Understanding the Global Tapestry of Temperature: A Comprehensive Guide to World Weather Maps
Related Articles: Understanding the Global Tapestry of Temperature: A Comprehensive Guide to World Weather Maps
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Understanding the Global Tapestry of Temperature: A Comprehensive Guide to World Weather Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding the Global Tapestry of Temperature: A Comprehensive Guide to World Weather Maps
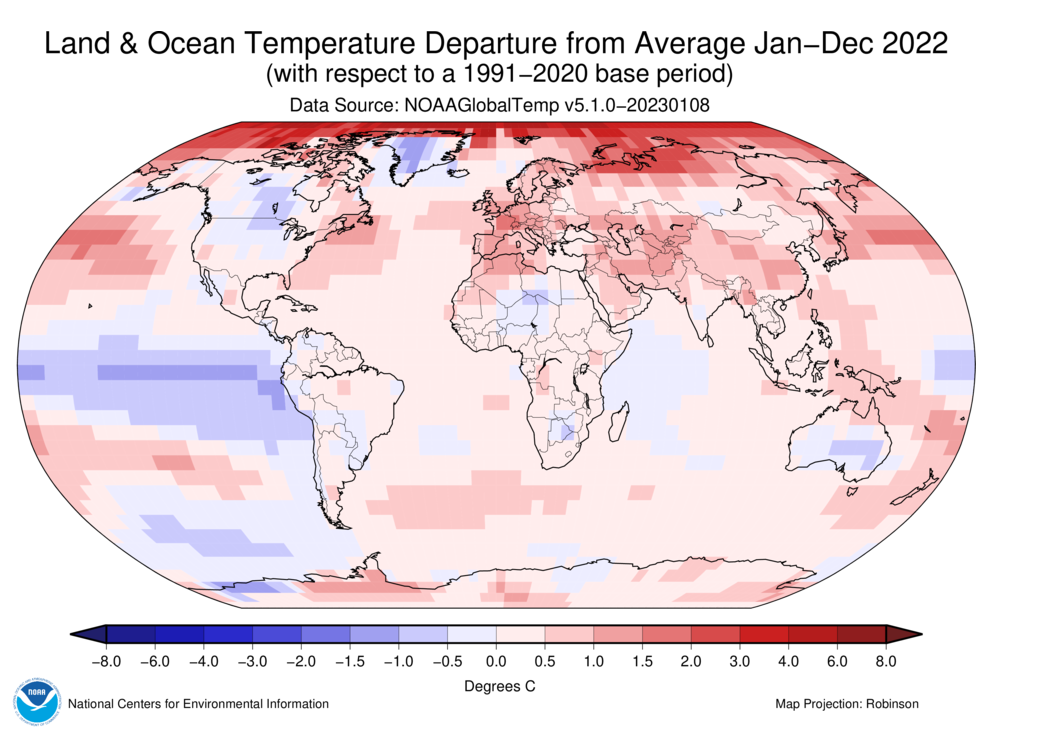
The Earth’s climate is a complex and dynamic system, constantly shifting and evolving. Understanding this intricate dance of weather patterns is crucial for a myriad of reasons, from informing our daily lives to guiding crucial decisions in agriculture, transportation, and disaster preparedness. A powerful tool in this endeavor is the world weather map, a visual representation of global temperatures that provides a snapshot of the planet’s thermal state.
