Unveiling the Power of Visual Knowledge: A Comprehensive Guide to Concept Map Images
Related Articles: Unveiling the Power of Visual Knowledge: A Comprehensive Guide to Concept Map Images
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Power of Visual Knowledge: A Comprehensive Guide to Concept Map Images. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Unveiling the Power of Visual Knowledge: A Comprehensive Guide to Concept Map Images
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Unveiling the Power of Visual Knowledge: A Comprehensive Guide to Concept Map Images
- 3.1 Defining the Concept Map Image: A Visual Representation of Knowledge
- 3.2 The Anatomy of a Concept Map Image: Unveiling the Key Components
- 3.3 Applications of Concept Map Images: Unlocking the Potential Across Disciplines
- 3.4 Benefits of Concept Map Images: Enhancing Comprehension and Communication
- 3.5 Creating Effective Concept Map Images: A Step-by-Step Guide
- 3.6 Frequently Asked Questions: Addressing Common Concerns
- 3.7 Conclusion: Embracing the Power of Visual Knowledge
- 4 Closure
Unveiling the Power of Visual Knowledge: A Comprehensive Guide to Concept Map Images

In the realm of knowledge representation and communication, visual tools play a crucial role in facilitating understanding and retention. Among these tools, concept map images stand out as a powerful and versatile method for organizing information, revealing relationships, and promoting deeper comprehension. This comprehensive guide delves into the essence of concept map images, exploring their structure, applications, benefits, and potential for enhancing learning and communication.
Defining the Concept Map Image: A Visual Representation of Knowledge
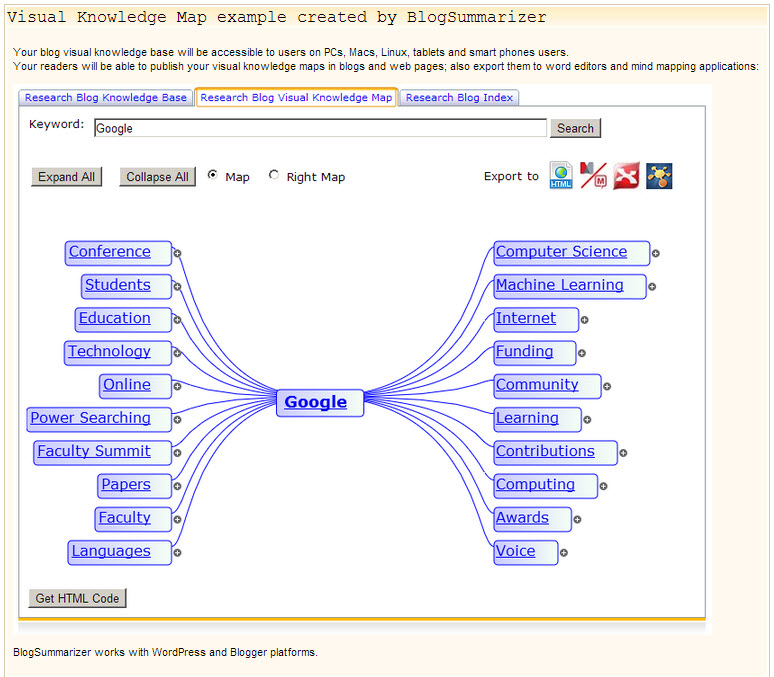
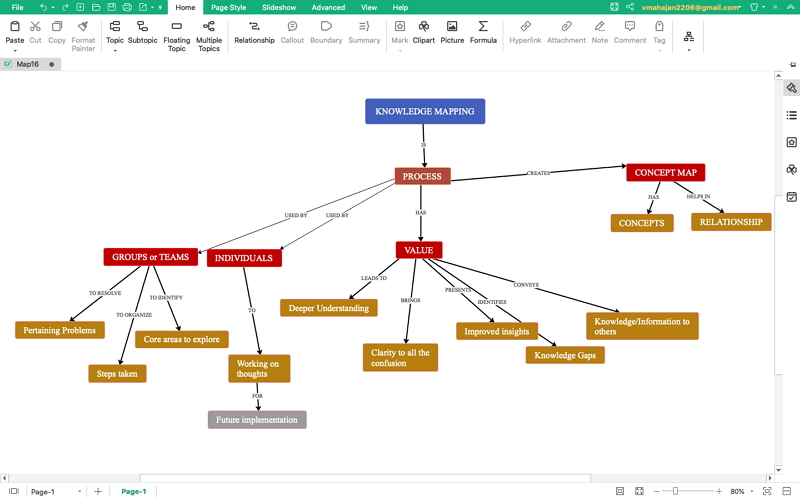
A concept map image, often referred to simply as a concept map, is a graphical representation that visually depicts the relationships between concepts. It employs nodes, which represent individual concepts, and connecting lines, which illustrate the links between them. These links can be labeled with words or phrases that describe the nature of the relationship, such as "is a," "causes," or "results in."
