Understanding the Significance of Scale in European Maps
Related Articles: Understanding the Significance of Scale in European Maps
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Understanding the Significance of Scale in European Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding the Significance of Scale in European Maps

Maps are essential tools for navigating, exploring, and understanding the world around us. When it comes to Europe, a continent with a rich history, diverse landscapes, and countless cultural landmarks, maps become even more crucial. However, the accuracy and usefulness of a European map depend heavily on its scale, a crucial element often overlooked by the casual observer.
What is Map Scale?
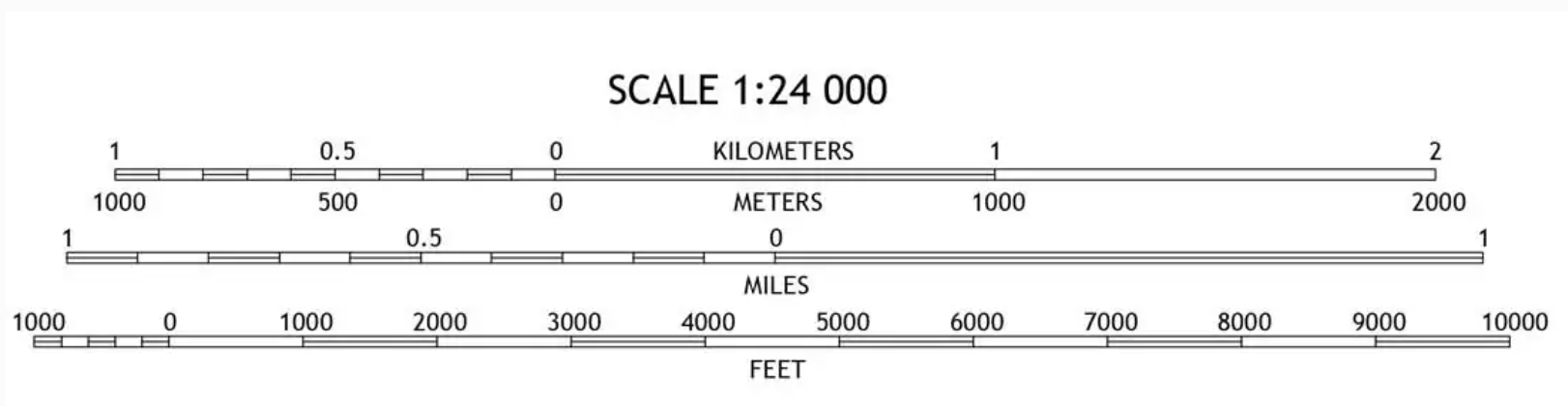
Map scale refers to the ratio between the distance on a map and the corresponding distance on the ground. It essentially dictates how much the real world is shrunk down to fit on a piece of paper or a digital screen. This ratio can be expressed in various ways:
- Verbal Scale: This uses words to describe the relationship, for example, "1 centimeter on the map represents 10 kilometers on the ground."
- Representative Fraction (RF): This uses a fraction to represent the scale, for instance, 1:100,000. This means that one unit on the map represents 100,000 of the same units on the ground.
- Graphic Scale: This uses a visual representation of the scale, usually a line divided into segments that correspond to specific distances on the ground.
The Importance of Scale in European Maps:
The choice of map scale significantly influences the level of detail and the type of information conveyed.
