Unveiling Iraq’s Terrain: A Comprehensive Exploration of Its Topographic Map
Related Articles: Unveiling Iraq’s Terrain: A Comprehensive Exploration of Its Topographic Map
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Unveiling Iraq’s Terrain: A Comprehensive Exploration of Its Topographic Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling Iraq’s Terrain: A Comprehensive Exploration of Its Topographic Map
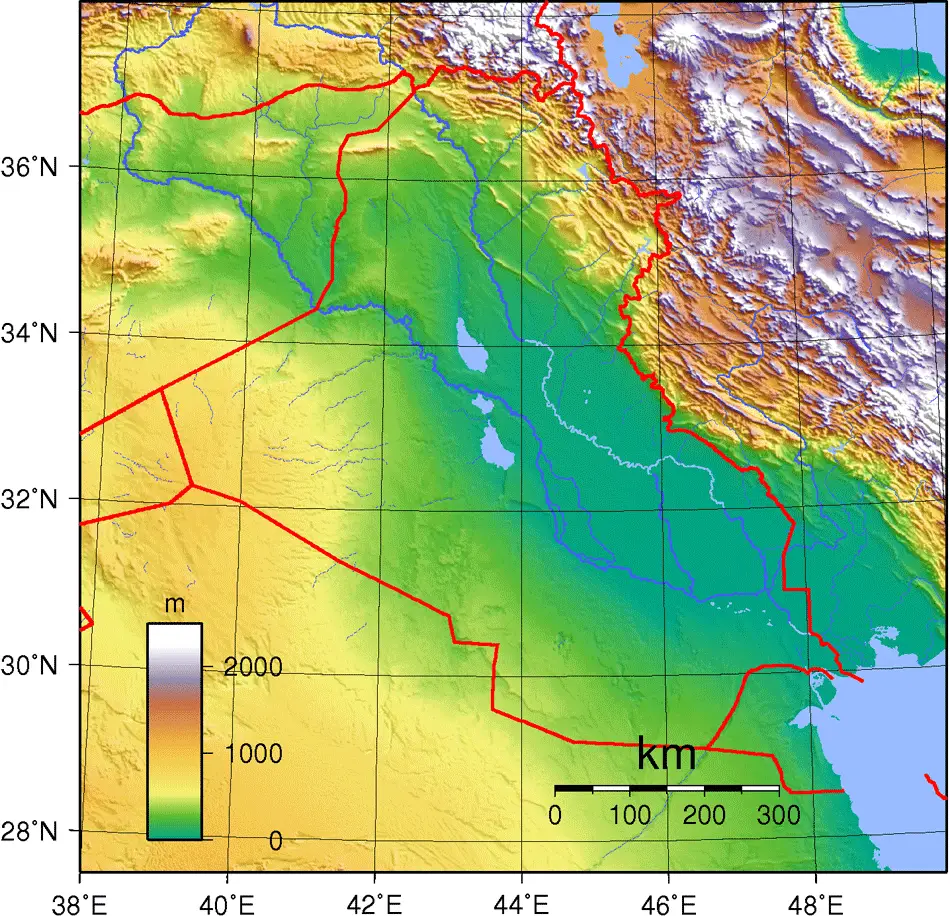
Iraq, a nation situated in the heart of the Middle East, boasts a diverse and intricate landscape shaped by millennia of geological processes. Understanding this topography is crucial for comprehending the country’s history, culture, and current challenges. A topographic map, with its detailed portrayal of elevation, terrain features, and hydrological networks, serves as an invaluable tool for navigating and analyzing this complex environment.
A Journey Through Iraq’s Topographic Landscape
The topographic map of Iraq reveals a tapestry of contrasting features, each contributing to the nation’s unique character:
1. The Mesopotamian Plain: Stretching across central and southern Iraq, this vast, low-lying plain is the cradle of civilization, where the Tigris and Euphrates rivers converge, creating fertile land for agriculture and supporting a dense population. This region, known as Mesopotamia, has witnessed the rise and fall of empires, leaving behind a rich legacy of archaeological treasures.
2. The Zagros Mountains: Rising dramatically in the north and east, the Zagros Mountains form a natural barrier between Iraq and Iran. This imposing range, characterized by rugged peaks, deep valleys, and winding gorges, is a testament to the tectonic forces that shaped the region. The Zagros Mountains are home to diverse ecosystems, including forests, grasslands, and alpine meadows, and play a crucial role in regulating Iraq’s water resources.
3. The Western Desert: Occupying a significant portion of western Iraq, this vast expanse of arid land is characterized by sand dunes, salt flats, and occasional oases. The harsh climate and limited resources make this region sparsely populated, but its unique geological formations and ancient archaeological sites hold immense scientific and cultural value.
4. The Mesopotamian Marshes: Located in southern Iraq, these sprawling wetlands are a vital habitat for a multitude of bird species, fish, and other aquatic life. The marshes, once a thriving ecosystem, have faced significant challenges due to drainage projects and environmental degradation. Their restoration is crucial for maintaining biodiversity and preserving Iraq’s natural heritage.
5. The Iraqi Kurdistan Region: Situated in the north, this autonomous region encompasses a diverse topography, ranging from the foothills of the Zagros Mountains to the plains of the Tigris River. The region is known for its rich Kurdish culture and its oil and gas reserves, making it a significant economic contributor to Iraq.