Concept maps are not mere diagrams; they are active tools for knowledge construction. They encourage users to:
- Identify key concepts: The process of creating a concept map necessitates identifying the central ideas and sub-concepts within a given topic.
- Establish connections: By drawing links between concepts, users actively explore the relationships and connections that exist within the information.
- Organize information: The hierarchical structure of a concept map provides a clear and organized framework for understanding complex information.
The Anatomy of a Concept Map Image: Unveiling the Key Components
Understanding the fundamental components of a concept map image is crucial for appreciating its effectiveness. These components work in synergy to create a visually coherent and informative representation of knowledge.
Nodes:
- Central Concept: The starting point of a concept map is the central concept, which serves as the main idea or topic being explored. It is typically placed at the top or center of the map.
- Sub-Concepts: These are the concepts that branch out from the central concept, representing its various aspects or sub-topics.
- Supporting Details: Additional nodes may be included to provide further information or examples related to the sub-concepts.
Links:
- Connecting Lines: Lines are drawn between nodes to visually represent the relationships between concepts.
- Labels: These labels are attached to the connecting lines and clarify the nature of the relationship between the connected concepts.
Hierarchies:
- Hierarchical Structure: Concept maps typically follow a hierarchical structure, with the central concept at the top and sub-concepts branching out below.
- Levels: The hierarchical structure is formed by organizing concepts into different levels, with higher levels representing broader concepts and lower levels representing more specific details.
Applications of Concept Map Images: Unlocking the Potential Across Disciplines
The versatility of concept map images extends across various disciplines, making them valuable tools for learning, teaching, and communication. Here are some key applications:
Education:
- Learning: Concept maps can aid students in understanding complex concepts, identifying key relationships, and organizing information for better retention.
- Teaching: Educators can use concept maps to visualize course content, facilitate class discussions, and assess student understanding.
- Assessment: Concept maps can be used as assessment tools to evaluate student comprehension and identify areas for improvement.
Business and Industry:
- Project Planning: Concept maps can help visualize the different components of a project, identify dependencies, and track progress.
- Problem Solving: By mapping out the components of a problem, concept maps can facilitate brainstorming solutions and identifying potential obstacles.
- Communication: Concept maps can be used to communicate complex ideas clearly and concisely to stakeholders, fostering understanding and collaboration.
Research and Development:
- Literature Reviews: Concept maps can help researchers organize and synthesize information from various sources, identifying key themes and gaps in knowledge.
- Hypothesis Generation: By mapping out the relationships between concepts, researchers can generate new hypotheses and research questions.
- Data Analysis: Concept maps can be used to visualize data relationships, revealing patterns and insights that might otherwise be missed.
Other Applications:
- Personal Development: Concept maps can be used for goal setting, personal reflection, and planning for the future.
- Decision Making: Concept maps can help individuals or groups visualize the different options and consequences associated with a decision, aiding in informed choices.
