Unveiling the World: A Comprehensive Guide to Earth Maps
Related Articles: Unveiling the World: A Comprehensive Guide to Earth Maps
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the World: A Comprehensive Guide to Earth Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the World: A Comprehensive Guide to Earth Maps

The Earth, our home planet, is a vast and intricate sphere, teeming with life and diverse landscapes. To understand its complexities and navigate its vastness, we rely on maps – visual representations that depict geographical features, political boundaries, and other important information. This article delves into the world of Earth maps, exploring their evolution, types, uses, and the invaluable insights they provide.
The Evolution of Earth Maps:
The history of Earth maps stretches back millennia, evolving alongside human understanding of the world. Early civilizations, like the ancient Egyptians and Babylonians, created rudimentary maps based on observations and journeys. These maps were often schematic, focusing on key landmarks and routes.
The advent of cartography in ancient Greece marked a significant advancement. Greek scholars, like Eratosthenes, developed the concept of latitude and longitude, allowing for more accurate and detailed mapping. The Roman Empire further contributed to cartography, creating road maps and surveying vast territories.
During the Age of Exploration, European cartographers embarked on ambitious expeditions, charting new lands and oceans. The invention of the printing press facilitated the mass production and dissemination of maps, making geographical knowledge more accessible.
Types of Earth Maps:
Earth maps come in various forms, each serving a specific purpose and highlighting different aspects of the planet. Here are some common types:
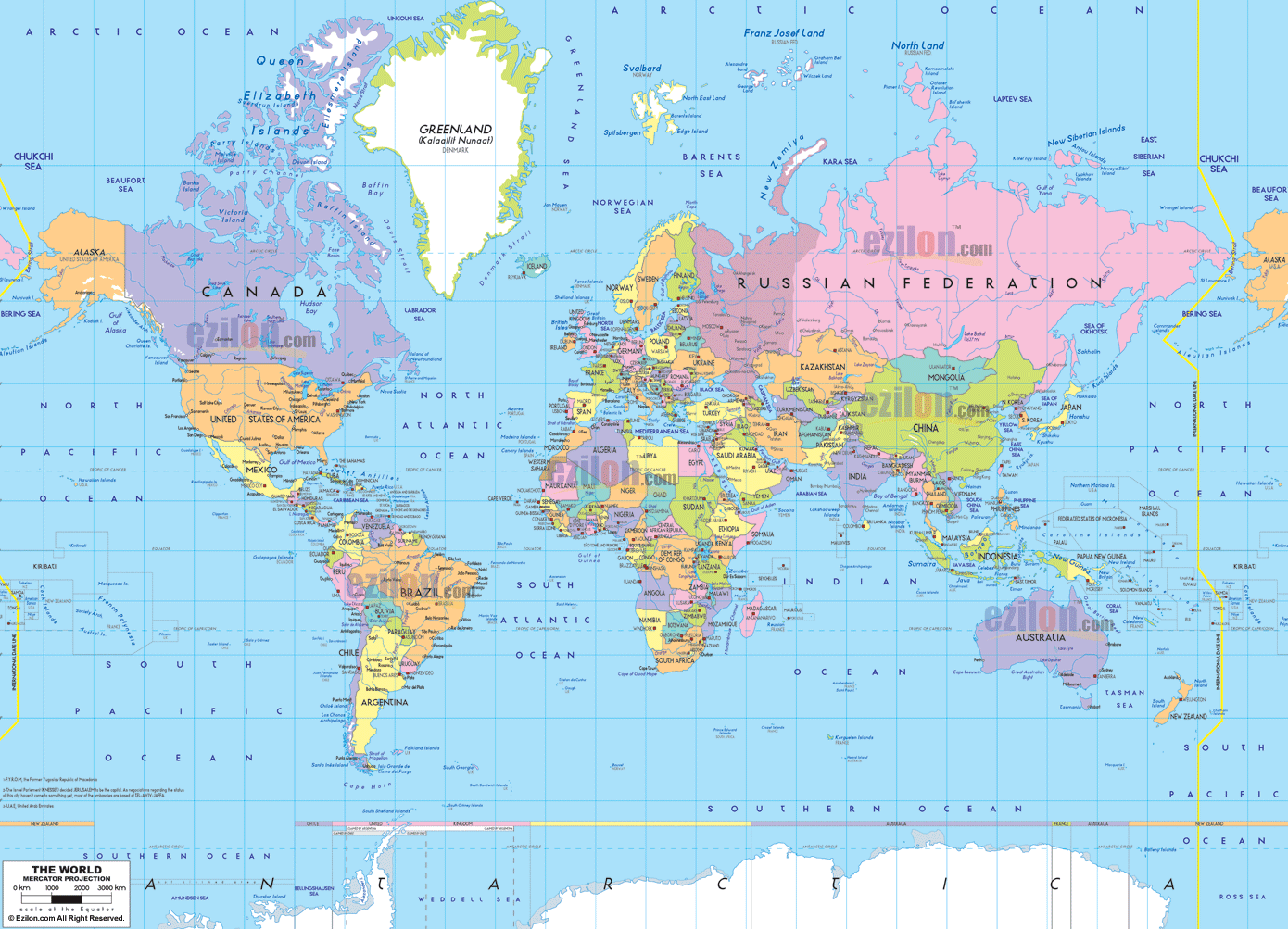
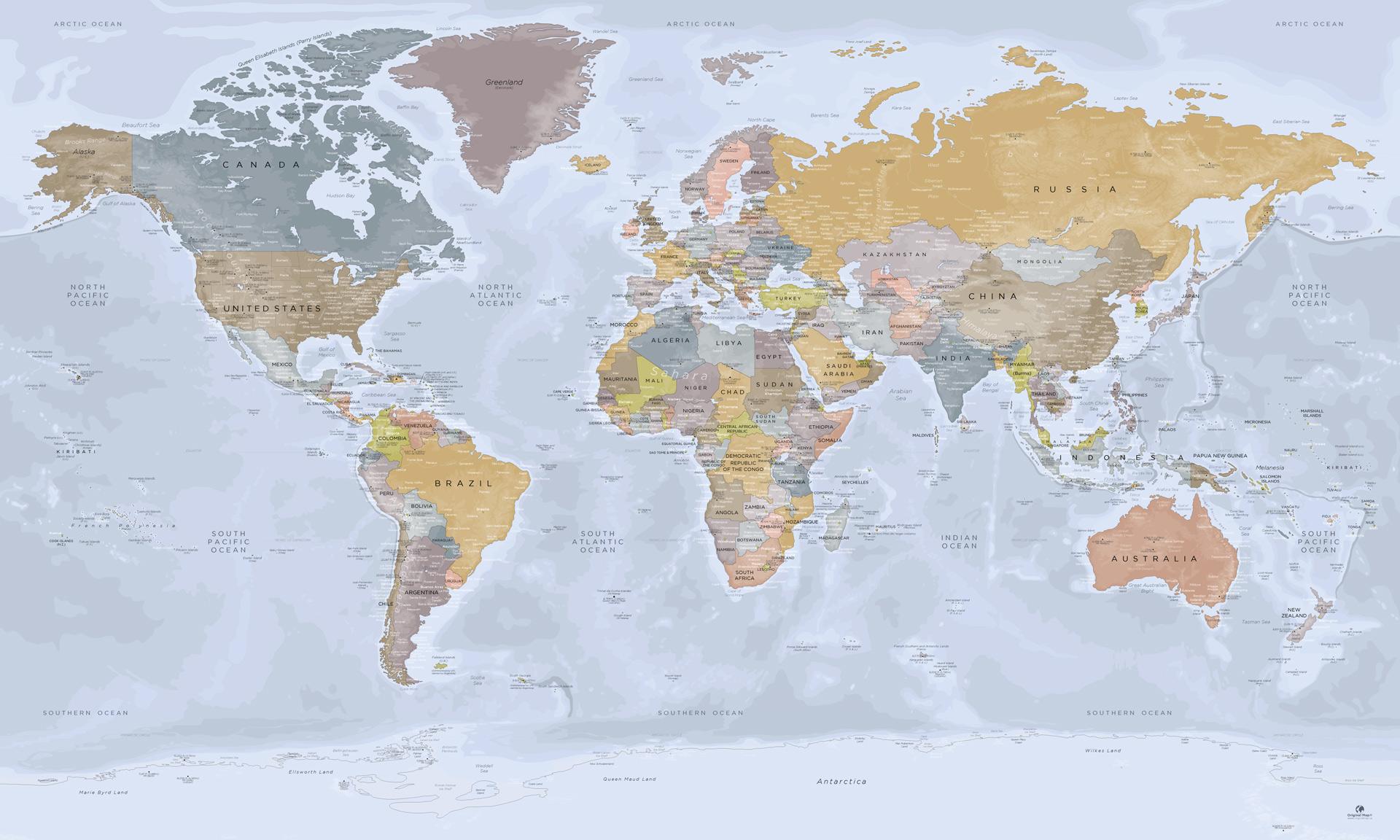
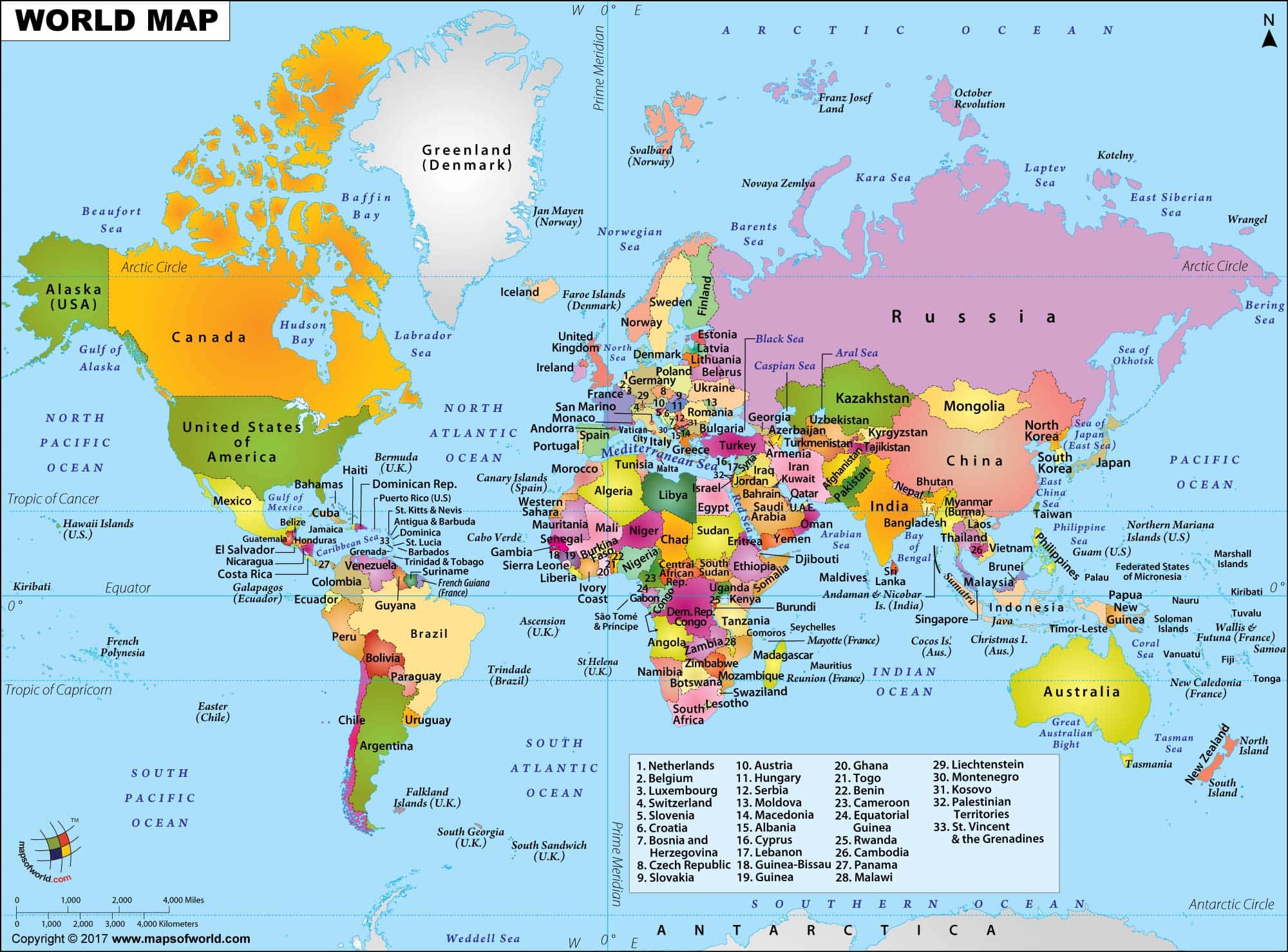
- World Maps: These maps depict the entire globe, typically in a flattened projection. They are used for general reference, illustrating continents, oceans, and major geographical features.