The World Weather Map: A Visual Representation of Temperature
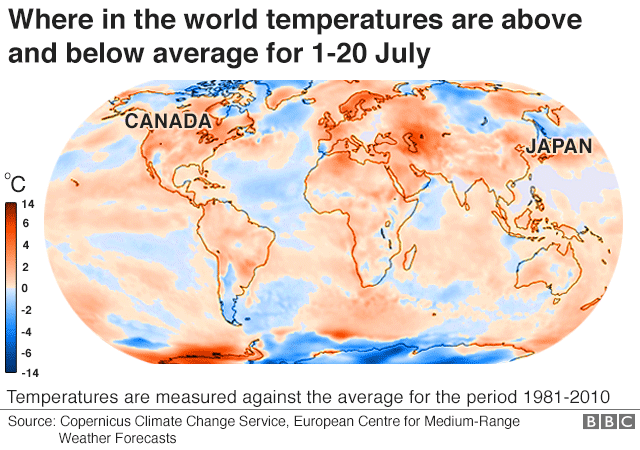
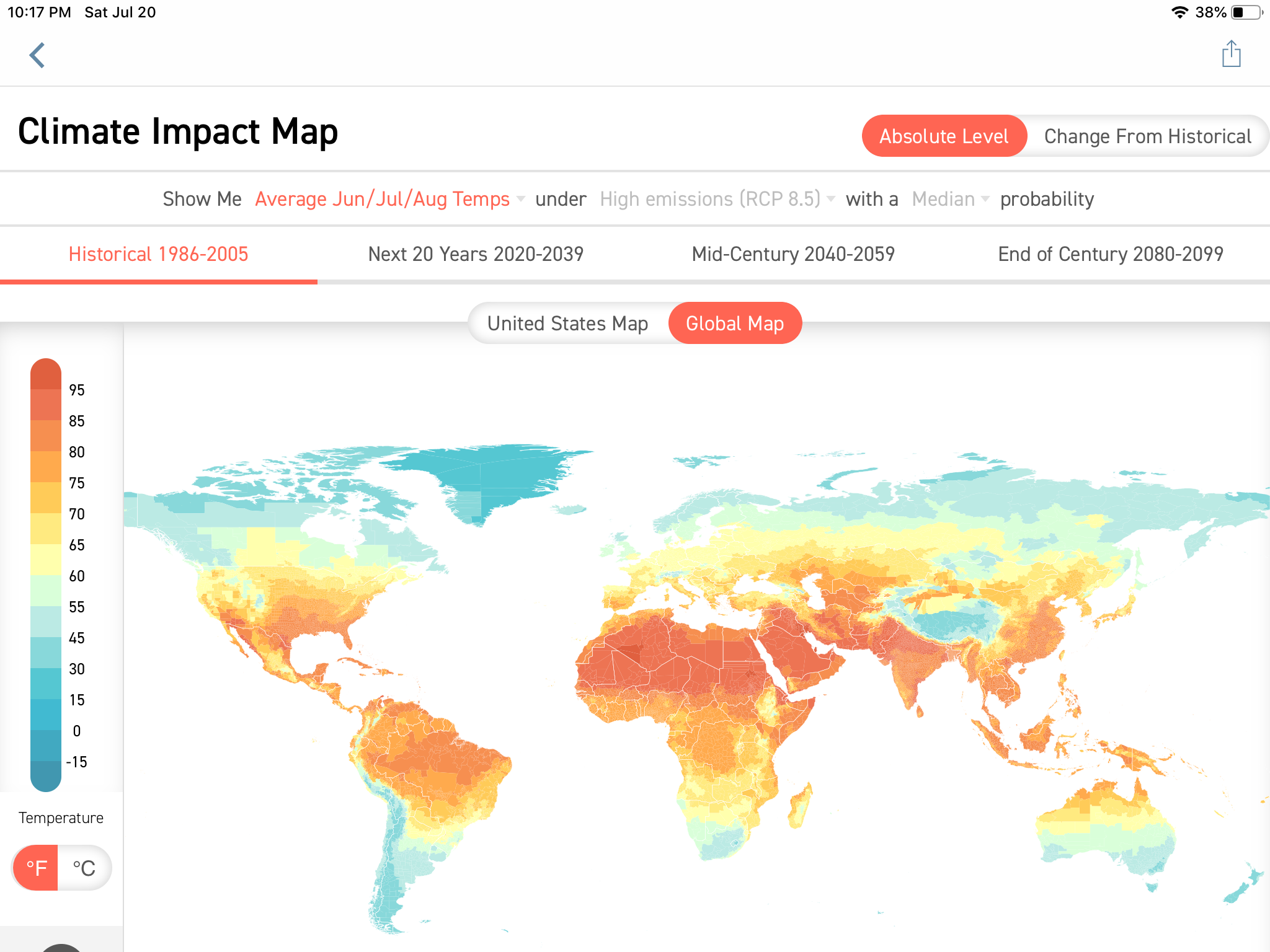
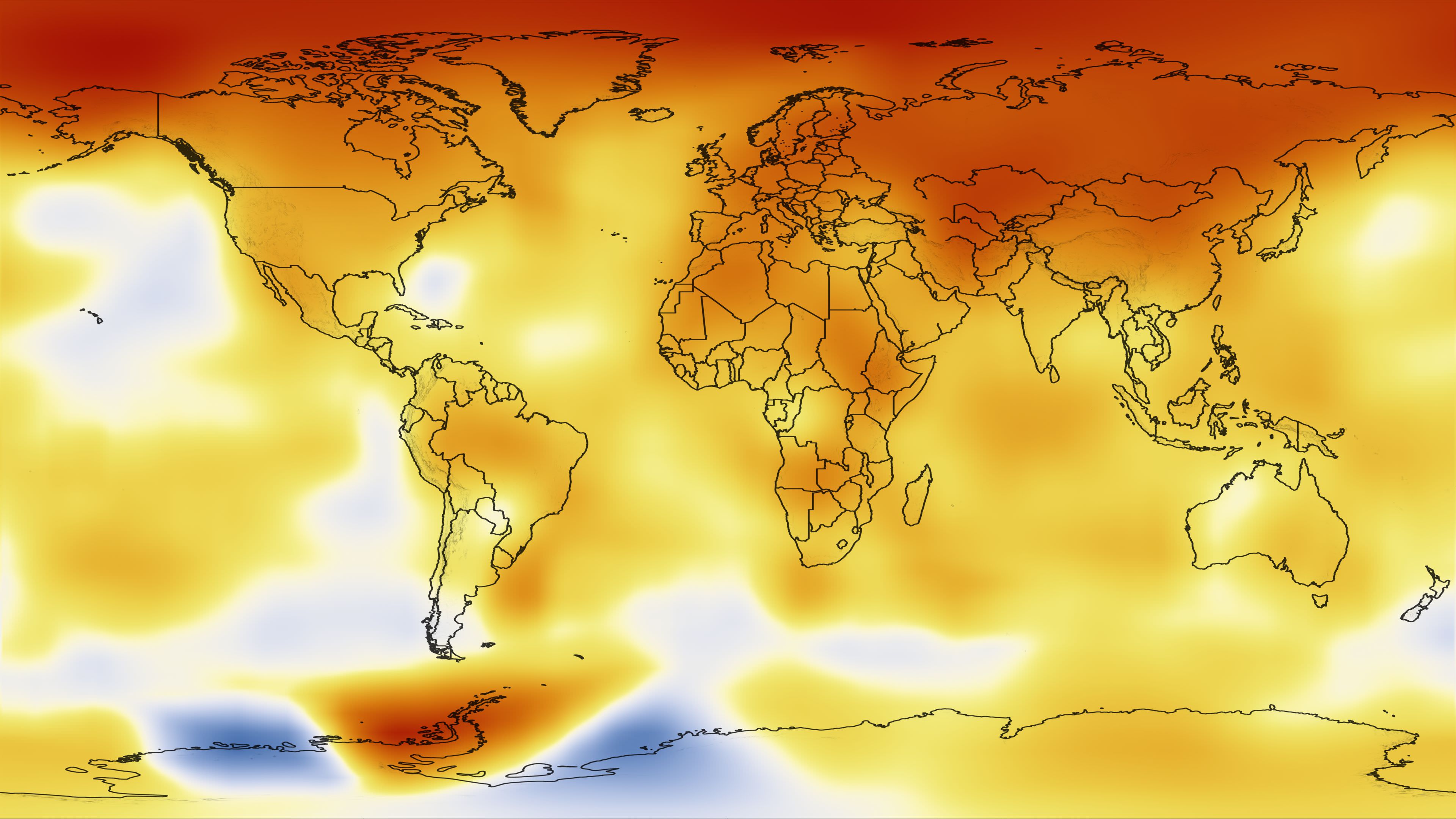
World weather maps, often presented as colorful visualizations, depict temperature variations across the globe. They utilize a color-coded scale, where warmer temperatures are represented by shades of red and orange, while cooler temperatures are depicted in blues and greens. This visual representation allows for quick and easy comprehension of temperature trends across continents, oceans, and even specific regions.
The Importance of World Weather Maps
The significance of these maps extends beyond simple visual appeal. They serve as a vital resource for various sectors:
- Meteorology and Forecasting: Weather maps provide meteorologists with a crucial tool for analyzing current weather conditions and predicting future patterns. They help in identifying areas prone to extreme weather events like heatwaves, cold snaps, and storms, enabling timely warnings and mitigating potential risks.
- Agriculture: Farmers rely on weather maps to plan planting and harvesting schedules, optimize irrigation, and protect crops from adverse weather conditions. Understanding temperature trends allows them to make informed decisions that impact their yields and overall success.
- Transportation: The aviation and maritime industries utilize weather maps to navigate safely and efficiently. Pilots and captains rely on temperature data to plan flight paths, avoid turbulent weather, and ensure smooth operations.
- Public Health: Temperature fluctuations can significantly impact public health. Heatwaves and cold spells can lead to health complications, particularly for vulnerable populations. Weather maps help health authorities monitor these risks and implement preventive measures.