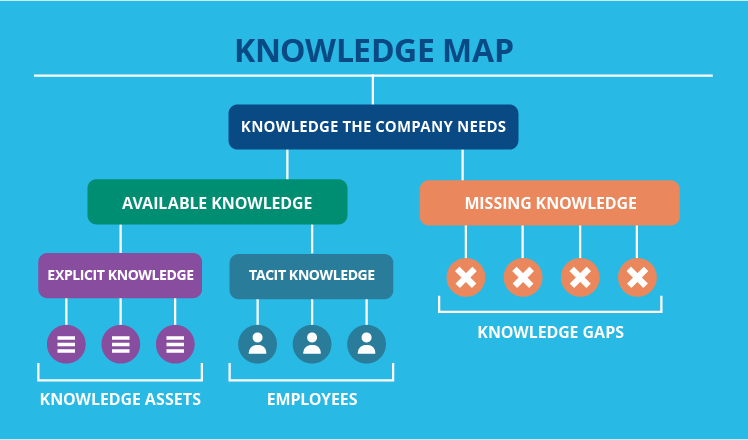
- Knowledge Management: Concept maps can be used to organize and share knowledge within organizations, facilitating collaboration and information access.
Benefits of Concept Map Images: Enhancing Comprehension and Communication
The power of concept map images lies in their ability to enhance understanding, promote critical thinking, and facilitate effective communication. Here are some key benefits:
Enhanced Understanding:
- Visual Representation: Concept maps provide a visual representation of information, making it easier to grasp complex relationships and concepts.
- Active Learning: The process of creating a concept map encourages active engagement with the information, leading to deeper understanding and retention.
- Hierarchical Structure: The hierarchical structure of concept maps helps organize information into meaningful categories, aiding in understanding the overall structure of the knowledge.
Improved Critical Thinking:
- Identifying Relationships: Creating a concept map requires users to analyze information and identify the relationships between concepts, fostering critical thinking skills.
- Problem Solving: Concept maps can be used to map out the components of a problem, encouraging creative solutions and identifying potential obstacles.
- Decision Making: Concept maps can facilitate informed decision-making by visualizing the different options and consequences associated with each choice.
Effective Communication:
- Clear and Concise: Concept maps provide a clear and concise way to communicate complex ideas, making them accessible to a wider audience.
- Visual Appeal: The visual nature of concept maps makes them engaging and memorable, improving communication effectiveness.
- Shared Understanding: Concept maps can foster shared understanding among individuals or groups, promoting collaboration and knowledge sharing.
Creating Effective Concept Map Images: A Step-by-Step Guide
Creating a concept map image that effectively communicates information requires careful planning and execution. Here is a step-by-step guide to creating effective concept maps:
1. Define the Topic: Clearly identify the central concept or topic that you want to represent in the map.
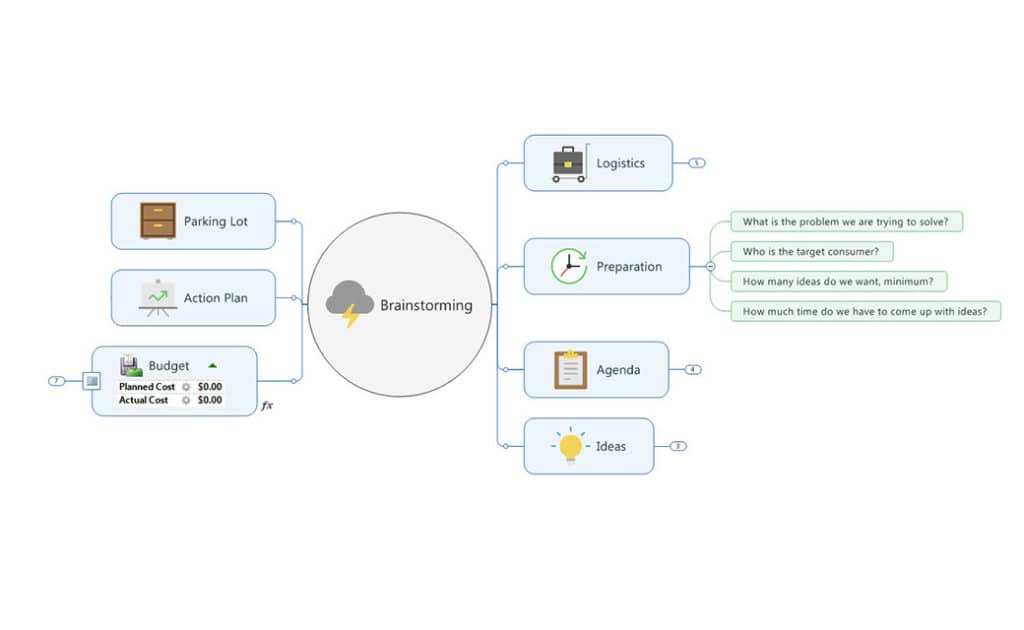
2. Brainstorm Concepts: Identify the key concepts and sub-concepts related to the topic. Use brainstorming techniques, such as mind mapping, to generate a comprehensive list.
3. Organize Concepts: Arrange the concepts in a hierarchical structure, with the central concept at the top and sub-concepts branching out below.
4. Connect Concepts: Draw lines between nodes to visually represent the relationships between concepts.
5. Label Links: Label the connecting lines with words or phrases that describe the nature of the relationship.
6. Add Details: Include supporting details, examples, or definitions as necessary to provide further context and understanding.
7. Review and Revise: Review the map for clarity, accuracy, and completeness. Make revisions as needed to improve the effectiveness of the map.
Frequently Asked Questions: Addressing Common Concerns
Q: What are the different types of concept maps?
A: There are various types of concept maps, each with its own unique structure and purpose. Some common types include:
- Hierarchical Concept Maps: These maps follow a hierarchical structure, with the central concept at the top and sub-concepts branching out below.
- Spider Maps: These maps are radial in structure, with the central concept in the center and sub-concepts radiating outward.
- Flow Maps: These maps depict the flow of information or processes, using arrows to indicate direction and sequence.
Q: How can I use concept maps for learning?
A: Concept maps can be a powerful tool for learning by:
- Organizing information: Concept maps help organize complex information into a clear and structured format, facilitating understanding.
- Identifying relationships: By connecting concepts, concept maps reveal the relationships between different ideas, promoting deeper comprehension.
- Active learning: The process of creating a concept map encourages active engagement with the material, leading to better retention.
Q: What are some software tools for creating concept maps?
A: There are numerous software tools available for creating concept maps, both online and offline. Some popular options include:
- MindManager: A comprehensive mind mapping and concept mapping software.
- XMind: A free and open-source mind mapping and concept mapping tool.
- Coggle: A collaborative online concept mapping and mind mapping tool.
- ConceptDraw: A professional diagramming software that includes a concept map template.
Q: What are some tips for creating effective concept maps?
A: Here are some tips for creating effective concept maps:
- Keep it simple: Avoid overloading the map with too much information. Focus on the key concepts and relationships.
- Use clear and concise language: Choose clear and concise words and phrases to label nodes and links.
- Visually appealing: Use different colors, shapes, and fonts to make the map visually appealing and engaging.
- Iterative process: Treat concept map creation as an iterative process, reviewing and revising the map as needed.
Conclusion: Embracing the Power of Visual Knowledge
Concept map images are a powerful tool for organizing information, revealing relationships, and promoting deeper understanding. Their versatility extends across various disciplines, making them valuable assets for learning, teaching, communication, and problem-solving. By embracing the power of visual knowledge, individuals and organizations can unlock new levels of comprehension, collaboration, and innovation.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Power of Visual Knowledge: A Comprehensive Guide to Concept Map Images. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!