Unveiling the Topography of the Middle East: A Comprehensive Look at its Elevation Map
Related Articles: Unveiling the Topography of the Middle East: A Comprehensive Look at its Elevation Map
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Topography of the Middle East: A Comprehensive Look at its Elevation Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Topography of the Middle East: A Comprehensive Look at its Elevation Map
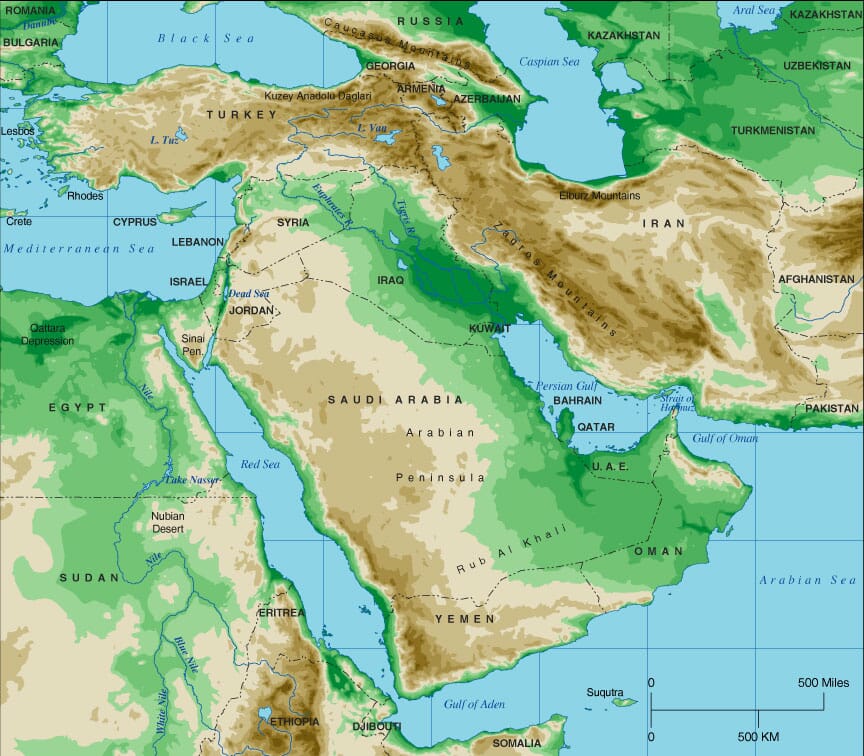
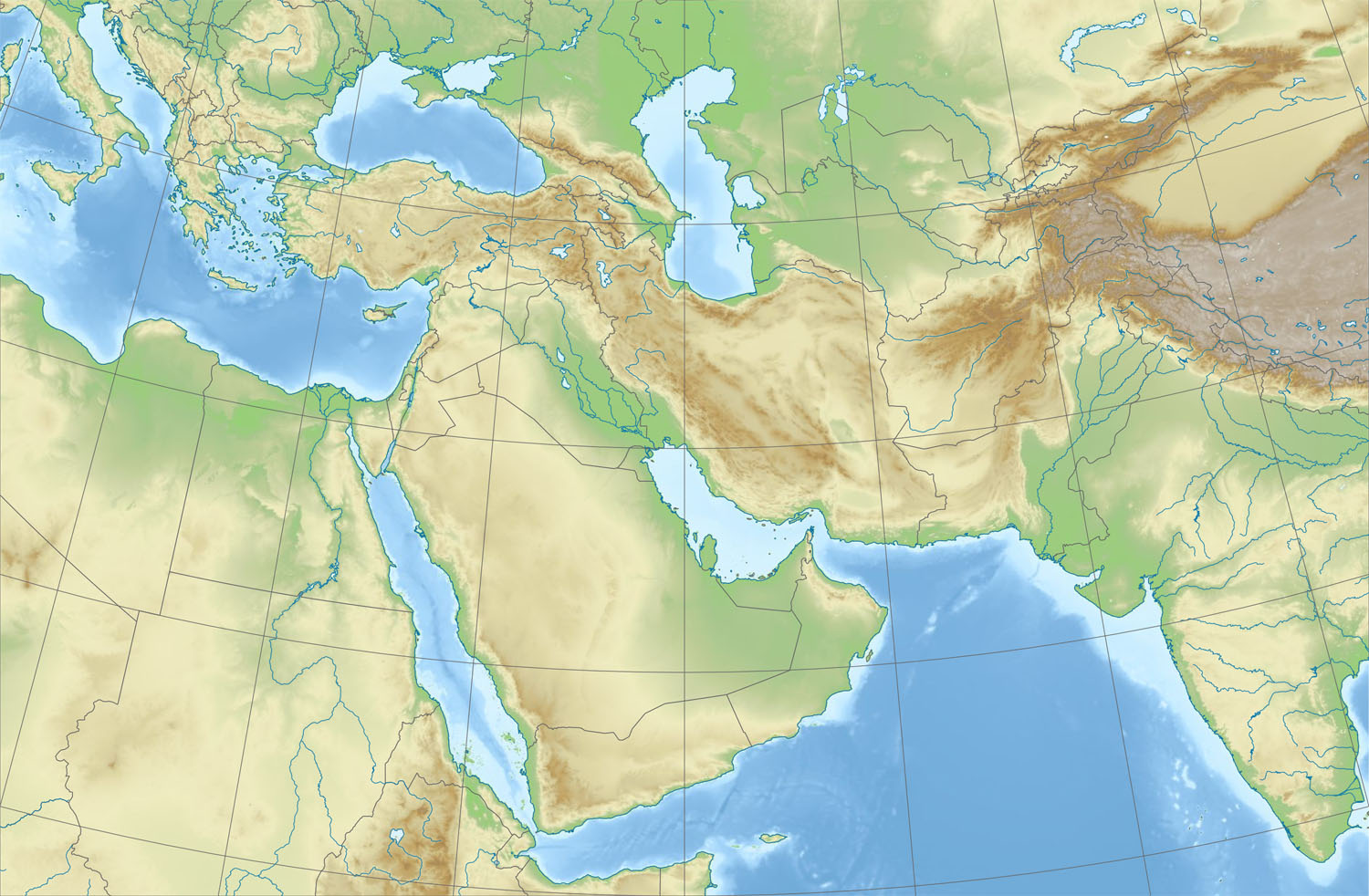
The Middle East, a region steeped in history and diverse cultures, is equally fascinating in its geographical landscape. Understanding its elevation map is crucial for appreciating the complexities of its environment, the challenges faced by its inhabitants, and the potential opportunities it presents. This article delves into the intricacies of the Middle East’s elevation map, exploring its key features, significance, and implications.
A Diverse Landscape Shaped by Tectonic Forces
The Middle East’s elevation map reveals a mosaic of contrasting terrains, a direct consequence of the region’s complex geological history. The Arabian Plate, a massive tectonic plate encompassing most of the Arabian Peninsula, has been steadily moving northward for millions of years, colliding with the Eurasian Plate. This collision, along with the presence of numerous fault lines, has sculpted the region’s dramatic topography.
The Arabian Plateau: A Vast Elevated Plain
Dominating the Middle East’s elevation map is the Arabian Plateau, a vast, elevated plain that stretches across the Arabian Peninsula. This plateau, averaging between 1,000 and 1,500 meters above sea level, is characterized by its arid climate and sparse vegetation. The plateau’s elevation is a crucial factor in shaping its climate, creating a dry, desert environment with limited rainfall.
Mountain Ranges: Guardians of the Middle East
The Middle East is also home to several prominent mountain ranges, including the Zagros Mountains, the Taurus Mountains, and the Lebanon Mountains. These ranges, formed by the collision of tectonic plates, rise dramatically from the surrounding plains, reaching heights of over 5,000 meters in some cases. The mountains play a crucial role in influencing regional climates, acting as barriers to moisture-laden winds and creating distinct microclimates on their slopes.