- Energy Production: Energy production is heavily influenced by weather conditions. Wind power generation, for example, is directly affected by wind speed and direction, which can be visualized on weather maps. This information allows for efficient energy management and resource allocation.
- Environmental Monitoring: Climate change is a pressing global concern. Weather maps provide valuable data for monitoring long-term temperature trends, identifying areas experiencing significant warming, and understanding the impact of climate change on various ecosystems.
Beyond the Average: Understanding Temperature Variations
While the world weather map provides a general overview of global temperatures, it’s crucial to understand that temperature is not uniform. Various factors contribute to regional and local variations, including:
- Latitude: Temperature generally decreases with increasing latitude, due to the angle at which sunlight strikes the Earth’s surface. Areas closer to the equator receive more direct sunlight and experience warmer temperatures.
- Altitude: Higher elevations experience colder temperatures due to lower atmospheric pressure and thinner air.
- Proximity to Water: Oceans and large bodies of water have a moderating effect on temperature, leading to cooler summers and warmer winters compared to inland areas.
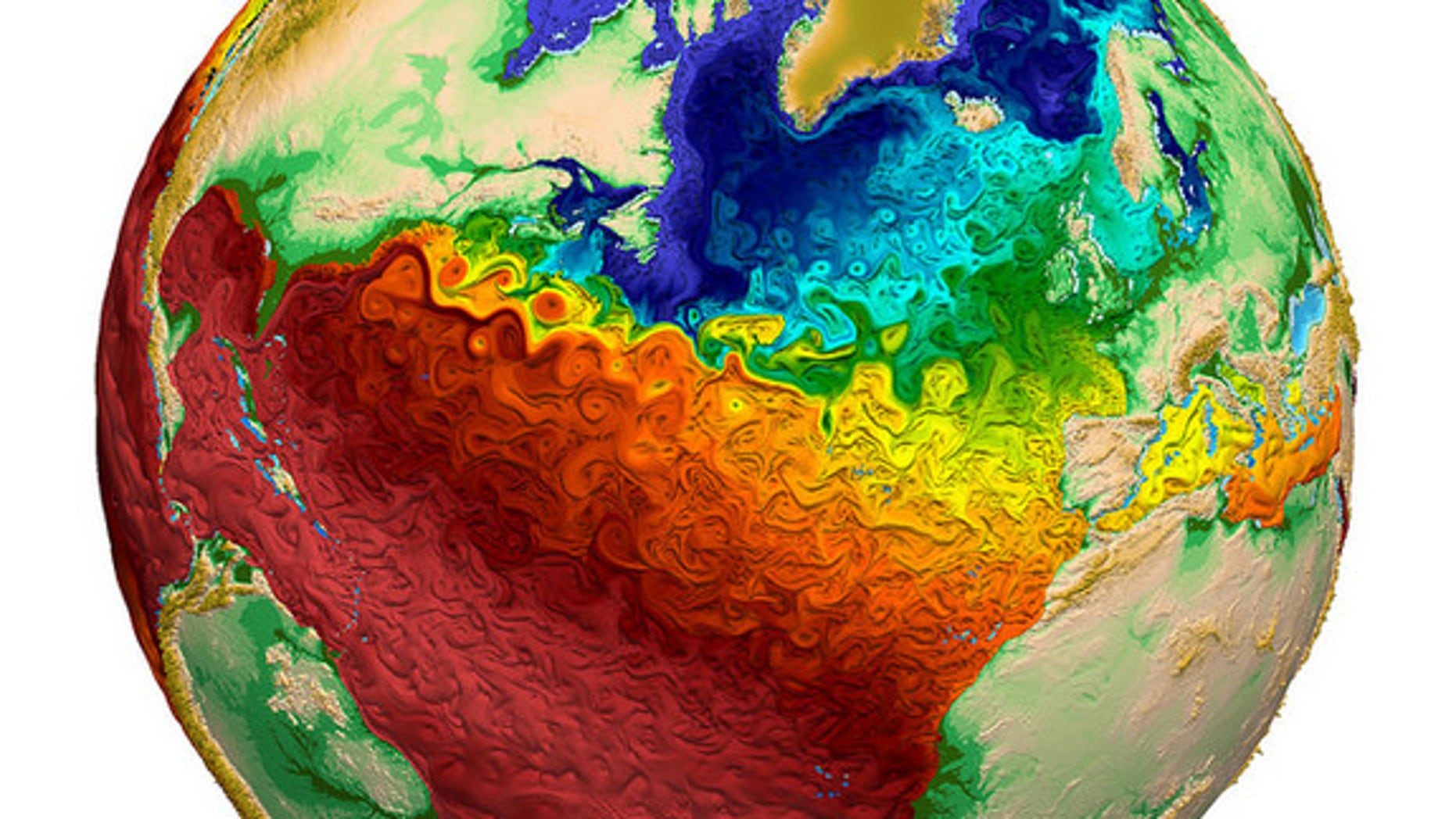
- Ocean Currents: Warm and cold ocean currents influence regional temperatures, transporting heat from the tropics towards the poles and vice versa.
