Unveiling the Geography Behind an IP Address: A Guide to Geolocation
Related Articles: Unveiling the Geography Behind an IP Address: A Guide to Geolocation
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Geography Behind an IP Address: A Guide to Geolocation. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Unveiling the Geography Behind an IP Address: A Guide to Geolocation
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Unveiling the Geography Behind an IP Address: A Guide to Geolocation
- 3.1 The Fundamentals of IP Addresses and Geolocation
- 3.2 Applications of IP Address Geolocation: A Spectrum of Possibilities
- 3.3 Limitations and Considerations: Navigating the Complexities
- 3.4 FAQs: Addressing Common Questions
- 3.5 Tips for Effective Geolocation: Maximizing the Benefits
- 3.6 Conclusion: Embracing the Power of Geolocation
- 4 Closure
Unveiling the Geography Behind an IP Address: A Guide to Geolocation

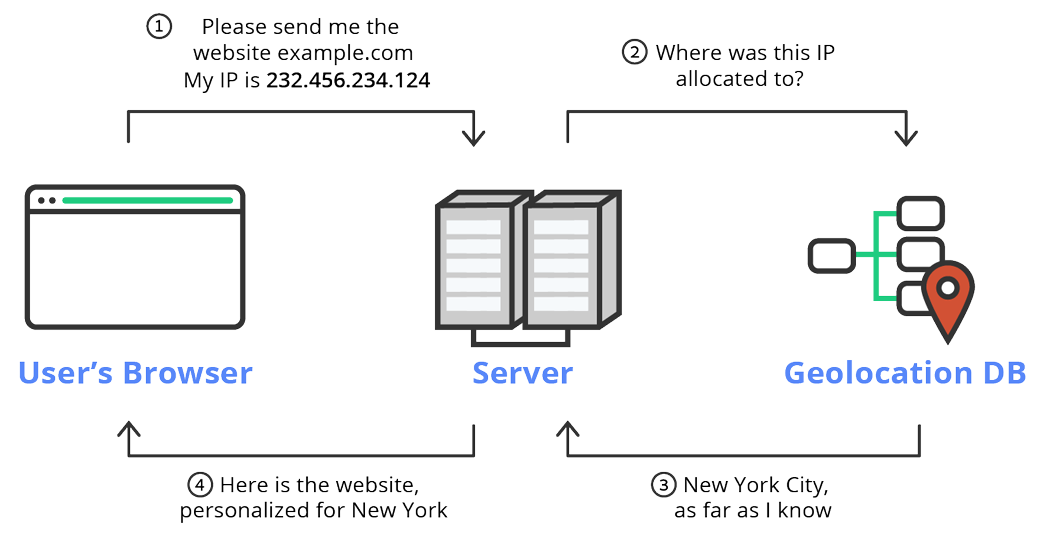
In the digital realm, where information flows effortlessly across continents, understanding the physical location associated with an IP address becomes increasingly crucial. Geolocation, the process of determining the geographical coordinates of a device based on its IP address, offers valuable insights into user behavior, network security, and even personal safety. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of IP address geolocation, exploring its mechanisms, applications, and potential limitations.
The Fundamentals of IP Addresses and Geolocation
An IP address (Internet Protocol address) serves as a unique identifier for every device connected to the internet. It acts as a postal code for the digital world, enabling communication between devices. While an IP address itself does not directly reveal a physical location, geolocation techniques leverage various factors to approximate the device’s geographical coordinates.