Depressions and Basins: The Lowlands of the Middle East
In contrast to the elevated plateaus and mountain ranges, the Middle East also features several depressions and basins, areas that lie below sea level. The most prominent of these is the Dead Sea, located in the Jordan Rift Valley, which holds the distinction of being the lowest point on Earth’s land surface. These depressions are often characterized by arid conditions, limited rainfall, and high salinity.
The Importance of the Middle East’s Elevation Map
Understanding the Middle East’s elevation map is essential for various reasons:
- Climate and Weather Patterns: Elevation plays a crucial role in shaping the region’s climate and weather patterns. Higher elevations experience cooler temperatures, while lower elevations are generally hotter and drier. The mountains act as barriers to moisture-laden winds, influencing rainfall patterns and creating distinct microclimates.
- Water Resources: The Middle East’s elevation map is intricately linked to its water resources. The mountains act as sources for rivers and streams, while the depressions and basins often hold important groundwater reserves. Understanding the elevation map helps in managing water resources efficiently, especially in a region facing water scarcity.
- Agriculture and Land Use: The elevation map influences agricultural practices and land use patterns. Higher elevations are often suitable for certain crops, while lower elevations are better suited for others. The elevation map also helps in identifying areas suitable for grazing, forestry, and other land uses.
- Infrastructure Development: Understanding the elevation map is crucial for planning infrastructure development, particularly for transportation routes, dams, and irrigation systems. The elevation map helps engineers and planners identify suitable locations for these projects, considering factors like terrain, slope, and accessibility.
- Environmental Sustainability: The elevation map provides valuable insights into the region’s environmental vulnerabilities. Understanding the distribution of different elevations helps in identifying areas prone to desertification, soil erosion, and other environmental threats. This knowledge is crucial for developing sustainable land management practices and mitigating environmental risks.
FAQs about the Middle East’s Elevation Map
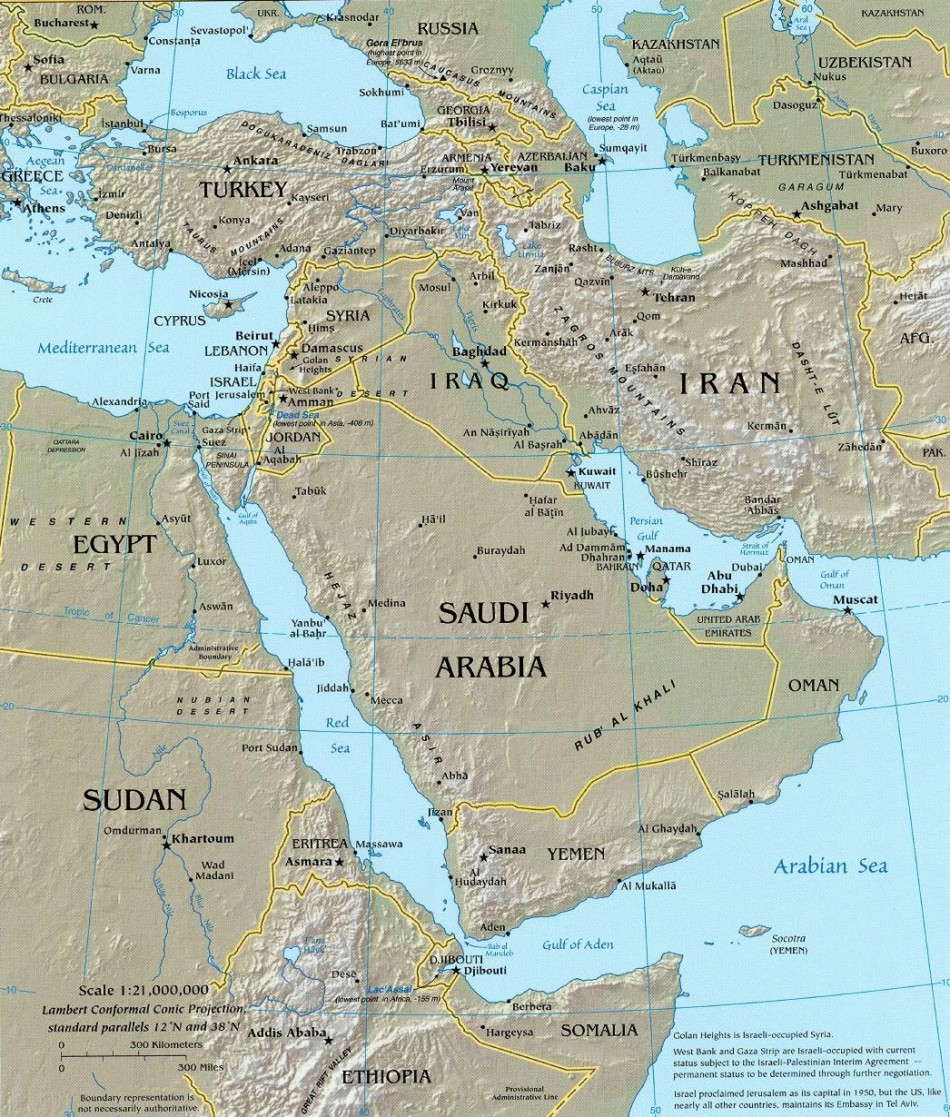