- Topography: Mountain ranges and valleys create microclimates, influencing local temperature patterns.
Interpreting World Weather Maps: A Guide to Key Features
To effectively utilize world weather maps, it’s essential to understand their key features:
- Isotherms: Lines connecting points of equal temperature are called isotherms. They provide a visual representation of temperature gradients and help identify areas with similar temperature ranges.
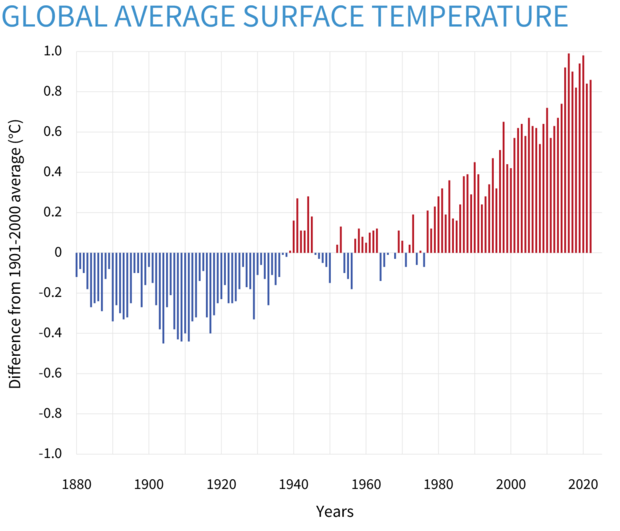
- Temperature Anomalies: These are deviations from average temperatures for a specific time period. They highlight areas experiencing unusually warm or cold conditions, potentially indicating extreme weather events.
- Temperature Trends: By analyzing weather maps over time, it’s possible to identify long-term temperature trends, such as global warming or regional cooling patterns.
FAQs About World Weather Maps
Q: What are the main sources of data for world weather maps?
A: World weather maps rely on data collected from various sources, including:
- Weather Satellites: Satellites orbiting the Earth continuously collect data on temperature, cloud cover, and other weather parameters.
- Ground Stations: Meteorological stations around the world measure temperature, humidity, wind speed, and other atmospheric conditions.
- Buoys and Ships: Oceanic buoys and ships equipped with sensors provide data on sea surface temperature and other oceanographic parameters.
Q: How frequently are world weather maps updated?
A: World weather maps are typically updated every few hours, providing near real-time information on global temperature patterns.
Q: What are some limitations of world weather maps?
A: While valuable, world weather maps have limitations:
- Spatial Resolution: Maps often have limited spatial resolution, meaning they may not accurately capture temperature variations within smaller regions.
- Data Accuracy: Data collection methods and sensor accuracy can influence the reliability of the information presented on weather maps.
- Dynamic Nature of Weather: Weather patterns are constantly changing, and maps may not always reflect the most up-to-date conditions.
Tips for Using World Weather Maps Effectively
- Consider the Source: Always check the source of the weather map and ensure it’s a reliable and reputable provider.
- Pay Attention to Time Stamps: Ensure the map you’re viewing is current and reflects the latest data available.
- Understand the Scale: Familiarize yourself with the temperature scale used on the map and the units of measurement.
- Look for Trends: Analyze the map over time to identify patterns and trends in temperature variations.
- Correlate with Other Data: Combine weather map information with other data sources, such as satellite images or weather reports, for a more comprehensive understanding of weather conditions.
Conclusion: The Power of Visualizing Global Temperature
World weather maps are indispensable tools for understanding the Earth’s intricate climate system. They provide a visual representation of global temperature patterns, enabling us to monitor current conditions, predict future trends, and make informed decisions across various sectors. From guiding agricultural practices to mitigating disaster risks, these maps play a crucial role in our daily lives and contribute to a more informed and resilient future.


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding the Global Tapestry of Temperature: A Comprehensive Guide to World Weather Maps. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!