- Political Maps: These maps focus on political boundaries, showcasing countries, states, and other administrative divisions. They are essential for understanding global politics and international relations.
- Physical Maps: These maps highlight physical features of the Earth, such as mountains, rivers, deserts, and forests. They provide valuable insights into the planet’s topography and natural resources.
- Thematic Maps: These maps focus on a specific theme or data, such as population density, climate zones, or economic activity. They are used for data visualization and analysis, highlighting patterns and trends across the globe.
- Road Maps: These maps focus on transportation networks, showing roads, highways, and other routes. They are indispensable for travelers and commuters.
- Topographic Maps: These maps depict elevation changes and landforms, using contour lines to represent terrain. They are used for hiking, camping, and other outdoor activities.
The Importance of Earth Maps:
Earth maps serve a multitude of purposes, playing a vital role in various aspects of human life:
- Navigation and Exploration: Maps provide crucial information for navigation, guiding travelers, explorers, and mariners across land and sea.
- Understanding the World: Maps offer a visual representation of the Earth, helping us comprehend its vastness, diversity, and interconnectedness.
- Decision-Making: Maps are used by governments, businesses, and individuals to make informed decisions regarding resource allocation, infrastructure development, and environmental management.
- Education and Research: Maps are essential tools for education, helping students learn about geography, history, and social studies. They are also used by researchers to study various aspects of the Earth, from climate change to biodiversity.
- Communication and Collaboration: Maps facilitate communication and collaboration, providing a shared understanding of geographical information across different groups and cultures.
Benefits of Using Earth Maps:
- Visual Representation: Maps offer a clear and concise visual representation of complex geographical information.
- Spatial Awareness: Maps enhance our spatial awareness, helping us understand the relative positions and relationships between different locations.
- Data Visualization: Maps are powerful tools for visualizing data, highlighting trends, patterns, and anomalies across geographical regions.
- Problem-Solving: Maps assist in problem-solving by providing a visual framework for analyzing situations and identifying solutions.
- Historical Insights: Maps provide valuable historical insights, showcasing the evolution of geographical boundaries, settlements, and transportation networks.
FAQs About Earth Maps:
Q: What is the difference between a globe and a map?
A: A globe is a three-dimensional representation of the Earth, while a map is a two-dimensional representation. Globes are more accurate in depicting the Earth’s true shape and proportions, but maps are more practical for everyday use due to their portability and ease of manipulation.
Q: What are map projections?
A: Map projections are mathematical techniques used to flatten the Earth’s spherical surface onto a two-dimensional plane. Different projections distort the Earth’s shape in various ways, resulting in different visual representations of the globe.
Q: How are maps made?
A: Maps are made using a combination of surveying, aerial photography, satellite imagery, and Geographic Information Systems (GIS) technology. Data collected from these sources is processed and analyzed to create accurate and detailed maps.
Q: What are some of the challenges in mapmaking?
A: Mapmaking faces challenges such as accurately representing the Earth’s curved surface on a flat plane, keeping up with changing geographical boundaries, and ensuring accessibility for diverse users.
Tips for Using Earth Maps:
- Choose the right map for your needs: Consider the purpose of your map and select the type that best suits your requirements.
- Understand the map’s projection: Be aware of the projection used in a map, as it can affect the accuracy and appearance of geographical features.
- Pay attention to the map’s scale: The scale indicates the ratio between distances on the map and actual distances on the Earth.
- Use a legend: The legend explains the symbols, colors, and other elements used on the map.
- Consider digital maps: Digital maps offer interactive features, real-time updates, and access to a wide range of data.
Conclusion:
Earth maps are indispensable tools for navigating the world, understanding its complexities, and making informed decisions. From ancient civilizations to modern societies, maps have played a crucial role in shaping our understanding of the planet and guiding our interactions with it. As technology advances, mapmaking continues to evolve, offering new possibilities for exploring and understanding our world. By embracing the power of maps, we can gain deeper insights into the Earth’s intricate tapestry and navigate its vastness with greater knowledge and clarity.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the World: A Comprehensive Guide to Earth Maps. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!