Methods of IP Address Geolocation:
-
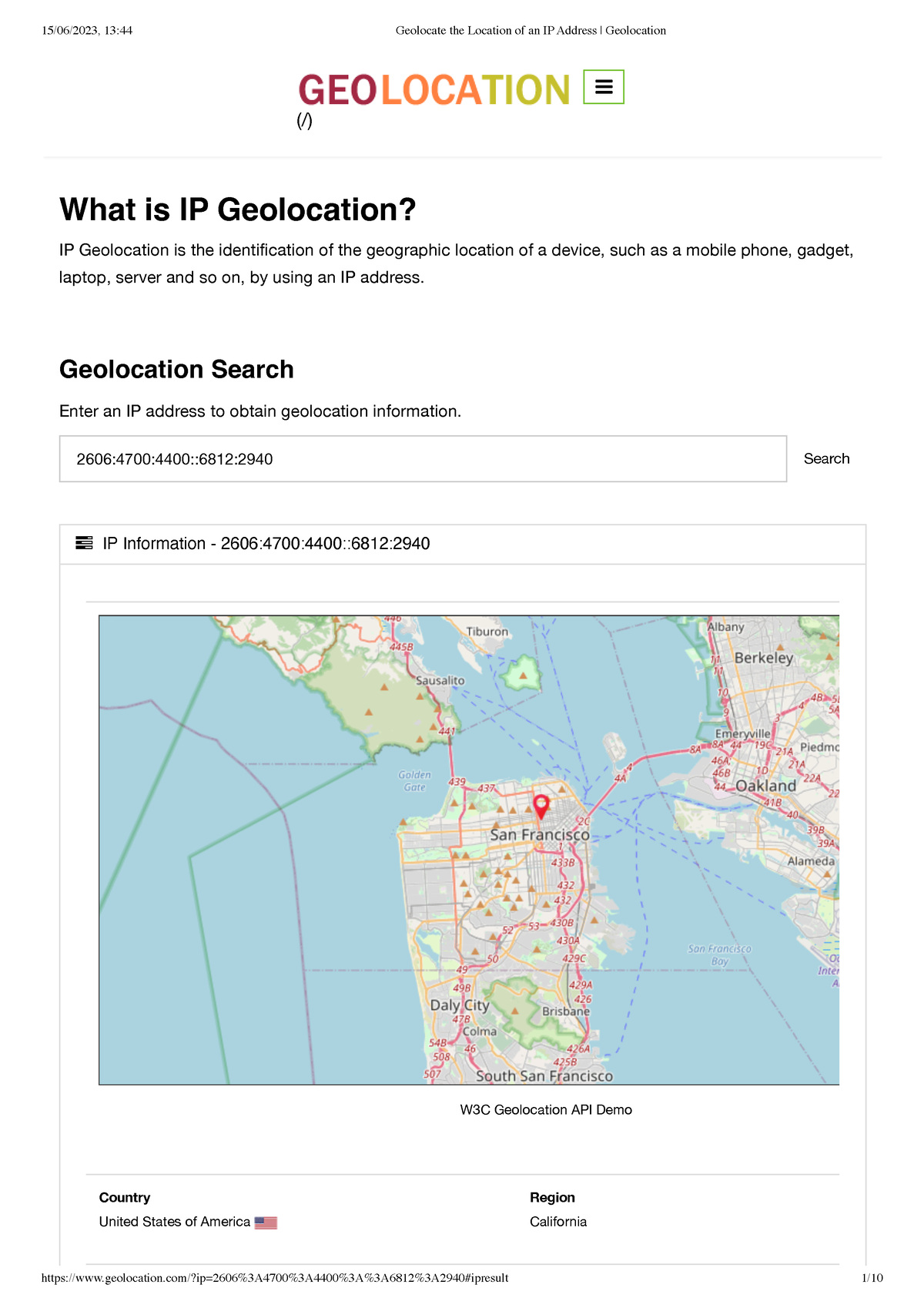
IP-to-Location Databases: These databases store vast amounts of data correlating IP addresses with geographical locations. These databases are regularly updated and rely on information provided by internet service providers (ISPs), who assign IP addresses to their customers.
-
GeoIP Lookup Services: Numerous online services offer geolocation capabilities. These services utilize algorithms and databases to analyze IP addresses and provide estimated locations. Some services offer free basic geolocation information, while others provide more detailed and accurate results through paid subscriptions.
-
Network Analysis: By analyzing network traffic patterns, it is possible to infer the approximate location of a device. This method involves examining the paths data takes from the source to the destination, often revealing the geographical region of the device.
-
GPS Data: In devices equipped with GPS capabilities, the location can be directly determined through satellite signals. This method provides the most accurate geolocation information but is limited to devices with GPS functionality.
Applications of IP Address Geolocation: A Spectrum of Possibilities
The ability to pinpoint the geographical location of an IP address opens doors to a wide range of applications, spanning various industries and aspects of our digital lives.
1. Enhancing User Experience:
-
Personalized Content Delivery: Geolocation enables websites and applications to tailor content based on the user’s location. This includes displaying localized language, relevant advertisements, and region-specific information.
-
Location-Based Services: Geolocation powers mobile applications like navigation apps, local search engines, and ride-hailing services, providing users with location-aware experiences.
-
Weather and Traffic Updates: Geolocation allows users to access real-time weather forecasts and traffic conditions based on their current location.