1. What is the highest point in the Middle East?
The highest point in the Middle East is Mount Damavand, located in Iran, with an elevation of 5,610 meters (18,406 feet).
2. What is the lowest point in the Middle East?
The lowest point in the Middle East is the Dead Sea, located in the Jordan Rift Valley, with an elevation of -430.5 meters (-1,412 feet) below sea level.
3. How does elevation affect the climate in the Middle East?
Higher elevations in the Middle East experience cooler temperatures and higher rainfall compared to lower elevations. The mountains act as barriers to moisture-laden winds, creating distinct microclimates on their slopes.
4. What are the major mountain ranges in the Middle East?
The major mountain ranges in the Middle East include the Zagros Mountains, the Taurus Mountains, and the Lebanon Mountains.
5. What are the major depressions and basins in the Middle East?
The major depressions and basins in the Middle East include the Dead Sea, the Jordan Rift Valley, and the Persian Gulf.
Tips for Interpreting the Middle East’s Elevation Map
- Pay attention to the contour lines: Contour lines connect points of equal elevation, providing a visual representation of the terrain’s shape.
- Look for areas of high and low elevation: Identify the highest and lowest points on the map to understand the overall elevation gradient.
- Consider the impact of elevation on climate: Understand how elevation influences temperature, rainfall, and other climatic factors.
- Relate the elevation map to other geographical features: Connect the elevation map to other features like rivers, lakes, and coastlines to gain a more comprehensive understanding of the landscape.
- Utilize online tools: Explore interactive online tools that allow you to explore the Middle East’s elevation map in detail and gain insights into specific areas.
Conclusion
The Middle East’s elevation map is a powerful tool for understanding the region’s diverse topography, complex climate, and unique challenges. By appreciating the intricate interplay between elevation and other geographical factors, we gain a deeper understanding of the region’s history, culture, and potential for future development. As we continue to explore and analyze the Middle East’s elevation map, we can unlock valuable insights that contribute to sustainable development, resource management, and environmental conservation in this vital region.