Understanding the Significance of Iraq’s Topography
The topographic map of Iraq is more than just a visual representation of the country’s physical features; it provides a fundamental understanding of its key aspects:
1. Resource Management: The map highlights the distribution of water resources, enabling efficient management of irrigation systems, water supply networks, and hydroelectric power generation. It also helps identify areas prone to flooding and drought, aiding in disaster preparedness and mitigation.
2. Infrastructure Development: The map assists in planning and constructing roads, railways, pipelines, and other infrastructure projects, ensuring they are optimally located and minimize environmental impact. It also aids in identifying suitable sites for urban development, considering factors like elevation, slope, and proximity to water sources.
3. Environmental Conservation: The map aids in understanding the distribution of ecosystems, identifying areas of ecological significance, and prioritizing conservation efforts. It helps in monitoring land use changes, identifying areas prone to desertification, and developing sustainable land management practices.
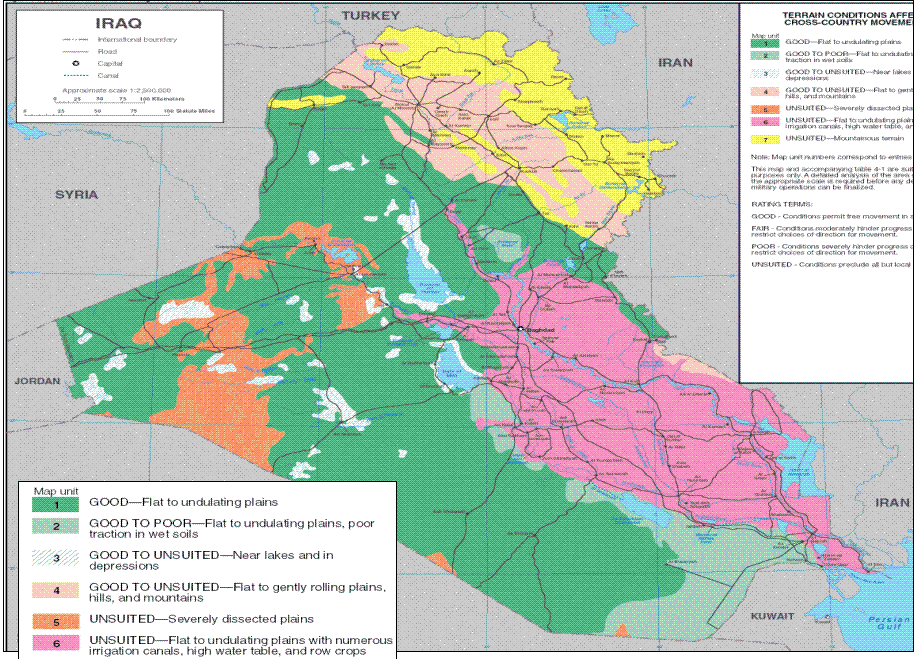
4. Conflict and Security: The map provides insights into the terrain’s strategic importance, identifying potential chokepoints, natural barriers, and areas susceptible to conflict. It assists in planning military operations, deploying troops, and securing critical infrastructure.
5. Archaeological Exploration: The map helps identify potential archaeological sites, providing valuable information for historical research and cultural preservation. It assists in understanding the distribution of ancient settlements, trade routes, and irrigation systems, shedding light on the past and its influence on the present.
FAQs about the Topographic Map of Iraq
1. What are the major topographic features of Iraq?
Iraq’s landscape is dominated by the Mesopotamian Plain, the Zagros Mountains, the Western Desert, the Mesopotamian Marshes, and the Iraqi Kurdistan Region.
2. How does the topographic map of Iraq help in managing water resources?
The map reveals the location of rivers, lakes, and groundwater sources, enabling efficient irrigation, water supply, and hydroelectric power generation. It also helps in identifying areas prone to flooding and drought, aiding in disaster management.
3. How does the map assist in infrastructure development?
The map facilitates planning and construction of roads, railways, pipelines, and other infrastructure projects, ensuring they are optimally located and minimize environmental impact.
4. What is the significance of the Mesopotamian Marshes in terms of topography?
The marshes are a unique and vital ecosystem, providing a habitat for numerous species and playing a crucial role in regulating water flow and preventing desertification.
5. How does the topographic map of Iraq aid in archaeological exploration?
The map helps identify potential archaeological sites, providing insights into ancient settlements, trade routes, and irrigation systems, contributing to historical research and cultural preservation.
Tips for Using the Topographic Map of Iraq
1. Understand the Scale: Pay attention to the map’s scale to accurately interpret distances and elevations.
2. Identify Key Features: Recognize prominent topographic features like mountains, rivers, and plains to gain a comprehensive understanding of the terrain.
3. Analyze Elevation Contours: Use contour lines to visualize changes in elevation, identifying potential obstacles and routes.
4. Consider the Context: Relate topographic features to historical, cultural, and environmental factors for a deeper understanding.
5. Utilize Digital Tools: Explore online topographic maps and GIS software for interactive analysis and data visualization.
Conclusion
The topographic map of Iraq provides a vital lens for understanding the country’s intricate landscape, its resource distribution, and its cultural and historical significance. By deciphering its contours, elevations, and features, we gain valuable insights into the complexities of Iraq’s environment, its challenges, and its potential for sustainable development. This knowledge empowers us to make informed decisions regarding resource management, infrastructure development, environmental conservation, and conflict resolution, ultimately contributing to a brighter future for Iraq.



.gif)
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling Iraq’s Terrain: A Comprehensive Exploration of Its Topographic Map. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!