining practices.
Importance of Coal Maps
Coal maps are indispensable for various reasons:
- Resource Assessment: Coal maps provide accurate information about the location, extent, and quality of coal reserves, enabling informed decisions about resource utilization and extraction strategies.
- Mining Planning: Detailed coal maps are essential for planning efficient and safe mining operations, minimizing environmental impacts, and maximizing resource recovery.
- Environmental Management: Coal maps help identify potential environmental risks associated with coal mining and inform the development of mitigation strategies.
- Energy Policy: Accurate data on coal reserves and their characteristics is crucial for formulating energy policies, ensuring energy security, and promoting sustainable energy development.
- Economic Development: Coal maps play a vital role in attracting investment, promoting economic growth in coal-producing regions, and supporting local communities.
Data Sources and Technologies for Coal Mapping
Coal maps are created using a combination of data sources and advanced technologies:
- Geological Surveys: Geological surveys provide fundamental data on the geology of coal deposits, including their age, formation, and structural features.
- Borehole Data: Drilling boreholes and analyzing the extracted core samples provide detailed information about the coal seams, their thickness, quality, and geological structure.
- Remote Sensing: Satellite imagery and aerial photographs offer a comprehensive view of the landscape and can identify potential coal deposits based on surface features.
- Geophysical Surveys: Techniques like seismic surveys and magnetic surveys can detect subsurface geological structures and identify potential coal deposits.
- Geographic Information Systems (GIS): GIS software is used to integrate, analyze, and visualize data from various sources, creating comprehensive coal maps that integrate geological, environmental, and economic information.
FAQs about Coal Maps
1. What are the key elements of a coal map?
Coal maps typically include:
- Location: Precise geographical coordinates of coal deposits.
- Extent: The area covered by coal seams.
- Depth: The depth at which coal seams are located.
- Thickness: The thickness of coal seams.
- Quality: The rank and properties of coal, such as ash content, sulfur content, and calorific value.
- Geological Structure: Information about folds, faults, and other geological features that can influence coal deposit characteristics.
- Environmental Data: Information about potential environmental impacts, such as water resources, land use, and biodiversity.
2. What are the benefits of using coal maps?
Coal maps provide numerous benefits, including:
- Improved Resource Management: Efficient utilization and extraction of coal resources.
- Enhanced Safety: Planning safe and efficient mining operations.
- Minimized Environmental Impacts: Identifying potential environmental risks and implementing mitigation strategies.
- Informed Policy Decisions: Providing data for informed decision-making regarding energy policy, land use, and environmental regulations.
- Economic Growth: Facilitating investment and promoting economic development in coal-producing regions.
3. What are the limitations of coal maps?
Coal maps are not perfect representations of reality and have limitations:
- Data Accuracy: Data accuracy depends on the quality of data sources and the methodologies used.
- Geological Complexity: Complex geological structures can make it challenging to accurately map coal deposits.
- Environmental Variability: Environmental factors can influence the quality and accessibility of coal deposits.
- Technological Advancements: Continuous technological advancements can lead to updates and revisions of existing coal maps.
4. How are coal maps used in the context of climate change?
Coal maps play a crucial role in understanding the environmental impacts of coal mining and informing the transition to cleaner energy sources. They provide data on coal reserves, their characteristics, and potential environmental risks, helping to inform policy decisions regarding carbon emissions reduction and the development of renewable energy sources.
5. What are the future trends in coal mapping?
Future trends in coal mapping include:
- Integration of Big Data: Incorporating large datasets from various sources, including remote sensing, geophysical surveys, and geological databases, to create more comprehensive and accurate coal maps.
- Advanced Analytics: Utilizing advanced analytics techniques, such as machine learning and artificial intelligence, to identify patterns and predict coal deposit characteristics.
- 3D Modeling: Developing three-dimensional models of coal deposits to provide a more realistic representation of their geological structure and resource potential.
- Integration with Environmental Monitoring: Combining coal maps with environmental monitoring data to assess the impacts of coal mining and inform sustainable mining practices.
Tips for Using Coal Maps Effectively
- Understand the Purpose: Clearly define the purpose of using a coal map to select the appropriate type and level of detail.
- Data Quality: Verify the data sources and accuracy of the information presented on the map.
- Scale and Resolution: Consider the scale and resolution of the map in relation to the intended use.
- Integration with Other Data: Combine coal maps with other relevant data, such as environmental data, population data, and economic data, for a more comprehensive understanding.
- Regular Updates: Keep abreast of technological advancements and update coal maps with new data and information.
Conclusion
Coal maps are essential tools for managing and utilizing coal resources responsibly. By providing accurate and comprehensive information about the location, extent, and characteristics of coal deposits, these maps enable informed decision-making regarding mining operations, environmental protection, and energy policy. As the world transitions towards a more sustainable energy future, coal maps will continue to play a vital role in understanding the role of coal in the global energy mix and informing the development of cleaner and more sustainable energy solutions.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Uncovering the Earth’s Black Gold: A Comprehensive Guide to Coal Maps. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!