2. Business Intelligence and Marketing:
-
Targeted Advertising: Geolocation enables businesses to target advertising campaigns to specific geographical regions, increasing the effectiveness of their marketing efforts.
-
Market Research and Analysis: Understanding the geographical distribution of users can provide valuable insights into market trends, customer demographics, and regional preferences.
-
Competitive Analysis: Geolocation can help businesses analyze the geographic reach of their competitors, identify potential market opportunities, and optimize their own strategies.
3. Network Security and Fraud Prevention:
-
Detecting Malicious Activity: Geolocation can help identify suspicious activity by comparing the location of a device with its expected location. This can assist in detecting fraudulent transactions, botnets, and other security threats.
-
Access Control and Authentication: Geolocation can be used to restrict access to certain resources based on the user’s location, enhancing network security.
-
IP Address Blocking: By identifying malicious IP addresses based on their location, network administrators can block access from specific regions or countries.
4. Law Enforcement and Public Safety:
-
Crime Investigation: Geolocation can assist law enforcement agencies in tracking down suspects, locating missing persons, and analyzing crime patterns.
-
Emergency Response: Geolocation plays a critical role in emergency response systems, enabling the swift dispatch of first responders to the scene of an incident.
-
Cybersecurity Investigations: Geolocation can help investigators identify the origin of cyberattacks and trace the activities of malicious actors.
Limitations and Considerations: Navigating the Complexities
While geolocation offers numerous benefits, it is important to acknowledge its limitations and potential drawbacks:
-
Accuracy and Reliability: Geolocation accuracy can vary significantly depending on the method used and the quality of the data. Factors like dynamic IP addresses, VPNs, and proxy servers can introduce inaccuracies.
-
Privacy Concerns: Geolocation raises privacy concerns as it can potentially reveal sensitive information about a user’s location and movements.
-
Legal and Ethical Considerations: The use of geolocation technology can be subject to legal and ethical constraints, particularly in relation to data privacy and surveillance.
-
Security Risks: Geolocation data can be vulnerable to hacking and misuse, potentially leading to identity theft and other security threats.
Addressing the Challenges:
-
Transparency and User Consent: Users should be informed about the use of geolocation technology and given the option to opt-in or opt-out.
-
Data Security and Privacy: Robust security measures should be implemented to protect geolocation data from unauthorized access and misuse.
-
Accuracy Improvement: Ongoing research and development are focused on enhancing geolocation accuracy and reliability.
-
Ethical Guidelines: Establishing ethical guidelines for the use of geolocation technology is crucial to ensure responsible and ethical practices.
FAQs: Addressing Common Questions
1. Can I find the exact location of an IP address?
While geolocation can provide an approximate location, it is generally impossible to determine the exact physical address of a device based solely on its IP address.
2. Is geolocation always accurate?
Geolocation accuracy can vary depending on the method used, the quality of the data, and factors like dynamic IP addresses and VPNs.
3. How can I protect my privacy when using geolocation services?
Consider using privacy-focused browsers, disabling location services when not necessary, and carefully reviewing app permissions.
4. Can I use geolocation to track someone’s location?
Using geolocation to track someone’s location without their consent is generally unethical and may be illegal.
5. What are the legal implications of using geolocation?
The legal implications of geolocation vary depending on the jurisdiction and the specific use case. It is essential to consult with legal experts to ensure compliance with applicable laws and regulations.
Tips for Effective Geolocation: Maximizing the Benefits
-
Choose Reliable Geolocation Services: Opt for reputable geolocation services with a proven track record of accuracy and reliability.
-
Understand the Accuracy Limitations: Be aware of the limitations of geolocation technology and avoid relying on it for critical decisions that require precise location information.
-
Prioritize User Privacy: Implement appropriate privacy measures to protect user data and ensure transparency in the use of geolocation.
-
Stay Informed about Legal and Ethical Considerations: Keep abreast of legal and ethical guidelines surrounding geolocation technology to ensure responsible and compliant practices.
Conclusion: Embracing the Power of Geolocation
Geolocation, the process of determining the geographical location of an IP address, provides valuable insights into user behavior, network security, and various other aspects of our digital world. While it presents limitations and raises privacy concerns, its potential benefits are undeniable. By understanding the mechanisms, applications, and ethical considerations surrounding geolocation, we can harness its power responsibly and ethically, unlocking new possibilities in a connected world.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Geography Behind an IP Address: A Guide to Geolocation. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!