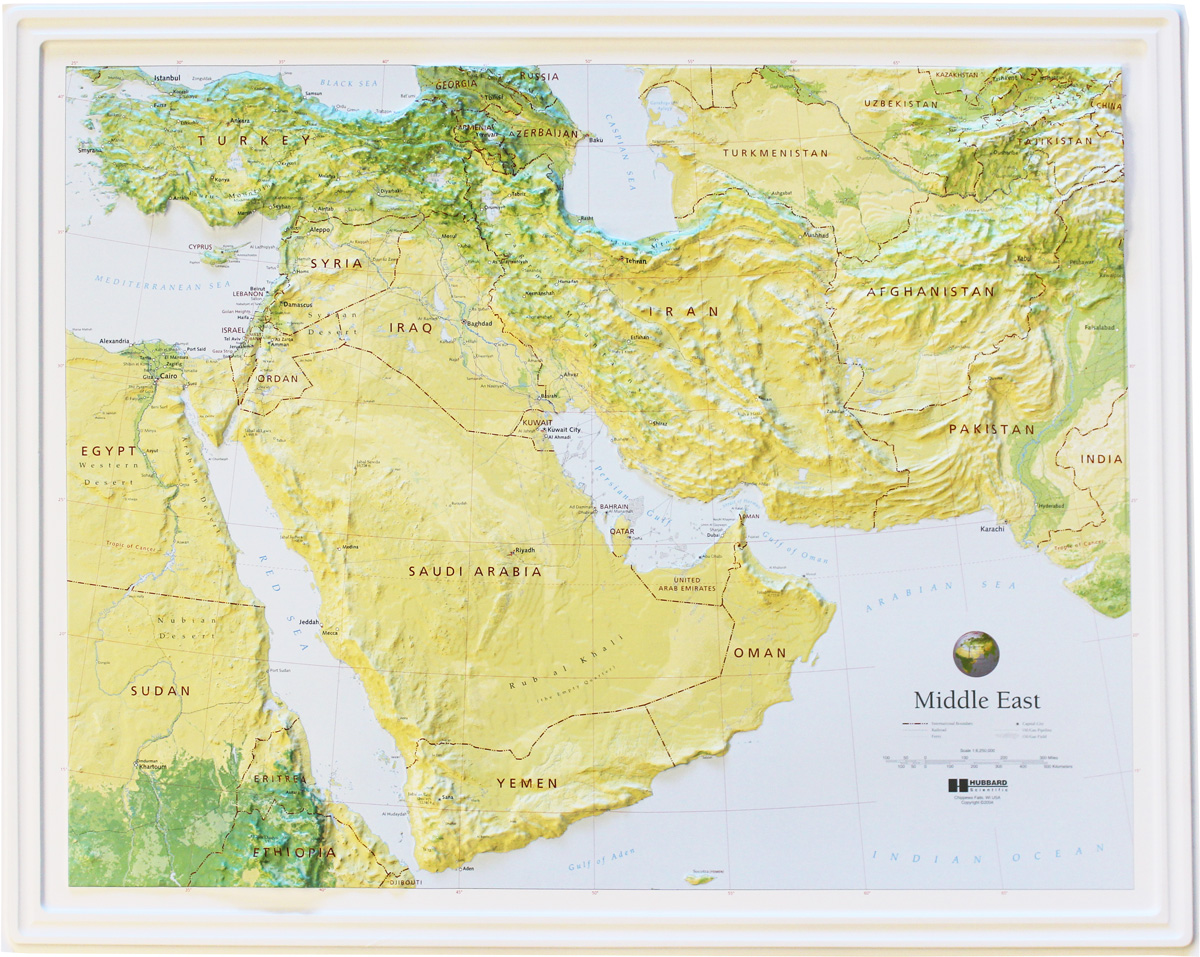
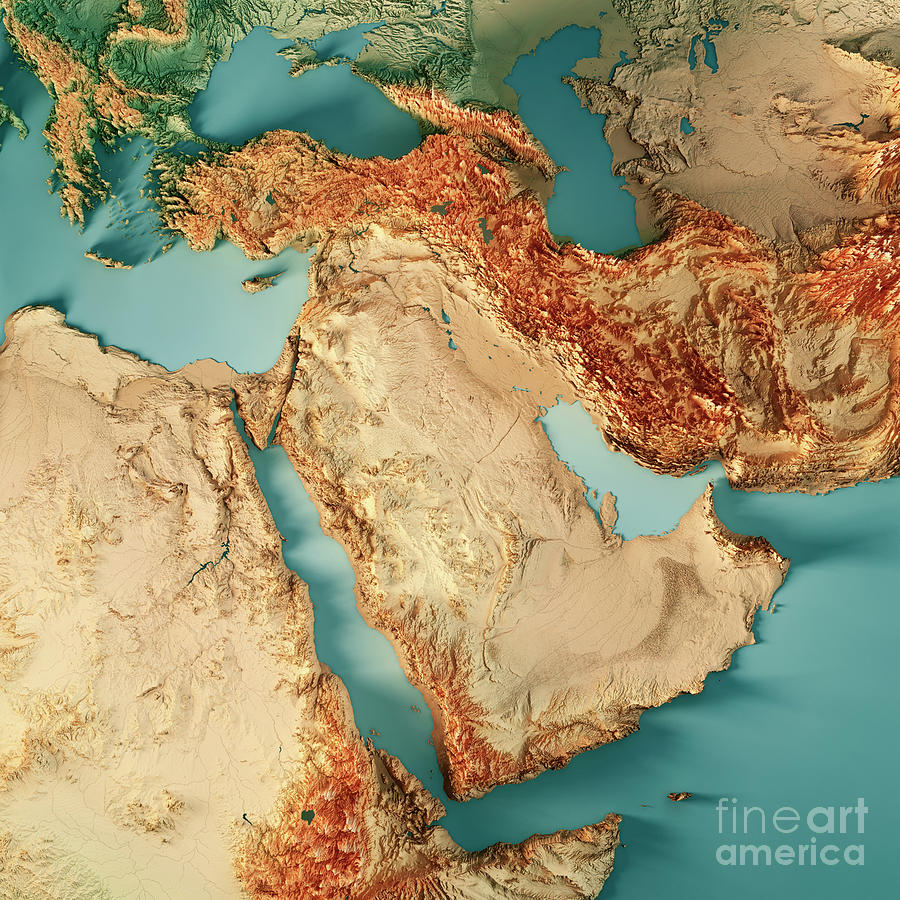
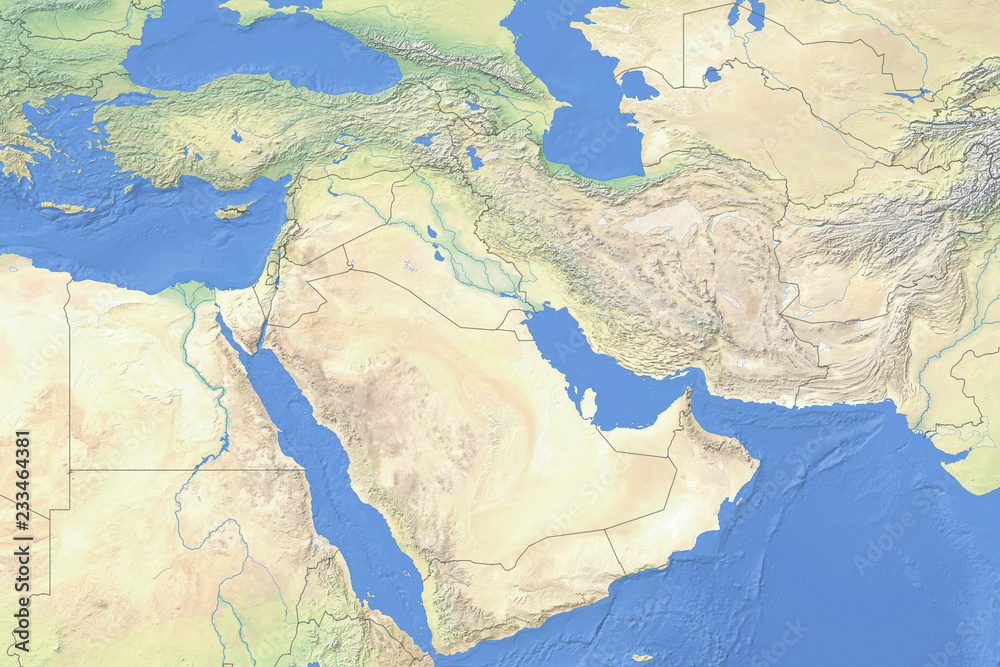


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Topography of the Middle East: A Comprehensive Look at its Elevation Map. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!