Unlocking the Power of Visual Communication: A Comprehensive Guide to Indicator Maps
Related Articles: Unlocking the Power of Visual Communication: A Comprehensive Guide to Indicator Maps
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Unlocking the Power of Visual Communication: A Comprehensive Guide to Indicator Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unlocking the Power of Visual Communication: A Comprehensive Guide to Indicator Maps
In the realm of data visualization, the ability to effectively communicate complex information is paramount. This is where indicator maps, also known as thematic maps, emerge as powerful tools. These maps go beyond simple geographical representations, transforming raw data into visually compelling narratives that illuminate trends, patterns, and relationships within a specific geographic context.
Understanding Indicator Maps: A Visual Language for Data
At their core, indicator maps are cartographic representations that utilize visual symbols, colors, and patterns to depict the spatial distribution of a particular variable or set of variables. This variable could be anything from population density and income levels to crime rates and environmental pollution. By visually associating data with specific locations, indicator maps provide a clear and intuitive understanding of geographic variations and their underlying causes.
Key Components of an Effective Indicator Map
To effectively convey information, indicator maps rely on a carefully chosen combination of elements:
- Base Map: The foundation of an indicator map is the base map, which provides the geographic framework. This could be a simple outline of a country, a detailed city map, or even a global projection.
- Data: The heart of the map lies in the data itself. This data must be relevant to the intended message and accurately represent the chosen variable.
- Symbols: Visual symbols, such as points, lines, or areas, are used to represent the data values. These symbols can be varied in size, shape, or color to represent different data ranges.
- Legend: A legend is crucial for interpreting the map. It explains the meaning of the symbols, colors, and patterns used to represent the data.
- **

![The Power of Visual Communication [Infographic]](https://capsicummediaworks.com/wp-content/uploads/Power-Of-Visual-Communcation-infographic.jpg)
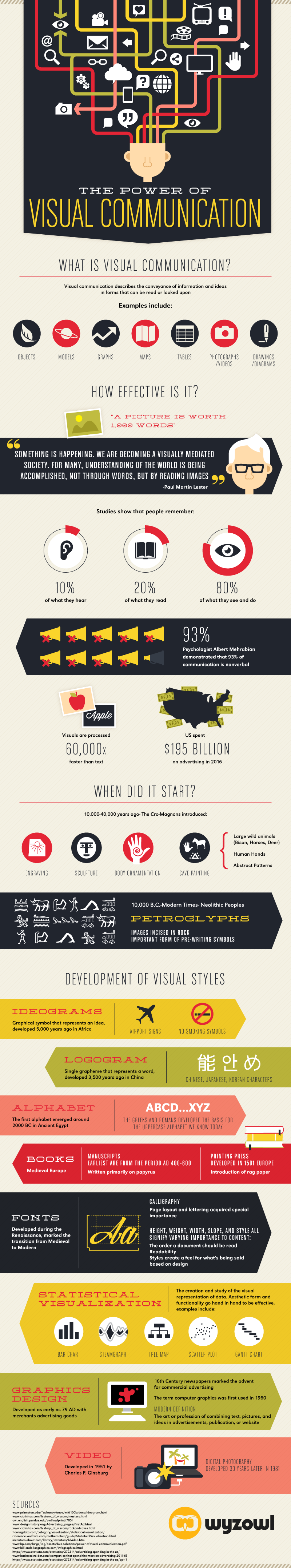
![The Power of Visual Communication [Infographic]](https://capsicummediaworks.com/wp-content/uploads/Power-of-Visual-Communication-Feature.jpg)



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unlocking the Power of Visual Communication: A Comprehensive Guide to Indicator Maps. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!