-
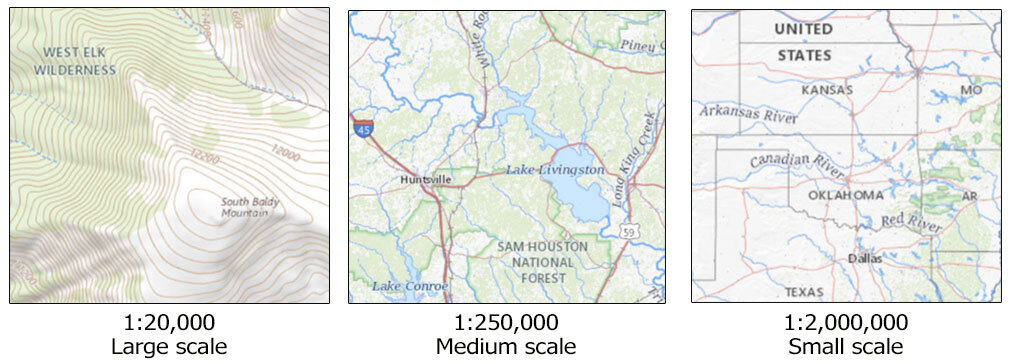
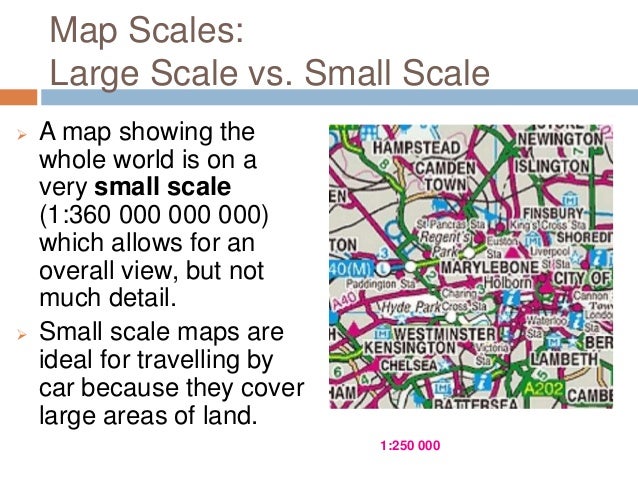
Large-Scale Maps: These maps have a small ratio, meaning they show a smaller area with greater detail. They are ideal for navigating specific regions, cities, or even individual buildings. For example, a map with a scale of 1:10,000 would be useful for exploring a city center, showcasing individual streets, parks, and landmarks.
-
Small-Scale Maps: These maps have a large ratio, depicting a vast area with less detail. They are suitable for understanding the overall geography of Europe, showing the relative locations of countries, major mountain ranges, and rivers. For example, a map with a scale of 1:10,000,000 would be useful for understanding the relative positions of major European cities and the overall shape of the continent.
Choosing the Right Scale:
The appropriate scale for a European map depends on the intended use.
- Travelers: A mid-range scale (e.g., 1:250,000) is typically ideal for navigating between cities and exploring regional attractions.
- Researchers: They might require a range of scales, from large-scale maps for analyzing urban development to small-scale maps for studying regional climate patterns.
- Students: They might use a variety of scales depending on the subject matter. A large-scale map might be used to study the history of a particular city, while a small-scale map might be used to understand the geopolitical landscape of Europe.
Beyond the Basic Scale:
While the basic scale ratio is crucial, other factors contribute to the effectiveness of a European map:
- Projection: The method used to project the three-dimensional Earth onto a flat surface can distort distances and shapes, especially at smaller scales. Different projections are suitable for different purposes.
- Map Symbols: Clear and consistent symbols are essential for quickly identifying features like roads, rivers, and cities.
- Accuracy and Data: The map’s accuracy depends on the quality of the underlying data and the methods used to collect and process it.
FAQs about Map Scale in Europe:
Q: How do I determine the appropriate scale for my needs?
A: Consider the specific region you are interested in, the level of detail required, and the intended use of the map. A larger scale is needed for detailed information, while a smaller scale provides a broader overview.
Q: Are online maps always accurate in terms of scale?
A: While online maps offer convenience and interactivity, their accuracy can vary depending on the data source, the chosen projection, and the level of zoom. It’s essential to be aware of these limitations.
Q: Can I use a map with a different scale for different purposes?
A: Yes, but it’s crucial to understand the limitations of each scale. Using a large-scale map for navigating a country might lead to difficulties, while using a small-scale map for studying a city’s street layout might be insufficiently detailed.
Tips for Using European Maps:
- Read the scale: Always pay attention to the scale indicated on the map. It will help you understand the relationship between distances on the map and distances on the ground.
- Consider the projection: Be aware of the projection used for the map, as it can influence the accuracy of distances and shapes, especially at smaller scales.
- Use a variety of scales: Don’t hesitate to use multiple maps with different scales to gain a comprehensive understanding of the region.
- Consult multiple sources: Compare maps from different publishers to ensure accuracy and gain a more complete picture.
Conclusion:
Map scale is a fundamental element of European maps, influencing their accuracy, detail, and usefulness. Understanding the concept of scale is crucial for making informed choices about the maps used for travel, research, or education. By considering the intended use, the level of detail required, and the limitations of different scales, users can select the most appropriate maps for their needs and gain a deeper appreciation for the complexity and beauty of the European landscape.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding the Significance of Scale in European Maps. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!